一、AOP场景
AOP即面向切面编程,相比OOP--面向对象编程,由于面向对象中最基本的单位是类,实例,很自然会想到AOP中最基本的单位可能就是所谓的切面了,那切面又是个什么东西,先来看一段Spring中关于AOP的定义:
面向切面——Spring提供了面向切面编程的丰富支持,允许通过分离应用的业务逻辑与系统级服务(例如审计(auditing)和事务(transaction)管理)进行内聚性的开发。应用对象只实现它们应该做的——完成业务逻辑——仅此而已。它们并不负责(甚至是意识)其它的系统级关注点,例如日志或事务支持。
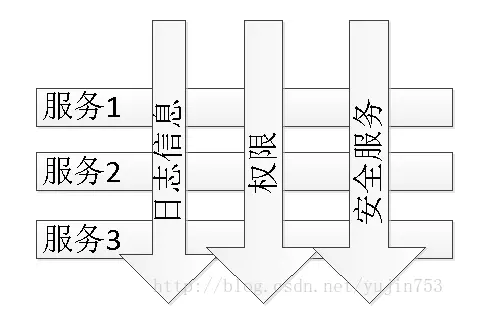
上面谈到,AOP可以分离系统的业务逻辑和系统服务(日志,安全等),这个功能不难明白(原理是使用了代理模式),但关键是为什么要将这两种进行分离呢?或者说这样做有什么好处?
在日常的软件开发中,拿日志来说,一个系统软件的开发都是必须进行日志记录的,不然万一系统出现什么bug,都不知道是哪里出了问题。举个小栗子,当你开发一个登陆功能,你可能需要在用户登陆前后进行权限校验并将校验信息(用户名,密码,请求登陆时间,ip地址等)记录在日志文件中,当用户登录进来之后,当他访问某个其他功能时,也需要进行合法性校验。想想看,当系统非常地庞大,系统中专门进行权限验证的代码是非常多的,而且非常地散乱,我们就想能不能将这些权限校验、日志记录等非业务逻辑功能的部分独立拆分开,并且在系统运行时需要的地方(连接点)进行动态插入运行,不需要的时候就不理,因此AOP是能够解决这种状况的思想吧!
二、AOP相关概念
1、关键字
切面(Aspect) :官方的抽象定义为“一个关注点的模块化,这个关注点可能会横切多个对象”。
连接点(Joinpoint) :程序执行过程中的某一行为。
通知(Advice) :“切面”对于某个“连接点”所产生的动作。
切入点 (Pointcut) :匹配连接点的断言,在AOP中通知和一个切入点表达式关联。
目标对象(Target Object) :被一个或者多个切面所通知的对象。
AOP代理(AOP Proxy) 在Spring AOP中有两种代理方式,JDK动态代理和CGLIB代理。
2、通知(Advice)类型
前置通知(Before advice) :在某连接点(JoinPoint)之前执行的通知,但这个通知不能阻止连接点前的执行。ApplicationContext中在<aop:aspect>里面使用<aop:before>元素进行声明。
后通知(After advice) :当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。ApplicationContext中在<aop:aspect>里面使用<aop:after>元素进行声明。
返回后通知(After return advice) :在某连接点正常完成后执行的通知,不包括抛出异常的情况。ApplicationContext中在<aop:aspect>里面使用<after-returning>元素进行声明。
环绕通知(Around advice) :包围一个连接点的通知,类似Web中Servlet规范中的Filter的doFilter方法。可以在方法的调用前后完成自定义的行为,也可以选择不执行。ApplicationContext中在<aop:aspect>里面使用<aop:around>元素进行声明。
抛出异常后通知(After throwing advice) : 在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。 ApplicationContext中在<aop:aspect>里面使用<aop:after-throwing>元素进行声明。
切入点表达式 :如execution(* com.spring.service.*.*(..))
