动画算法
jQuery 动画的原理还是很简单的,靠定时器不断的改变元素的属性,我们模拟下 animate 的大致实现,让元素执行一个 2 秒的动画到坐标为 left 50 的区域。
animate({
left: '50',
duration: '2000'
}
按照常规的思路,我们需要 3 个参数:
- 动画开始位置
- 动画的结束位置
- 动画的运行时间
思路一:等值变化
我们在 animate 内部还需要计算出当然元素的初始化布局的位置(比如 500px),那么我们在 2 秒的时间内需变换成 50px,也就是运行的路劲长就是 500-50 = 450px。
那么算法是不是呼之欲出了?
每毫秒移动的距离: pos = 450/2000 = 0.225px 每毫秒移动: left = 初始位置 (+/-) 每毫秒递增的距离(pos * 时间)
这样算法我们放到 setInterval 就会发现错的一塌糊涂,我们错在最本质的东西。
JS 是单线程,定时器都是排队列的,理论上也达不到 1ms 绘制一次 dom
所以每次产生的这个下一次绘制的时间差根本不是一个等比的,所以我们按照线性的等值递增是有误的。
思路二:动态计算
setInterval 的调用是不规律的,但是调用的时间是(2秒)是固定的,我们可以在每次调用的时候算法时间差的比值,用这个比值去计算移动的距离就比较准确了。
remaining = Math.max(0, startTime + duration - currentTime),
通过这个公司我们计算出,每次 setInterval 调用的时候,当前时间在总时间中的一个位置。
remainin 结果:
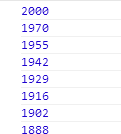
看到没有,这个值其实很符合定时器的特性,也是一个没有规律的值,根据这个值,我们可以得出当前位置的一个百分比了:
var remaining = Math.max(0, startTime + options.duration - createTime()) var temp = remaining / options.duration || 0; var percent = 1 - temp;
pecent结果
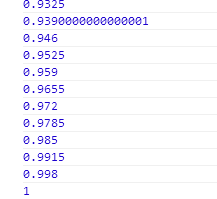
那么这个移动的距离就很简单了,我把整个公式就直接列出来了。
function tick(){
//每次变化的时间
var remaining = Math.max(0, startTime + duration - createTime())
var temp = remaining / duration || 0;
var percent = 1 - temp;
//最终每次移动的left距离
var leftPos = (endLeft- startLeft) * percent +startLeft;
}
leftPos 就是每次移动的距离了,基本上比较准确了,事实上 jQuery 内部也就是这么干的,这里 13 代表了动画每秒运行帧数,默认是13毫秒,属性值越小,在速度较快的浏览器中(例如,Chrome),动画执行的越流畅,但是会影响程序的性能并且占用更多的 CPU 资源,在新的游览器中,我们都可以采用 requestAnimationFrame 会更优。