如何在 PIL 中选择与图像边缘相邻的所有黑色像素?
我有一组图像培养皿,不幸的是不是最高质量(下面的示例,轴不是图像的一部分)。

我正在尝试选择背景并使用以下像素计算其面积:
image = Image.open(path)
black_image = 1 * (np.asarray(image.convert('L')) < 12)
black_region = black_image.sum()
这产生以下内容:
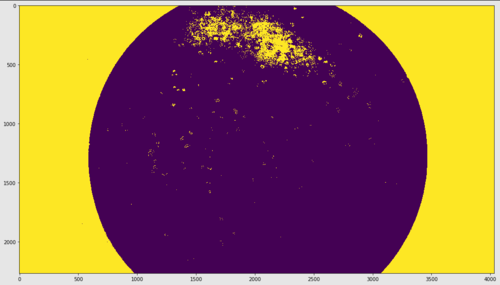
如果我对黑色像素的选择更严格,我会错过其他图像中的像素,如果我更宽松,我最终会选择过多的培养皿本身。有没有办法我只能选择亮度值小于 12 并且与边缘相邻的像素?我也对 openCV 解决方案持开放态度。
 蓝山帝景
蓝山帝景浏览 324回答 2
2回答
-

犯罪嫌疑人X
希望我没有把问题简单化,但从我的角度来看,使用 OpenCV 和简单的阈值、形态学操作,findContours应该可以完成这项工作。请看下面的代码:import cv2import numpy as np# Inputinput = cv2.imread('images/x0ziO.png', cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)# Input to grayscalegray = cv2.cvtColor(input, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# Binary threshold_, gray = cv2.threshold(gray, 20, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)# Morphological improvements of the maskgray = cv2.morphologyEx(gray, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (5, 5)))gray = cv2.morphologyEx(gray, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (11, 11)))# Find contourscnts, _ = cv2.findContours(gray, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)# Filter large size contours; at the end, there should only be one leftlargeCnts = []for cnt in cnts: if (cv2.contourArea(cnt) > 10000): largeCnts.append(cnt)# Draw (filled) contour(s)gray = np.uint8(np.zeros(gray.shape))gray = cv2.drawContours(gray, largeCnts, -1, 255, cv2.FILLED)# Calculate background pixel areabgArea = input.shape[0] * input.shape[1] - cv2.countNonZero(gray)# Put result on input imageinput = cv2.putText(input, 'Background area: ' + str(bgArea), (20, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL, 1.0, (255, 255, 255))cv2.imwrite('images/output.png', input)中间的“面具”图像如下所示:并且,最终输出如下所示: -

隔江千里
由于您对 OpenCV 方法持开放态度,因此您可以使用 SimpleBlobDetector显然我得到的结果也不完美,因为有很多超参数需要设置。超参数使它非常灵活,因此是一个不错的起点。这就是 Detector 的作用(请参阅此处的详细信息):阈值:通过使用从 minThreshold 开始的阈值对源图像进行阈值处理,将源图像转换为多个二值图像。这些阈值递增thresholdStep直到maxThreshold。所以第一个阈值是minThreshold,第二个是minThreshold + thresholdStep,第三个是minThreshold + 2 x thresholdStep,依此类推。分组:在每个二值图像中,连接的白色像素被分组在一起。让我们称这些为二进制 blob。合并:计算二进制图像中二进制 blob 的中心,并且比minDistBetweenBlobs合并位置更近的 blob 。中心和半径计算:计算并返回新合并的 blob 的中心和半径。找到图片下方的代码。# Standard importsimport cv2import numpy as np# Read imageim = cv2.imread("petri.png", cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)# Setup SimpleBlobDetector parameters.params = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector_Params()# Change thresholdsparams.minThreshold = 0params.maxThreshold = 255# Set edge gradientparams.thresholdStep = 5# Filter by Area.params.filterByArea = Trueparams.minArea = 10# Set up the detector with default parameters.detector = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector_create(params)# Detect blobs.keypoints = detector.detect(im)# Draw detected blobs as red circles.# cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS ensures the size of the circle corresponds to the size of blobim_with_keypoints = cv2.drawKeypoints(im, keypoints, np.array([]), (0, 0, 255), cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS)# Show keypointscv2.imshow("Keypoints", im_with_keypoints)cv2.waitKey(0)
 随时随地看视频慕课网APP
随时随地看视频慕课网APP
相关分类


 Python
Python