事件及监听并不是SpringBoot的新功能,Spring框架早已提供了完善的事件监听机制,在Spring框架中实现事件监听的流程如下:
自定义事件,继承org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent抽象类
定义事件监听器,实现org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener接口
在Spring容器中发布事件
实现自定义事件及监听
定义事件
1 //自定义事件 2 public class ApplicationEventTest extends ApplicationEvent { 3 4 public ApplicationEventTest(Object source) { 5 super(source); 6 } 7 8 /** 9 * 事件处理事项10 * @param msg11 */12 public void printMsg(String msg)13 {14 System.out.println("监听到事件:"+ApplicationEventTest.class);15 }16 }定义监听器
1 //自定义事件监听器 2 //@Component 3 public class ApplicationListenerTest implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEventTest> { 4 5 @Override 6 public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEventTest event) { 7 8 event.printMsg(null); 9 }10 }在Spring容器中发布事件
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(SpringbootdemoApplication.class); 4 //需要把监听器加入到spring容器中 5 application.addListeners(new ApplicationListenerTest()); 6 Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners = application.getListeners(); 7 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = application.run(args); 8 //发布事件 9 context.publishEvent(new ApplicationEventTest(new Object()));10 11 context.close();12 }上面的示例是在SpringBoot应用中简单的测试一下。
实际开发中实现监听还有其他的方式,在Spring框架中提供了两种事件监听的方式:
编程式:通过实现ApplicationListener接口来监听指定类型的事件
注解式:通过在方法上加@EventListener注解的方式监听指定参数类型的事件,写该类需要托管到Spring容器中
在SpringBoot应用中还可以通过配置的方式实现监听:
3. 通过application.properties中配置context.listener.classes属性指定监听器
下面分别分析一下这三种监听方式
编程式实现监听
实现ApplicationListenser接口:
1 @Component2 public class ApplicationListenerTest implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEventTest> {3 4 @Override5 public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEventTest event) {6 7 event.printMsg(null);8 }9 }控制台输出测试:
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(SpringbootdemoApplication.class); 4 //需要把监听器加入到spring容器中 5 //application.addListeners(new ApplicationListenerTest()); 6 //Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners = application.getListeners(); 7 8 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = application.run(args); 9 //发布事件10 context.publishEvent(new ApplicationEventTest(new Object()));11 }那么我们跟踪一下源码,看一下事件是如何发布出去的,又是如何被监听到的呢?
AbstractApplicationContext.java中截取部分代码
1 protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { 2 Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null"); 3 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 4 logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event); 5 } 6 7 // Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary 8 /将object转成ApplicationEvent 9 ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;10 if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {11 applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;12 }13 else {14 applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);15 if (eventType == null) {16 eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();17 }18 }19 20 // Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized22 if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {23 this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);24 }25 else {26 // SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 获取事件发布器,发布事件27 getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);28 }29 30 // Publish event via parent context as well...31 if (this.parent != null) {32 if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {33 ((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);34 }35 else {36 this.parent.publishEvent(event);37 }38 }39 }查看一下ApplicationContext类结构图可以发现:应用上下文AbstractApplicationContext实际还是通过继承ApplicationEventPublisher接口,实现了其中的事件发布的方法,使得Spring应用上下文有了发布事件的功能,在AbstractApplicationContext内部通过SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster事件发布类,将具体事件ApplicationEvent发布出去。
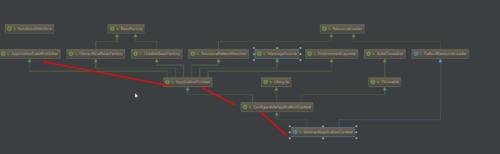
那么事件发布出去后又是如何被监听到的呢?下面看一下具Spring中负责处理事件发布类SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 中multicastEvent方法具体实现过程
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java部分代码,实际尝试将当前事件逐个广播到指定类型的监听器中(listeners已经根据当前事件类型过滤了)
1 @Override 2 public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { 3 ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event)); 4 // getApplicationListeners(event, type) 筛选监听器,在context.publish(ApplicationEvent event)中已经将事件传入,getApplicationListeners中将可以根据这个event类型从Spring容器中检索出符合条件的监听器 5 6 for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) { 7 Executor executor = getTaskExecutor(); 8 if (executor != null) { 9 executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));10 }11 else {12 //尝试逐个向监听器广播13 invokeListener(listener, event);14 }15 }16 }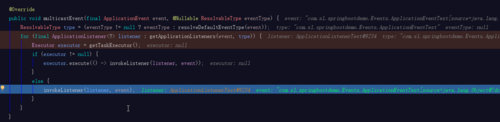
@EventListener注解方式实现
定义注解方法
@Componentpublic class MyEventHandleTest { /**
* 参数为Object类型时,所有事件都会监听到
* 参数为指定类型事件时,该参数类型事件或者其子事件(子类)都可以接收到 */
@EventListener public void event(ApplicationEventTest event){
event.printMsg(null);
}
}实现过程分析:
@EventListener注解主要通过EventListenerMethodProcessor扫描出所有带有@EventListener注解的方法,然后动态构造事件监听器,并将监听器托管到Spring应用上文中。
1 protected void processBean( 2 final List<EventListenerFactory> factories, final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) { 3 4 if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType)) { 5 Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null; 6 try { 7 //查找含有@EventListener注解的所有方法 8 annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType, 9 (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method ->10 AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));11 }12 catch (Throwable ex) {13 // An unresolvable type in a method signature, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.14 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {15 logger.debug("Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);16 }17 }18 if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) {19 this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetType);20 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {21 logger.trace("No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType.getName());22 }23 }24 else {25 // Non-empty set of methods26 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = getApplicationContext();27 //遍历含有@EventListener注解的方法28 for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {29 for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {30 if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) {31 Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName));32 //动态构造相对应的事件监听器33 ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =34 factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);35 if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {36 ((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaluator);37 }38 //将监听器添加的Spring应用上下文中托管39 context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);40 break;41 }42 }43 }44 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {45 logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @EventListener methods processed on bean '" +46 beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods);47 }48 }49 }50 }在application.properties中配置context.listener.classes
添加如下配置:
context.listener.classes=com.sl.springbootdemo.Listeners.ApplicationListenerTest
查看一下DelegatingApplicationListener类中实现逻辑:
1 public class DelegatingApplicationListener 2 implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>, Ordered { 3 4 private static final String PROPERTY_NAME = "context.listener.classes"; 5 6 private int order = 0; 7 //Spring framework提供的负责处理发布事件的类,前面说的Spring应用上下文中也是通过这个类发布事件的 8 private SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster multicaster; 9 10 @Override11 public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {12 if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {13 // getListeners内部实现读取context.listener.classes配置的监听器14 List<ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>> delegates = getListeners(15 ((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event).getEnvironment());16 if (delegates.isEmpty()) {17 return;18 }19 this.multicaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();20 for (ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> listener : delegates) {21 this.multicaster.addApplicationListener(listener);22 }23 }24 //发布事件25 if (this.multicaster != null) {26 this.multicaster.multicastEvent(event);27 }28 }Spring-boot-{version}.jar包中提供一个类DelegatingApplicationListener,该类的作用是从application.properties中读取配置context.listener.classes,并将事件广播给这些配置的监听器。通过前面一章对SpringBoot启动流程分析,我们已经了解到SpringBoot启动时会从META-INF/spring.factories中读取key为org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener的所有监听器。DelegatingApplicationListener的功能可以让我们不需要创建META-INF/spring.factories,直接在application.properties中配置即可。
原文出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/ashleyboy/p/9566579.html


 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