@Before 前置通知(Before advice) :在某连接点(JoinPoint)之前执行的通知,但这个通知不能阻止连接点前的执行。
@After 后通知(After advice) :当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。
@AfterReturning 返回后通知(After return advice) :在某连接点正常完成后执行的通知,不包括抛出异常的情况。
@Around 环绕通知(Around advice) :包围一个连接点的通知,类似Web中Servlet规范中的Filter的doFilter方法。可以在方法的调用前后完成自定义的行为,也可以选择不执行。
@AfterThrowing 抛出异常后通知(After throwing advice) : 在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。
特点
1)、降低模块之间的耦合度
2)、使系统容易扩展
3)、更好的代码复用。
3、动态AOP自定义标签
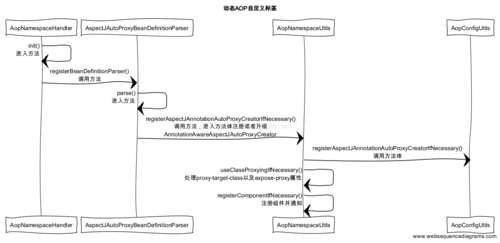
1). AopNamespaceHandler
通过时序图,我们可以看到,最先调用的方法是AopNamespaceHandler。在这个类中,一旦解析到”aspect-autoproxy”注解时就会使用解析器AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser进行解析。
public void () {
// In 2.0 XSD as well as in 2.1 XSD.
registerBeanDefinitionParser("config", new ConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
<strong>registerBeanDefinitionParser("aspectj-autoproxy", new AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser());</strong>
registerBeanDefinitionDecorator("scoped-proxy", new ScopedProxyBeanDefinitionDecorator());
// Only in 2.0 XSD: moved to context namespace as of 2.1
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
}2). AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser
在调用解析器AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser类后,我们跟踪代码进行这个类,会发现,这个类是实现接口BeanDefinitionParser,所以会去调用方法BeanDefinition()。在BeanDefinition()方法中,主要做的事情就是:注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator和对于注解中子类的处理。
public (Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
//注解AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
<strong>AopNamespaceUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);</strong>
//对于注解中子类的处理
extendBeanDefinition(element, parserContext);
return null;
}要启用AOP,我们一般会在Spring里面配置<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> ,所以在配置文件中在遇到aspectj-autoproxy标签的时候我们会采用AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser解析器
3)进入AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser解析器后,调用AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser已覆盖BeanDefinitionParser的parser方法,然后parser方法把请求转交给了AopNamespaceUtils的registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary去处理
3). AopNamespaceUtils
进入到AopNamespaceUtils的类中,查看registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary类,其实这个是我们所关心的,也是关键逻辑的实现。这里要实现的两件事。
1) 注册或升级AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator:beaName设置为org.Springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition。
2) 对proxy-target-class 以及expose-proxy属性的处理。
3) 注册组件并通知,便于监听器做进一步处理。
public static void (
ParserContext parserContext, Element sourceElement) {
//注册或升级AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,
//定义beanName为org.Springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition
<strong>BeanDefinition beanDefinition = AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
parserContext.getRegistry(), parserContext.extractSource(sourceElement));</strong>
//对于proxy-target-class以及expose-proxy属性的处理
<strong>(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement);</strong>
//其中beanDefintion的className为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
(beanDefinition, parserContext);
}4)进入AopNamespaceUtils的registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary方法后,先调用AopConfigUtils的registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary方法,里面在转发调用给registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired,注册或者升级AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类。对于AOP的实现,基本是靠AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator去完成的,它可以根据@point注解定义的切点来代理相匹配的bean。
5)AopConfigUtils的registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary方法处理完成之后,接下来会调用useClassProxyingIfNecessary() 处理proxy-target-class以及expose-proxy属性。如果将proxy-target-class设置为true的话,那么会强制使用CGLIB代理,否则使用jdk动态代理,expose-proxy属性是为了解决有时候目标对象内部的自我调用无法实现切面增强。
6)最后的调用registerComponentIfNecessary 方法,注册组建并且通知便于监听器做进一步处理。
创建AOP代理
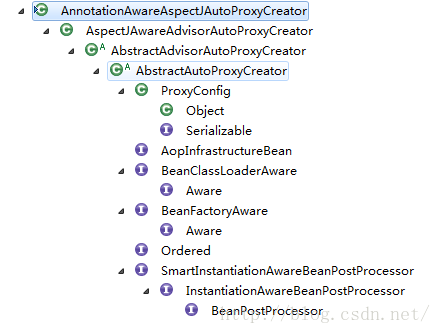
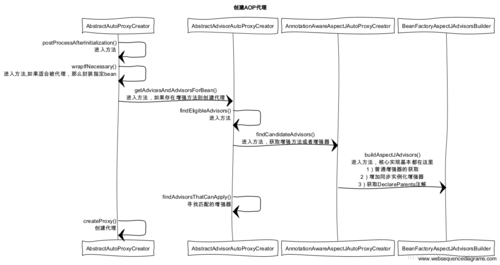
流程说明
1)spring 容器启动,每个bean的实例化之前都会先经过AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessAfterInitialization()这个方法,然后接下来是调用wrapIfNecessary方法。
/**
* Create a proxy with the configured interceptors if the bean is
* identified as one to proxy by the subclass.
