-

- 旅行的癞蛤蟆 2023-09-17
Bean1代码改造前和改造后的对比:
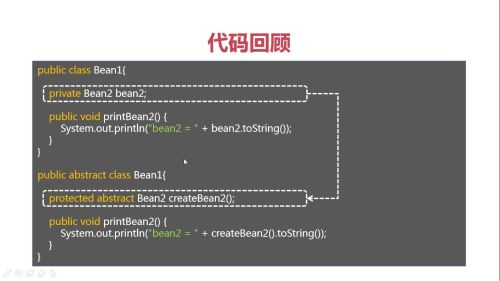
Spring配置文件中的改造:

- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 旅行的癞蛤蟆 2023-09-17

单例bean1情况下实现多实例bean2:
在bean1里添加protected的抽象类Bean2

- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_慕丝5234928 2022-08-01

bean1单例,Bean2多例的时候
如果想要注入的bean2是不同bean2时,可以用
类中定义abstract抽象方法,protect abstract Bean2 createBean2();
配置文件种 原来property标签注入的,改用lookup-method标签注入name制定泪中方法,bean制定注入bean2
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 0柠檬0 2022-06-05
通过Spring的xml文件配置Bean作用域:(Spring默认作用域是Singleton)
1、Singleton作用域(单例模式:通过Spring容器实现单例模式,具有局限性:保证在一个Spring上下文(ApplicationContext)是单例模式,多个AppliactionContext单例模式就失效了。
定义:如果一个<bean>的作用域为Singleton,则该<bean>只会被实例化一次,只有一个Bean会被创建。(每次向Spring上下文(ApplicationContext生命周期存活)请求这个实例时,Spring都会返回同一个实例)。

2、prototype作用域(多例模式)
定义:如果一个<bean>的作用域为prototype,则该<bean>会被实例化多次,有多个Bean会被创建(每次向Spring上下文请求该Bean都会new一个新的实例)。
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕宸 2021-11-06
作用域
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- silence1210 2021-04-25
测试集中情况: 第一种:被引用bean1为单例模式,bean也为单例模式
<bean id = "bean1" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean1" scope="singleton" /> <bean id = "bean" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean" scope="singleton"> <property ref="bean1" name="bean1"/> </bean>

第二种:被引用类bean1为多例模式,bean为单例模式 <bean id = "bean1" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean1" scope="prototype" /> <bean id = "bean" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean" scope="singleton"> <property ref="bean1" name="bean1"/> </bean>

第三种:被引用类bean1为单例,bean为多例模式 <bean id = "bean1" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean1" scope="singleton" /> <bean id = "bean" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean" scope="prototype"> <property ref="bean1" name="bean1"/> </bean>

第四种:被引用类bean1为多例模式,bean为多例模式 <bean id = "bean1" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean1" scope="prototype" /> <bean id = "bean" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean" scope="prototype"> <property ref="bean1" name="bean1"/> </bean>

bean是单例模式singleton,bean1是多例模式prototype,bean依赖bean1.我们希望每次调用Bean的某个方法时, 该方法拿到的Bean1都是一个新的实例,做法如下:
package com.example.spring.ioc.class7; public abstract class Bean { protected abstract Bean1 createBean1(); public void printBean1(){ System.out.println(createBean1()); }}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id = "bean1" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean1" scope="prototype" /> <bean id = "bean" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean" scope="singleton"> <lookup-method bean="bean1" name="createBean1"/> </bean> </beans>
package com.example.spring.ioc.class7; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class BeanTest { @Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); System.out.println("--------------------------这是第一个Spring Context 上下文----------------------------"); Bean bean = ac.getBean("bean",Bean.class); bean.printBean1(); bean.printBean1(); bean.printBean1(); System.out.println("--------------------------这是第二个Spring Context 上下文----------------------------"); ApplicationContext ac1 = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); Bean bean_1 = ac1.getBean("bean",Bean.class); bean_1.printBean1(); bean_1.printBean1(); bean_1.printBean1(); } }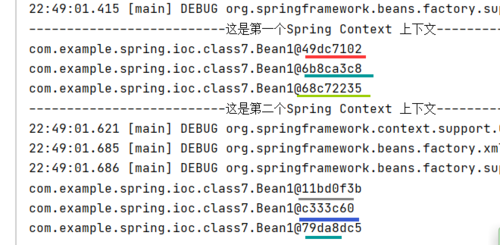
实体改造前: package com.example.spring.ioc.class7; public class Bean { public void printBean1(){ System.out.println("bean1 = " + bean1); } private Bean1 bean1; public Bean1 getBean1() { return bean1; } public void setBean1(Bean1 bean1) { this.bean1 = bean1; } } <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id = "bean1" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean1" scope="prototype" /> <bean id = "bean" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean" scope="singleton"> <property name="bean1" ref="bean1"/> </bean> </beans> package com.example.spring.ioc.class7; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class BeanTest { @Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); System.out.println("--------------------------这是第一个Spring Context 上下文----------------------------"); Bean bean = ac.getBean("bean",Bean.class); bean.printBean1(); bean.printBean1(); bean.printBean1(); System.out.println("--------------------------这是第二个Spring Context 上下文----------------------------"); ApplicationContext ac1 = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); Bean bean_1 = ac1.getBean("bean",Bean.class); bean_1.printBean1(); bean_1.printBean1(); bean_1.printBean1(); } }
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- silence1210 2021-04-25

