Spring MVC 视图技术(下)
1. 前言
本章节将向大家讲解 Thymeleaf 视图技术 。Thymeleaf 和 Spring MVC 或 Spring Boot 有着较完美的契合度,是 Spring 官方建议的首选视图技术。
通过本节章节,你将学习到:
- Spring MVC 中如何使用 Thymeleaf 。这是本章节的重点也是难点;
- Thymeleaf 的特点;
2. Spring MVC 和 Thymeleaf
本章节继续和大家一起讲解 Spring MVC 支持的视图技术。其实除了有服务器端的视图技术,还有客户端的视图技术。区别在于,服务器端视图技术的模板引擎采用服务器端语言,客户端的视图技术采用客户端语言。
两者各有优势。主流开发模式更偏向于客户端的视图技术。在客户端对页面进行渲染,有效地减少了对服务器端的依赖,可以降低服务器端的承受压力。
这并不是绝对的,最后的选择还是要根据项目的运行场景做决定。
在 Spring MVC 项目中使用 Thymeleaf ,配置过程并不复杂。跟着流程走,你将体验到 Thymeleaf 的魅力。
视图技术至少需要提供模板和模板引擎,Thymeleaf 也不例外。如果要在 Spring MVC 中使用 Thymeleaf ,需要告诉 Spring MVC 模板存放在哪里?模板引擎是谁?
Tips: 本章节使用纯 JAVA 方法进行配置。
2.1 配置流程
- 打开项目中的 pom.xml 文件,添加项目对 Thymeleaf 包的依赖;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
- 打开项目中的 WebConfig 配置类。在类中添加一个 ApplicationContext 类型的属性。并让 Spring 自动注入进来;
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
Tips: Thymeleaf 相关组件需要依赖上下文容器对象。
- 在 WebConfig 配置类中配置 Thymeleaf 模板组件信息,并指定模板文件存放位置;
@Bean
public SpringResourceTemplateResolver templateResolver() {
SpringResourceTemplateResolver templateResolver = new SpringResourceTemplateResolver();
templateResolver.setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
templateResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/templates/");
templateResolver.setSuffix(".html");
templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML);
templateResolver.setCacheable(true);
//templateResolver.setOrder(1);
return templateResolver;
}
Tips: Spring MVC 项目中可以使用多视图技术。可以使用模板对象的 setOrder ( ) 指定查找顺序。本章节主要讲解 Thymeleaf 视图技术。
所以,请大家注释掉配置过的其它视图技术的相关信息。
-
在 WebConfig 配置类中指定模板引擎对象;
先配置 SpringTemplateEngine 组件: 从字面上很好理解,模板引擎组件。
@Bean
public SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine() {
SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine();
templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver());
templateEngine.setEnableSpringELCompiler(true);
return templateEngine;
}
Tips: 这里有组件与组件的依赖关系。
配置 ThymeleafViewResolver 组件: 视图解析组件,依赖于模板引擎,模板引擎依赖模板资源。
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver(SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine) {
ThymeleafViewResolver viewResolver = new ThymeleafViewResolver();
viewResolver.setTemplateEngine(templateEngine);
viewResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
return viewResolver;
}
经过上述配置后,Spring MVC 就具有了对 Thymeleaf 的支持。
2.2 测试流程
-
在项目的 WEB-INF 目录下新建 templates 目录,并在此目录下新建名为 hello.html 的文件。
Tips: hello.html 虽然扩展名是 html。 其实是遵循 Thymeleaf 模板语法规范的模板文件。本课程主要讲解在 Spring MVC 中如何使用 Thymeleaf , 会讲解一点 Thymeleaf 模板语法,但更多的了解需要你移步到 Thymeleaf 的官方网站:https://www.thymeleaf.org/。
hello.html 文件的内容:
<div>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>name</th>
<th>password</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td th:text="${user.userName}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.userPassword}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
Tips: hello.html 文件内容和普通的 HTML 页面没有多大的区别,区别于在 HTML 页面标签中使用了 Thymeleaf 提供的一些语法元素,如:th:text 用来动态读取作用域中的数据。
- 编写控制器;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafAction {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String thymeleaf(ModelMap map) {
User user=new User("mk", "123456");
map.addAttribute("user", user);
return "hello";
}
}
- 发布项目、启动 tomcat、打开浏览器,在浏览器中输入: http://localhost:8888/sm-demo/thymeleaf/hello。
Tips: 再声明一下,为了让 Thymeleaf 的测试更干净,注释或删除掉原来配置过的视图技术相关信息。
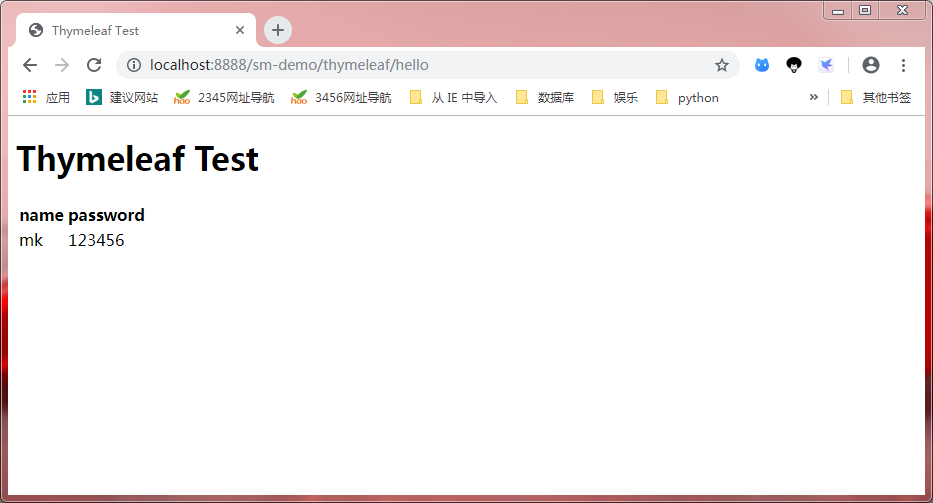
Thymeleaf 的语法元素也称其为指令,以 th 开头,如前面用到的 th:text。
3. Thymeleaf 的特点
Thymeleaf 与其它的视图技术相比较,最大的优点在于动静结合。
何谓动静给合?
Thymeleaf 的模板是纯正的 html 代码。Thymeleaf 提供的模板语法指令都是以 HTML 标签属性方式嵌入进去的,没有为页面添加额外的元素,页面的整体风格不会被破坏。
当运行在服务器端时,才会由模板引擎解析。如果直接由浏览器打开,浏览器会忽视 Thymeleaf 指令属性,把模板文件当成 HTML 代码,可以直接在浏览器显示。
动静结合的优点:
- 不影响前后端工程师对页面的设计和调整;
- 没有在页面中侵入非 HTML 语言代码,保持了原始页面的风格。
除了动静给合,还有一个较大的特点就是与 Spring MVC 或 Spring Boot 完美结合,Spring 提供有对接 Thymeleaf 的接口组件,使用起来方便直接。
正因为 Thymeleaf 的优点,建议作为项目开发中的首选方案。
4. 小结
本节课程和大家一起讲解了 Spring MVC 中如何使用 Thymeleaf。
使用 Thymeleaf 之前需要做些简单的配置,一定要注意组件之间的依赖关系。本课程并没有深入的讲解 Thymeleaf 的模板语法,但其语法并不复杂 。如果你对 Thymeleaf 有兴趣,可以进入官方网站了解更多。