* @see #getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
*/
public Object <strong>postProcessAfterInitialization</strong>(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
return (bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}2)进入wrapIfNecessary方法后,我们直接看重点实现逻辑的方法getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean,这个方法会提取当前bean 的所有增强方法,然后获取到适合的当前bean 的增强方法,然后对增强方法进行排序,最后返回。
/**
* Wrap the given bean if necessary, i.e. if it is eligible for being proxied.
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param cacheKey the cache key for metadata access
* @return a proxy wrapping the bean, or the raw bean instance as-is
*/
protected Object (Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.containsKey(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = <strong>getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean</strong>(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = (bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}3)获取到当前bean的增强方法后,便调用createProxy方法,创建代理。先创建代理工厂proxyFactory,然后获取当前bean 的增强器advisors,把当前获取到的增强器添加到代理工厂proxyFactory,然后设置当前的代理工的代理目标对象为当前bean,最后根据配置创建JDK的动态代理工厂,或者CGLIB的动态代理工厂,然后返回proxyFactory
/**
* Create an AOP proxy for the given bean.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param specificInterceptors the set of interceptors that is
* specific to this bean (may be empty, but not null)
* @param targetSource the TargetSource for the proxy,
* already pre-configured to access the bean
* @return the AOP proxy for the bean
* @see #buildAdvisors
*/
protected Object (
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
// Copy our properties (proxyTargetClass etc) inherited from ProxyConfig.
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to
// the target's interfaces only.
Class<?>[] targetInterfaces = ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanClass, this.proxyClassLoader);
for (Class<?> targetInterface : targetInterfaces) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(targetInterface);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
}
proxyFactory.<strong>setTargetSource</strong>(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
}AOP动态代理执行
关于AOP的动态代理执行,有两种主要的方式JDK的动态代理和CGLIB的动态代理,
接下来,我们先来看看AOP动态代理的实现选择方式,先上核心实现代码:
public AopProxy (AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException(
"TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface()) {
}
}
else {
}
}Spring JDK动态代理实现
在上面的第三步骤说道或根据用户的配置(例如是否配置了proxyTargetClass属性为true),选择创建的代理类型,这个的代理类型分两种实现,都是比较高效的,下面根据JDK的动态代理来说明AOP的执行,也是先上JdkDynamicAopProxy的核心代码invoke方法:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)throwsThrowable {
MethodInvocation invocation = null;
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Class targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
//eqauls()方法,具目标对象未实现此方法
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)){
return (equals(args[0])? Boolean.TRUE : Boolean.FALSE);
}
//hashCode()方法,具目标对象未实现此方法
if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)){
return newInteger(hashCode());
}
//Advised接口或者其父接口中定义的方法,直接反射调用,不应用通知
if (!this.advised.opaque &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface()
&&method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations onProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return
}
Object retVal = null;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available ifnecessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}//获得目标对象的类
target = targetSource.getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
//获取可以应用到此方法上的Interceptor列表
List chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method,targetClass);
//如果没有可以应用到此方法的通知(Interceptor),
//此直接反射调用 method.invoke(target, args)
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
retVal =
} else {
//创建MethodInvocation
invocation = newReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
if (retVal != null && retVal == target
&&method.getReturnType().isInstance(proxy)
&&!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned"this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Notethat we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself inanother returned object.
retVal = proxy;}return retVal;
} finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come fromTargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
/**
* Invoke the given target via reflection, as part of an AOP method invocation.