Singleton作用于如下如:bean作为属性会被注入到anotherBean1 anotherBean2 anotherBean3中,这里注意,bean作为单例模式的话,只会有一个bean实例,所以注入到以上实体中的bean都是同一bean
在一个Spring上下文环境下,单例模式会生成一个实例,如果在多个上下文环境下则会一个Spring上下文环境单例模式会生成一个实例,多个Spring上下文每个Spring上下文都会生成一个单例模式!!!

package com.example.spring.ioc.class7; public class Bean { private Bean1 bean1; public Bean1 getBean1() { return bean1; } public void setBean1(Bean1 bean1) { this.bean1 = bean1; } @Override public String toString() { return "Bean{" + "bean1=" + bean1 + '}'; } }package com.example.spring.ioc.class7; public class Bean1 { }<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id = "bean1" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean1" scope="singleton" /> <bean id = "bean" class="com.example.spring.ioc.class7.Bean"> <property name="bean1" ref="bean1"/> </bean> </beans>
package com.example.spring.ioc.class7; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class BeanTest { @Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); Bean bean = ac.getBean("bean",Bean.class); Bean1 bean1 = ac.getBean("bean1",Bean1.class); System.out.println("Bean = " + bean); System.out.println("Bean1 = " + bean1); System.out.println(bean.toString()); System.out.println("--------------------------这是第二个Spring Context 上下文----------------------------"); ApplicationContext ac1 = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); Bean bean_1 = ac1.getBean("bean",Bean.class); Bean1 bean1_1 = ac1.getBean("bean1",Bean1.class); System.out.println("bean = " + bean_1); System.out.println("bean1 = " + bean1_1); System.out.println(bean.toString()); } }
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 爱学习的九亿少女 2020-12-22
Bean1和Bean2的作用域

- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 独进青楼 2020-11-15
Bean作用域
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
第二步,在spring.xml中去除<property />修改为<lookup-method />
<lookup-method name="createBean2" bean="bean2"/>
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
方法注入步骤:
第一步,将原本直接定义Bean2,修改为由虚函数方法导入。(图中上下对比)
protected abstract Bean2 createBean2();
注意:需要把类也定义成虚类。
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
方法注入 应用场景:
Bean1是singleton,Bean2是prototype,Bean1依赖Bean2。我们希望每次调用Bean1的某个方法是,该方法拿到的Bean2都是一个新的实例。
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
- <table width="0"><tbody><tr class="firstRow"><td valign="top" rowspan="2" colspan="2"> </td><td valign="top" rowspan="1" colspan="2">Bean1作用域<br /></td></tr><tr><td width="68" valign="top">singleton</td><td width="68" valign="top">prototype</td></tr><tr><td width="68" valign="top" rowspan="2" colspan="1">Bean2作用域</td><td width="68" valign="top">singleton</td><td width="68" valign="top"><p>Bean1单实例</p><p>Bean2单实例</p></td><td width="68" valign="top"><p>Bean1多实例</p><p>Bean2单实例</p></td></tr><tr><td width="68" valign="top">prototype</td><td width="68" valign="top"><p>Bean1单实例</p><p>Bean2单实例</p></td><td width="68" valign="top"><p>Bean1多实例</p><p>Bean2多实例</p></td></tr></tbody></table><p><br /></p>
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
如果Bean2是多例模式,Bean1是单例模式,Bean1和Bean2都是单实例。
如果Bean2是单例模式,Bean1是多例模式,那么创建的两个Bean1不一样,但注入Bean1的两个Bean2是同一个实例。
-
截图0赞 · 1采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
测试Prototype作用域结果:
每次获取bean2的实例都是不一样的,而且用bean2创建的bean1也是不一样的。
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
Prototype作用域写法:
是在<bean />标签中加上scope=“prototype”
<bean class="com.imooc.spring.ioc.class007.Bean2" id="bean2" scope="prototype"/>
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
测试Singleton作用域的test代码
在同一上下文context中,获取的bean2一样。
注意:Singleton作用域具有只在同一个上下文context中适用的局限性,两个上下文contest获取的bean2不一样。
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
Singleton作用域写法:
是在<bean />标签中加上scope=“singleton”
<bean class="com.imooc.spring.ioc.class007.Bean2" id="bean2" scope="singleton"/>
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
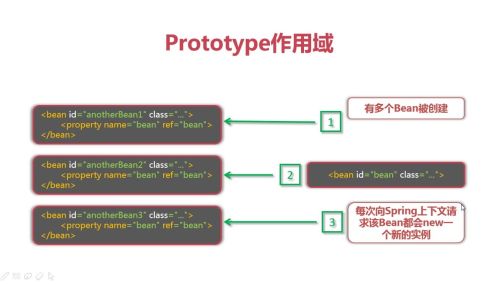
Prototype作用域(多例模式)
有多个Bean被创建,每次想Spring上下文请求该Bean都会new一个新的实例。
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
Singleton作用域(单例模式)
只有一个Bean被创建,且这个Bean被注入到任何需要它的地方。
没加scope,默认为Singleton作用域(单例模式)。
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Mk仔 2020-08-02
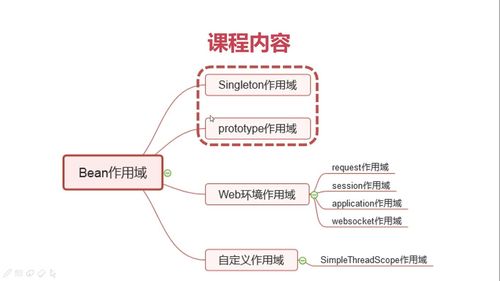
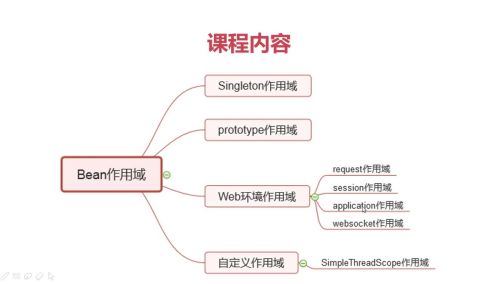
Bean作用域 课程内容
Singleton作用域
prototype作用域
Web环境作用域
request作用域
session作用域
application作用域
websocket作用域
自定义作用域
SimpleThreadScope作用域
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 白石溪 2020-04-16
singleton 单例模式 每次向同一个Spring上下文环境请求实例时,都返回同一个实例。
prototype 多例模式 每次向Spring上下文环境请求实例时都是全新的实例。
bean1依赖于bean2
bean1、bean2都单例,都只创建一个实例
bean1单例、bean2多例,都只创建一个实例
bean1多例、bean2单例,2个bean1不同,bean2都是一个实例、
bean1、bean2都多例,bean1、bean2都是不同实例
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕粉42788080 2020-03-06
3333333333333333333333333
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕粉42788080 2020-03-06
sssssssssssssss
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕粉42788080 2020-03-06
Prototype作用域
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕粉42788080 2020-03-06
Singleton作用域
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- JadeOrion 2020-02-06
相互依赖Bean不同作用域组合
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- JadeOrion 2020-02-05
bean的作用域
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Felixle 2020-01-06
123456
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- YogurtJ 2019-12-09
单例模式:每次向Spring上下文请求bean的时候它都会给你返回同一个实例
-
截图0赞 · 0采集















