-

- 斯巴达汉子 2022-01-31
10.子查询中的null问题
单行子查询中的null问题----结果是空值
多行子查询中的null问题
示例:查询不是老板的员工
select *
from emp
where empno not in (select mgr from emp);
-- 因为子查询中有null,导致返回空数据
select *
from emp
where empno not in (select mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕设计4302654 2021-10-13
单行子查询中的null值问题:若员工表中不存在Tom员工,主查询的提交就永远为假

多行子查询中的null值问题:案列:查询不是老板的员工。即查询下图的叶子节点即8条记录【员工表中MGR列表示该员工的老板员工号 】

not in 的空值问题【a not in {10,20,null}等价于 a !=10 and a!=20 and a!=null;判断一个值是否为空永远为假]

员工表中MGR列的员工KING为空值

即查询如下语句无返回结果:
select *
from emp
where empno not in (select mgr from emp)
正确的使用多行子查询中不包含空值
select *
from emp
where empno not in (select mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_羽悦_03291187 2020-09-28
子查询空值问题not in ,is not null
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_羽悦_03291187 2020-09-28
单行子查询空值问题
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 若如芮蕾 2020-07-02
多行子查询的空值问题:
--查询所有不是老板的员工
select * from emp where empno
not in -- 只要子查询中的结果集包含空值,不要使用not in 因为not in 等同与 <> all 比如: a not in (10,20,null) 这句话的意思是 a != 10 && a != 20 && a != null
(
select mgr from emp --员工表中的老板号
)
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕粉13485244983 2020-03-15
- not in 后面的子查询结果集中不能含有控制,要跟 where mgr is not null
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_慕标5384168 2020-03-03
子查询中的NULL值问题
1、单行子查询中的NULL值问题(子查询不返回任何行)
2、多行子查询中的NULL值问题
查询不是老板的员工
select * from emp where empno not in (select mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- BZzzzzzz 2020-01-04
where ** not in (子查询)
子查询结果集中不能有null,子查询有空值,则主查询返回无结果
使用not in 时,子查询的where条件要加上查询结果列 is not null 才行
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕粉2136255539 2019-08-14
- 子查询中包含空值时不能用not in 但是可以用in not in 等同与<>ANY
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕仰5014332 2019-07-26
not in
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 如果成功会怎样 2019-06-04
多行子查询注意的问题
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕粉6666888 2019-04-28
第四章:子查询
1.子查询案例
示例:查询工资比员工scott高的员工信息
select * from emp
where sal>(select sal from emp where ename='SCOTT');
2.子查询注意的10个问题
子查询语法中的小括号
子查询的书写风格
可以使用子查询的位置:where,select,having,from
select empno,ename,sal,(select job from emp where empno=7839) 第四列
from emp ;
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno
having avg(sal)>(select max(sal) from emp where deptno=30);--having与where区别,having可以跟group by,where不可以。
不可以使用子查询的位置:group by
--按照部门查询部门平均工资
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno;--正确
select deptno,avg(sal) from
emp group by (select deptno from emp);--错误
强调:from后面的子查询
--from后面的子查询,看做新的表
--示例1:查询员工信息:员工号,姓名,月薪
select empno,ename,sal from emp;
--示例1:查询员工信息:员工号,姓名,月薪,年薪
select empno,ename,sal,(select sal*12 from emp) from emp;
select empno,ename,sal 月薪,sal*12 年薪 from emp;
select * from (select empno,ename,sal 月薪,sal*12 年薪 from emp);
主查询和子查询可以不是同一张表
--主查询和子查询可以不是同一张表
--示例:查询部门名称是SALES的员工信息
select * from dept;
