python:grads['dW1'] = dW1语法错误
coursera吴恩达的深度学习
课程 1
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
第4周作业:Deep Neural Network - Application
错误和报错如下:
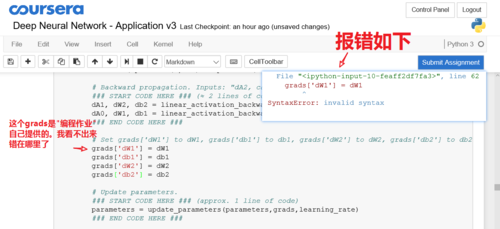
代码如下:
# GRADED FUNCTION: two_layer_model
def two_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate = 0.0075, num_iterations = 3000, print_cost=False):
"""
Implements a two-layer neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID.
Arguments:
X -- input data, of shape (n_x, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples)
layers_dims -- dimensions of the layers (n_x, n_h, n_y)
num_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization loop
learning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update rule
print_cost -- If set to True, this will print the cost every 100 iterations
Returns:
parameters -- a dictionary containing W1, W2, b1, and b2
"""
np.random.seed(1)
impo
grads = {}
costs = [] # to keep track of the cost
m = X.shape[1] # number of examples
(n_x, n_h, n_y) = layers_dims
# Initialize parameters dictionary, by calling one of the functions you'd previously implemented
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x,n_h,n_y)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Get W1, b1, W2 and b2 from the dictionary parameters.
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Loop (gradient descent)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# Forward propagation: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Inputs: "X, W1, b1". Output: "A1, cache1, A2, cache2".
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
A1, cache1 = linear_activation_forward(X,W1,b1,"relu")
A2, cache2 = linear_activation_forward(A1,W2,b2,"sigmoid")
### END CODE HERE ###
# Compute cost
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
cost = compute_cost(A2,Y)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Initializing backward propagation
dA2 = - (np.divide(Y, A2) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - A2))
# Backward propagation. Inputs: "dA2, cache2, cache1". Outputs: "dA1, dW2, db2; also dA0 (not used), dW1, db1".
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
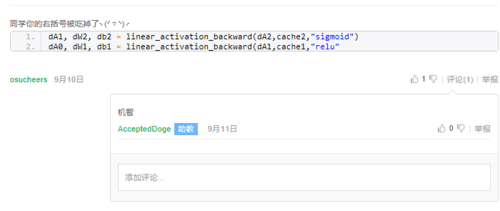
dA1, dW2, db2 = linear_activation_backward(dA2,cache2,"sigmoid")
dA0, dW1, db1 = linear_activation_backward(dA1,cache1,"relu"
### END CODE HERE ###
# Set grads['dWl'] to dW1, grads['db1'] to db1, grads['dW2'] to dW2, grads['db2'] to db2
grads['dW1'] = dW1
grads['db1'] = db1
grads['dW2'] = dW2
grads['db2'] = db2
# Update parameters.
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 1 line of code)
parameters = update_parameters(parameters,grads,learning_rate)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve W1, b1, W2, b2 from parameters
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Print the cost every 100 training example
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
print("Cost after iteration {}: {}".format(i, np.squeeze(cost)))
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parameters解决:
 无无法师
无无法师浏览 2967回答 0
0回答
 随时随地看视频慕课网APP
随时随地看视频慕课网APP
 Python
Python
 大数据
大数据