* @param target the target object
* @param method the method to invoke
* @param args the arguments for the method
* @return the invocation result, if any
* @throws Throwable if thrown by the target method
* @throws org.springframework.aop.AopInvocationException in case of a reflection error
*/
public static Object (
Object target, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// Use reflection to invoke the method.
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
}catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
// Invoked method threw a checked exception.
// We must rethrow it. The client won't see the interceptor.
throw ex.getTargetException();
}catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"AOP configuration seems to be invalid: tried calling method [" +
method + "] on target [" + target + "]", ex);
}catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new AopInvocationException("Could not access method [" + method + "]", ex);
}
}其实上面的注释也说的比较清楚,各个步骤执行的说明:
1)获取拦截器
2)判断拦截器链是否为空,如果是空的话直接调用切点方法
3)如果拦截器不为空的话那么便创建ReflectiveMethodInvocation类,把拦截器方法都封装在里面,也就是执行getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice方法
public List<Object> (Method method, Class targetClass) {
MethodCacheKeycacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);
List<Object>cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);
if(cached == null) {
cached= this.advisorChainFactory.(this,method, targetClass);
this.methodCache.put(cacheKey,cached);
}
return cached;
}4)其实实际的获取工作其实是由AdvisorChainFactory. getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice()这个方法来完成的,获取到的结果会被缓存,下面来分析下这个方法的实现:
/**
* 从提供的配置实例config中获取advisor列表,遍历处理这些advisor.如果是IntroductionAdvisor,
* 则判断此Advisor能否应用到目标类targetClass上.如果是PointcutAdvisor,则判断
* 此Advisor能否应用到目标方法method上.将满足条件的Advisor通过AdvisorAdaptor转化成Interceptor列表返回.
*/
public List (Advised config, Methodmethod, Class targetClass) {
// This is somewhat tricky... we have to process introductions first,
// but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.
List interceptorList = new ArrayList(config.getAdvisors().length);
//查看是否包含IntroductionAdvisor
boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config,targetClass);
//这里实际上注册一系列AdvisorAdapter,用于将Advisor转化成MethodInterceptor
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
Advisor[] advisors = config.getAdvisors();
for (int i = 0; i <advisors.length; i++) {
Advisor advisor = advisors[i];
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
// Add it conditionally.
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor= (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
if(config.isPreFiltered() ||pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
//TODO: 这个地方这两个方法的位置可以互换下//将Advisor转化成InterceptorMethod
Interceptor[]interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
//检查当前advisor的pointcut是否可以匹配当前方法Method
Matcher mm =pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm,method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) {
if(mm.isRuntime()) {
// Creating a newobject instance in the getInterceptors() method
// isn't a problemas we normally cache created chains.
for (intj = 0; j < interceptors.length; j++) {
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptors[j],mm));
}
}else {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
} else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor){
IntroductionAdvisor ia =(IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if(config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors= registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
} else {
Interceptor[] interceptors =registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
return interceptorList;
}5)这个方法执行完成后,Advised中配置能够应用到连接点或者目标类的Advisor全部被转化成了MethodInterceptor.
6)接下来货到invoke方法中的proceed方法 ,我们再看下得到的拦截器链是怎么起作用的,也就是proceed方法的执行过程
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex ==this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size()- 1) {
//如果Interceptor执行完了,则执行joinPoint
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
//如果要动态匹配joinPoint
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher){
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher)interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
//动态匹配:运行时参数是否满足匹配条件
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass,this.arguments)) {
//执行当前Intercetporreturndm.
interceptor.invoke(this);
}else {
//动态匹配失败时,略过当前Intercetpor,调用下一个Interceptor
return proceed();
}
}else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcutwill have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
//执行当前Intercetpor
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}7)好了拦截器到这边就可以执行了,复杂的代理终于可以起到他的作用了
Spring CGLIB动态代理实现
其实这两个代理的实现方式都差不多,都是创建方法调用链,不同的是jdk的动态代理创建的是
ReflectiveMethodInvocation调用链,而cglib创建的是CglibMethodInvocation。

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




