Spring 集成 JdbcTemplate
1. 前言
各位同学大家好,我们又见面了。在前面的一些小节中,我们已经学习了 Spring 的基本使用,包括概念解释,IOC 容器使用,AOP 面向切面编程。那么本小节,我们要学习哪些新知识呢?是有关 Spring 对于事务的操作相关知识。
慕课解释:
在我们之前的案例中,我们实现了对数据库的数据做增删改查,但是使用的类是 QueryRunner ,它是属于 DbUtils 中的一个操作数据库的工具类,是 Jdbc 技术中的范围。而 Jdbc 属于最底层的接口,是一个规范,定义了 Java 操作数据库必须实现的硬性要求。它虽然能满足项目的开发需求,但是它有以下弊端:
- Jdbc 的工具类需要手动获取连接,释放资源,频繁地开启和关闭连接,造成资源的浪费;
- 代码和 SQL 语句硬性编码在一起,耦合性太高,不利于维护。因为 SQL 语句的修改,涉及到 Java 代码的修改;
- 数据操作繁琐,参数的位置和类型匹配容错率极低;
- 最重要的,使用 Jdbc 的过程中,事务的控制,需要自己手动的回滚和提交,开发成本高。
那么如何优雅地解决呢?有请我们的主角登场…JdbcTemplate ,也是本小节我们重点学习的内容。
2. 实例演示
2.1 JdbcTemplate 使用介绍
概念解释:
JdbcTemplate 是 Spring 框架提供的一个类,对 Spring Jdbc 接口做了实现,负责处理资源的建立和释放,对于开发人员来说只需要提供 SQL 语句,使 JDBC 更加易于使用。
使用方式:
- 引入使用的依赖 jar 包文件: 既然是个封装的框架类,那么一定也需要引入框架中的依赖 jar 包;
- 在 Spring 框架的配置文件中配置 JdbcTemplate 类: 使用的类实例化的动作都交给 Spring ,它当然也不例外;
- 在 Dao 的实现类中,引入 JdbTemplate 的类属性: 既然作用是操作数据的工具类,它作用就是替换掉了之前使用的 Jdbc 中的 QueryRunner 。
2.2 工程搭建
1. 创建工程
2. 引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring jdbc 使用的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3. 准备代码
实体类代码
/**
* 账户的实体类
*/
public class Account implements Serializable {
//数据id
private Integer id;
//账号编码
private String accountNum;
//账号金额
private Float money;
}
接口代码
/**
* 账户的持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 根据Id查询账户
* @param accountId
* @return
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
/**
* 保存账户
* @param account
*/
void saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* 更新账户
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
}
实现类代码
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
//jdbc模板类属性
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//根据id查找
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id = ?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
return accounts.isEmpty()?null:accounts.get(0);
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values(?,?,?)",
account.getId(),account.getAccountNum(),account.getMoney());
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set accountnum=?,money=? where id=?",account.getAccountNum(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
}
4. 配置文件
<!--配置JdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///transmoney"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--路径扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.offcn.dao"></context:component-scan>
5. 测试代码
/**
* 测试数据的查询和修改
*/
public class JdbcTemplateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.获取对象
IAccountDao accountDao = ac.getBean(IAccountDao.class);
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(1);
System.out.println(account);
account.setMoney(2000f);
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
System.out.println("账号更改成功");
}
}
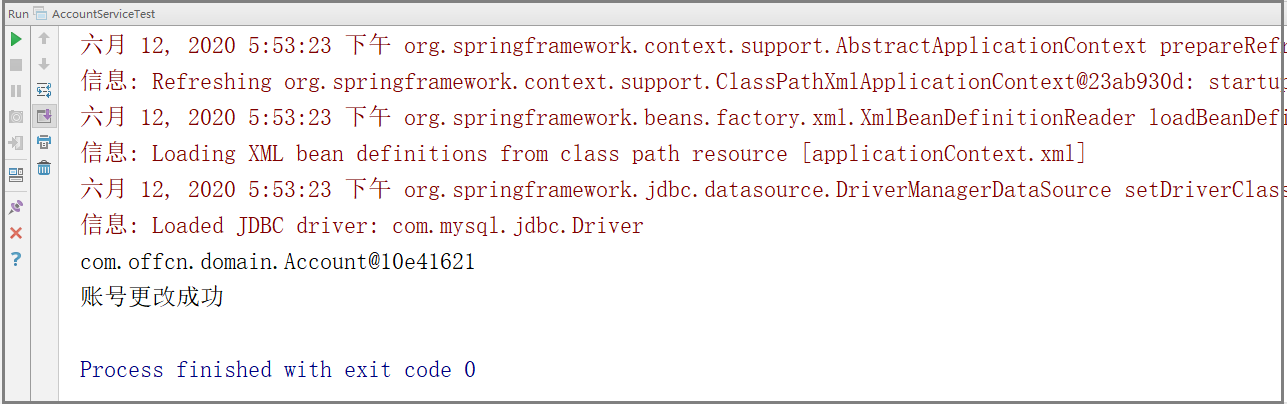
6. 测试结果:
3. 总结
好了,大家。通过上面的案例,我们已经看到了通过 JdbcTemplate 操作数据库的效果了。我们来做一个小的总结哈。
- 使用 JdbcTemplate 替换掉原来 Jdbc 的实现方式,代码更为整洁;
- Spring 的配置文件中,只配置 JdbcTemplate 模板类即可,配置更为简单;
- 数据库连接的获取与释放,无需手动调用方法,因为由 JdbcTemplate 帮助我们实现了,我们只需关注业务实现,无需考虑资源的使用,提升开发效率。
当然:对于事务的控制,本小节并没有体现,只是最为基础的使用。在下个小节的讲解中,我会带你体验 Spring 对事务的控制。本小节先到这里,谢谢大家的关注。
没有比人更高的山… 没有比脚更长的路… 继续加油哦!