select * from emp
where deptno=
(select deptno from DEPT where dname='SALES');
select e.* from emp e,dept d
where e.deptno=d.deptno
and d.dname='SALES';
--结果一致,理论上,下面的好与上面的,实际中,子查询好于多表查询,因为笛卡尔集很大
一般不在子查询中,使用排序;但在Top-N分析问题中,必须对子查询排序
--一般不在子查询中进行排序
--Top-N分析中要排序
--示例:找到员工表中工资最高的前三名
--rownum 行号 伪列 (查询语句中必须写出它)
--行号需要注意的两个问题:行号永远按照默认顺序生成,行号只能使用<.<=;不能使用>,>=
select rownum,empno,ename,sal from
(select * from emp order by sal desc)
where rownum<=3;--正确排序
select rownum,empno,ename,sal from emp
where rownum<=3
order by sal desc;
--只是前三条记录,没有按照薪水排序
一般先执行子查询,再执行主查询,但相关子查询例外
--示例:找到员工表中薪水大于本部门平均薪水的员工
select empno,ename,sal,(select avg(sal) from emp where deptno=e.deptno) avgsal
from emp e
where sal>(select avg(sal) from emp where deptno=e.deptno);
单行子查询只能使用单行操作符(查询语句返回一条记录);
多行子查询只能使用多行操作符(查询语句返回多条记录)
--子查询只返回一条记录叫单行子查询,返回两条及以上记录叫多行操作符
--单行子查询只能使用单行操作符,多行子查询只能使用多行操作符
--单行操作符:=,>,>=,<,<=,<>;多行操作符:in,any,all
--查询员工信息,要求:职位与7566员工一样,薪水大于7782员工的薪水
select * from emp
where job=(select job from emp where empno=7566) --单行子查询,
and sal>(select sal from emp where empno=7782);
--单行子查询只能使用单行操作符,一个查询语句中可以有多个单行子查询
--单行子查询
--查询工资最低的员工信息
select * from emp
where sal in (select min(sal) from emp);
select * from emp
where sal = (select min(sal) from emp); --单行子查询
--查询最低工资,大于10号部门最低工资,的部门号和部门的最低工资
select deptno,min(sal) from emp group by deptno;--所有部门的最低工资
(select min(sal) from emp where deptno=20) ;--10号部门最低工资
select * from (select deptno,min(sal) b from emp group by deptno)
where b>(select min(sal) from emp where deptno=20);--不使用having
select deptno,min(sal) from emp group by deptno
having min(sal)>(select min(sal) from emp where deptno=20) ;
--分组函数后面不能跟where,可以跟having代替where
--非法使用单行子查询
select empno,ename from emp
where sal = (select min(sal) from emp group by deptno);--子查询中是多行的集合,非法
--多行操作符in
--查询部门名称是SALES和ACCOUNTING的员工
select emp.* from emp,dept where emp.DEPTNO=dept.DEPTNO --多表查询
and dept.dname IN('SALES','ACCOUNTING');
select emp.* from emp,dept where emp.DEPTNO=dept.DEPTNO --多表查询
and (dept.dname ='SALES' or dept.dname ='ACCOUNTING');--优先级先and,后or
select * from emp --子查询
where deptno in
(select deptno from dept where dname ='SALES' or dname ='ACCOUNTING');
--多行操作符ANY
--查询工资比30号部门任意一个员工高的员工信息
select * from emp where sal>(select min(sal) from emp where deptno=30);
select * from emp where sal >any(select sal from emp where deptno=30);
--多行操作符ALL
select * from emp where sal >ALL(select sal from emp where deptno=30);
注意:子查询中是null值问题
--单行子查询中的null值问题,判断一个值等不等与null值不能用=或<>,因为永远是不等的,
--判断一个值等不等与null值,只能用IN 或is not
select * from emp
where job=
(select job from emp where ename='TOM');--子查询不返回任何行
--多行子查询中的空值
--查询不是老板的员工
select * from emp where empno in (select MGR from emp);
select * from emp where empno not in (select MGR from emp);--空值
--只要子查询中返回值包含null值,不要使用not in,因为not in 等同与<> ALL(不等于所有值)
select * from emp
where empno not in
(select MGR from emp where mgr is not null);--加上不为空的限制
- 2赞 · 2采集
-

