如何在Java中读取文本文件中行的特定部分?
我有一个文本文件,我在其中逐行编写了一些信息,如下所示:
name|Number|amount|PIN
如何以一种(例如)我能够在方法中仅使用“name”部分的方式回读数据?示例代码如下图所示。
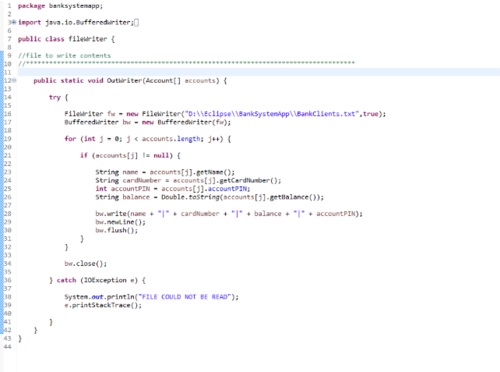
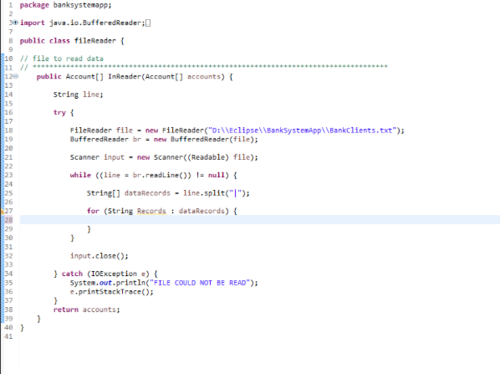
 慕娘9325324
慕娘9325324浏览 167回答 4
4回答
-

人到中年有点甜
在开始时声明一个列表来收集帐户:import java.util.ArrayList;...public Account[] inReader() { //BTW: why do you pass an Account[] here? ArrayList accountList = new ArrayList(); ...}将 替换为for(String records : dataRecords) {...}String name = dataRecords[0];String cardNumber = dataRecords[1];int pin = Integer.parseInt(dataRecords[2]); //to convert the String back to intdouble balance = Double.parseDouble(dataRecords[3]);Account account = new Account(name, cardNumber, pin, balance);accountList.add(account);因为您已经逐条记录地继续 (while ((line = br.readLine())!=null) {...})最后return accountList.toArray(new Account[0]); -

米脂
如上面的注释中所述,您可以简单地将分隔符上的行 ,然后从那里开始。split|像这样:public class Account { // ... public static Account parseLine(String line) { String[] split = line.split("|"); return new Account(split[0], split[1], split[2], split[3]); }}应该可以正常工作(假设你有一个构造函数,它接受你放入的四件事)。如果您的类具有比这更多的信息,则可以创建一个名称相似的类,该类仅包含此处提供的详细信息。有了这个,只需逐行迭代,将你的行解析为其中一个,并在调用其他需要的方法时使用它的属性(包括已经可用的 getter),等等。AccountAccountViewObjectname -

拉风的咖菲猫
有许多可能的方法可以做到这一点。其中之一是创建一个将保存数据的对象。例如,由于您知道您的数据将始终具有名称,数字,数量和引脚,因此您可以创建如下类:public class MyData { private String name; private String number; private double amount; private String pin; // Add getters and setters below}然后,在读取文本文件时,您可以列出并添加每个数据。你可以这样做:MyDatatry { BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("path\file.txt")); String line = reader.readLine(); ArrayList<MyData> myDataList = new ArrayList<MyData>(); while (line != null) { String[] dataParts = line.split("|"); // since your delimiter is "|" MyData myData = new MyData(); myData.setName(dataParts[0]); myData.setNumber(dataParts[1]); myData.setAmount(Double.parseDouble(dataParts[2])); myData.setPin(dataParts[3]); myDataList.add(myData); // read next line line = reader.readLine();} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();}然后,您可以使用如下数据:myDataList.get(0).getName(); // if you want to get the name of line 1myDataList.get(1).getPin(); // if you want to get the pin of line 2 -

富国沪深
您可以逐行读取文件,并在分隔符“|”上拆分。下面的示例假定文件路径位于 args[0] 中,并且将读取然后输出输入的名称组件:public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File(args[0]); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); while(String line = br.readLine()) != null) { String[] details = line.split("|"); System.out.println(details[0]); }}
 随时随地看视频慕课网APP
随时随地看视频慕课网APP
相关分类




 Java
Java