-

- WE_Xing 2021-07-29
Resource


- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 被踹踹子拥抱从现在做起 2021-04-12
 g
g- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 被踹踹子拥抱从现在做起 2021-04-12
 ;;
;;- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 程序员慕虎 2020-09-09
Resources:针对资源文件的统一接口,通过Spring加载一些资源文件的时候,可以通过它去控制。
——UrlResource:URL对应的资源,根据一个URL地址即可构建Resources。
——ClassPathResoure:获取类路径下的资源文件(相对路径)。
——FileSystemResource:获取文件系统里面的资源(绝对路径)。
——ServletContextResource:ServletContext封装的资源,用于访问ServletContext环境下的资源。(和Web相关的资源文件的入口)
——InputStreamResource:针对于输入流封装的资源。(构建它需要InputStream)
——ByteArrayResource:针对于字节数组封装的资源。(构建它需要ByteArray)
ResourceLoader:对Resource加载的一个类,在SpringIOC容器中,所有的ApplicationContext都实现了ResourceLoader接口,所有的ApplicationContext都可以用来获取Resource实例,所以可以通过getResource(String location)方法获取资源Resource。
ResourceLoader接口的声明(有个方法,输入为文件的位置,返回的是Resource的实例)
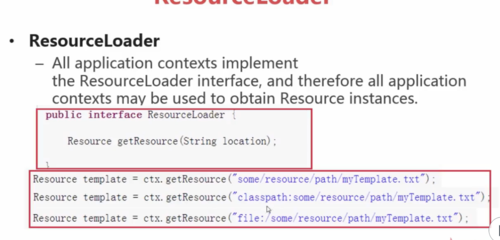
ResourceLoader注入参数时前缀的几种类型
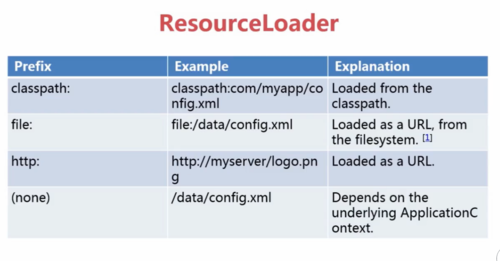
ResourceLoader前缀:classpath:(相对路径,加载文件)
file:(绝对路径,加载文件)
url: http(web路径、加载文件)
(none):直接输入路径,依赖ApplicationContext
案例:(Bean通过实现ApplicationContext接口,间接的实现了ResourceLoader接口(加载Resource实例),就可以使用getResource()获取Resource的实例,Resource拥有一系列的方法,比如获取文件名称(getFilename()和获取文件长度contentLength())
步骤1:
public class ResourceDemo implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext ac;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ac) throws BeansException {
this.ac=ac;
}
public void resource() throws IOException{
Resource r=ac.getResource("classpath:resourceDemo.txt");(直接写文件,而不写全路径,是因为Java build path 配置了source,所以这里是相对路径)
System.out.println(r.getFilename());
System.out.println(r.contentLength());
}
}
步骤2:
<bean id="resourceDemo" class="ResourceDemo" ></bean>
步骤3:
@Test
public void testBean() throws IOException{
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml");
ResourceDemo rd=(ResourceDemo)ac.getBean("resourceDemo");
rd.resource();
}
测试:
@Test
public void testBean() throws IOException{
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml");
ResourceDemo rd=(ResourceDemo)ac.getBean("resourceDemo");
rd.resource();
}
结果:(文件:resourceDemo.txt,在src——>resource文件夹下)
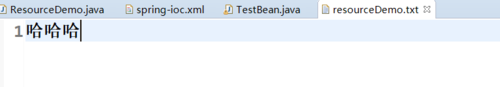
resourceDemo.txt
6
案例:file方式
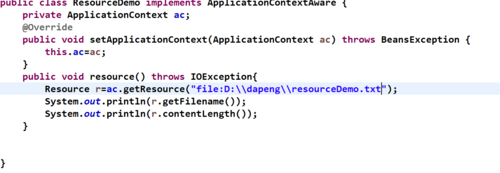
案例:url方式

- 0赞 · 1采集
-

- 慕莱坞9426565 2020-04-06
ResourceLoader API
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕莱坞9426565 2020-04-06
ResourceLoader
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕莱坞9426565 2020-04-06
Resources
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 丶彦彦 2019-12-26
 11111
11111-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕娘7173298 2019-10-08

当spring需要加载文件的时候会用到resources
resources 的加载类:

- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- Donreen 2019-10-03
这里的resource是
org.springframework.core.io.Resource
里面的,不要导错了。
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- SongNeil熊 2019-09-18
ResourceLoader
-
截图0赞 · 1采集
-

- SongNeil熊 2019-09-18
Resources
-
截图0赞 · 1采集
-

- qq_隆冬叮咚_0 2019-08-15
Resources


- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_蓝海_12 2019-08-12
ResourceLoader 注入方式
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_蓝海_12 2019-08-12
resourceloader例子
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- qq_蓝海_12 2019-08-12
resources
-
截图0赞 · 1采集
-