- Amousy 2019-03-30
a not in (10, 20, null ) => a!=10 and a!=20 and a!=null--这是不可能的,null不能用等不等于来衡量
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_星_20 2019-03-16
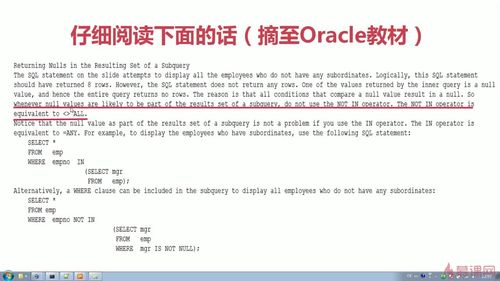
多行子查询中的null值问题
One of the values returned by the inner query is a null value,and hence the entire query returns no rows.The reason is that all conditions that compare a null value result in a null.So whenever null values are likely to be part of the results set of a subquery,do not use the not in operator.The NOT IN operator is quivalent to <>ALL.
Notice that the null value as part of the results set of a subquery is not a problem if you use the IN operator.The IN operator is equivalent to =ANY.For example,to display the employees who have subordinates,use the following SQL statement:
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE empno IN (SELECT mgr FROM EMP);
Alternatively,a WHERE clause can be included in the subquery to display all employees who do not have any subordinates:
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE empno NOT IN (SELECT mgr FROM emp WHERE mgr IS NOT NULL);
-----如果多行子查询出现null值,再使用not in进行多行子查询,将查不到任何记录,因为此时相当于不等于所有(<>all),所以在子查询中必须先在where条件中,把null值过滤掉,再使用not in
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- ldchenrj 2019-03-06
oracle中空值都比较特殊,不能直接用"="或"<>"号来比较,空值既不在等于的集内,也不在不等于的集内
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- weibo_fate自身难保_0 2018-12-19
如果集合中有空值不能使用not in 因为 not in等价于<>all,就是所以a not in (1,2,null)就是a!=1 and a!=2 and a!=null,因为a!=null永远是false所以最后是没有值返回的,当使用in 的集合中有null是可以的,因为此时是or的操作了。如果要使用not in集合中有空值,就是用where is not null过滤掉就可以了。
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕妹9209972 2018-12-11
多行子查询包含空值NULL时,不能使用not in 只能使用in
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_故事中的人_0 2018-06-24
1.查询不是老板的员工:
select *
from emp
where empno not in (select mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
2.not in(结果集):注意not in 后面括号里的结果集不能有空值,必须想办法过滤掉空值
- 0赞 · 1采集
-

- 慕斯9756157 2018-06-03
select *
from emp e
where e.empno not in
(select mgr from emp where mgr is not null)
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 小光头 2018-05-21
not in语句中不能有null值,否则返回空集,因为expr <> null永远为假。
所以在处理 in 的子查询的时候,要确保子查询中返回的值没有空值。
select * from emp where empno not in (select mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 不完美的小小鸟 2018-04-06
- 多行子查询中的空值问题
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 进击第一护妻狂魔 2017-11-18
- select * from emp where empno not in (select mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 回不去小艾 2017-10-31
- not in 后面不能加一个带有空值的集合,因为in null 始终是假命题,所以整个not in就是一个查询不到结果的条件
-
截图0赞 · 1采集
-

- nize1989 2017-10-13
- 多行子查询中的控制问题
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕沐8044423 2017-09-10
- 子查询注意十项
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- hellomingxing3448605 2017-08-28
- a!=null,永远是假的
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- hellomingxing3448605 2017-08-28
- not in (<>all)
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 秋天的木头 2017-07-20
- null值子查询问题
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_喂丶我的男人不准看_0 2017-06-28
- 多行子查询,需要注意使用not in时一定要排除null,not in等同于all。in可以包含空值,in等于与any。判断是否为空,使用isnull
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_喂丶我的男人不准看_0 2017-06-28
- not in里面包含空值,等同于他不等于里面的所有值,判断一个值是否为空一定为假,所以一定查不出来
- 0赞 · 0采集






