- BSSYNHDJZMH 2019-07-30
ResourceLoader
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- BSSYNHDJZMH 2019-07-30
Resources
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 大冬无敌 2019-07-30
Resources:针对资源文件的统一接口,通过Spring加载一些资源文件的时候,可以通过它去控制。
——UrlResource:URL对应的资源,根据一个URL地址即可构建Resources。
——ClassPathResoure:获取类路径下的资源文件(相对路径)。
——FileSystemResource:获取文件系统里面的资源(绝对路径)。
——ServletContextResource:ServletContext封装的资源,用于访问ServletContext环境下的资源。(和Web相关的资源文件的入口)
——InputStreamResource:针对于输入流封装的资源。(构建它需要InputStream)
——ByteArrayResource:针对于字节数组封装的资源。(构建它需要ByteArray)
ResourceLoader:对Resource加载的一个类,在SpringIOC容器中,所有的ApplicationContext都实现了ResourceLoader接口,所有的ApplicationContext都可以用来获取Resource实例,所以可以通过getResource(String location)方法获取资源Resource。
ResourceLoader接口的声明(有个方法,输入为文件的位置,返回的是Resource的实例)

ResourceLoader注入参数时前缀的几种类型

ResourceLoader前缀:classpath:(相对路径,加载文件)
file:(绝对路径,加载文件)
url: http(web路径、加载文件)
(none):直接输入路径,依赖ApplicationContext
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 程序猿天璇 2019-07-22
ResourceLoader 注入方式:
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 程序猿天璇 2019-07-22
Resources:针对于资源文件的统一接口
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- Uestc_L 2019-06-24
所有的 applicationContext 都实现了 resource 接口
如果什么都不写,就和 applicationContext 创建方式一样,例如 classpath: test.txt
- 0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕函数2222885 2019-06-03
- 哈哈
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 大鹏111 2019-05-16
Resources:针对资源文件的统一接口,通过Spring加载一些资源文件的时候,可以通过它去控制。
——UrlResource:URL对应的资源,根据一个URL地址即可构建Resources。
——ClassPathResoure:获取类路径下的资源文件(相对路径)。
——FileSystemResource:获取文件系统里面的资源(绝对路径)。
——ServletContextResource:ServletContext封装的资源,用于访问ServletContext环境下的资源。(和Web相关的资源文件的入口)
——InputStreamResource:针对于输入流封装的资源。(构建它需要InputStream)
——ByteArrayResource:针对于字节数组封装的资源。(构建它需要ByteArray)
ResourceLoader:对Resource加载的一个类,在SpringIOC容器中,所有的ApplicationContext都实现了ResourceLoader接口,所有的ApplicationContext都可以用来获取Resource实例,所以可以通过getResource(String location)方法获取资源Resource。
ResourceLoader接口的声明(有个方法,输入为文件的位置,返回的是Resource的实例)

ResourceLoader注入参数时前缀的几种类型

ResourceLoader前缀:classpath:(相对路径,加载文件)
file:(绝对路径,加载文件)
url: http(web路径、加载文件)
(none):直接输入路径,依赖ApplicationContext
案例:(Bean通过实现ApplicationContext接口,间接的实现了ResourceLoader接口(加载Resource实例),就可以使用getResource()获取Resource的实例,Resource拥有一系列的方法,比如获取文件名称(getFilename()和获取文件长度contentLength())

步骤1:
public class ResourceDemo implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext ac;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ac) throws BeansException {
this.ac=ac;
}
public void resource() throws IOException{
Resource r=ac.getResource("classpath:resourceDemo.txt");(直接写文件,而不写全路径,是因为Java build path 配置了source,所以这里是相对路径)
System.out.println(r.getFilename());
System.out.println(r.contentLength());
}
}
步骤2:
<bean id="resourceDemo" class="ResourceDemo" ></bean>
步骤3:
@Test
public void testBean() throws IOException{
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml");
ResourceDemo rd=(ResourceDemo)ac.getBean("resourceDemo");
rd.resource();
}
测试:
@Test
public void testBean() throws IOException{
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml");
ResourceDemo rd=(ResourceDemo)ac.getBean("resourceDemo");
rd.resource();
}
结果:(文件:resourceDemo.txt,在src——>resource文件夹下)

resourceDemo.txt
6
案例:file方式

案例:url方式

- 0赞 · 4采集
-

- 圣所中的少年 2019-04-28
ResourceLoader的bean装配
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 幕布斯7130376 2019-04-21
- 自动装配 byname bytype byname 根据名称 bytype 根据类型
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- ggartist 2019-04-16
Resources 针对于资源文件的统一接口
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 小鱼小鱼吃虾米 2019-04-14
Bean容器:
1)Bean配置项
2)Bean的作用域
3)Bean的生命周期
4)Bean的自动装配
5)Resources&ResourceLoader
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 小鱼小鱼吃虾米 2019-04-14
针对于资源文件的统一接口:
-
截图0赞 · 0采集
-

- 慕少4425114 2019-03-19
Resources
-
截图0赞 · 0采集






















