Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL IF function that returns a value based on a given condition.
Introduction to MySQL IF function
MySQL IF function is one of the MySQL control flow functions that returns a value based on a condition. The IFfunction is sometimes referred as IF ELSE or IF THEN ELSE function.
The syntax of the MySQL IF function is as follows:
IF(expr,if_true_expr,if_false_expr)
If the expr evaluates to TRUE i.e., expr is not NULL and expr is not 0, the IF function returns the if_true_expr, otherwise it returns if_false_expr. The IF function return a numeric or a string, depending on how it is used.
Please be careful not to confuse the IF function with the IF statement.
MySQL IF function Examples
Let’s practice with several examples to see how the MySQL IF function works.
A simple IF function example
You can use the IF function directly in the SELECT statement without the FROM and other clauses as follows:
SELECT IF(1 = 2,'true','false'); -- false SELECT IF(1 = 1,' true','false'); -- true
Displaying N/A instead of NULL using MySQL IF function
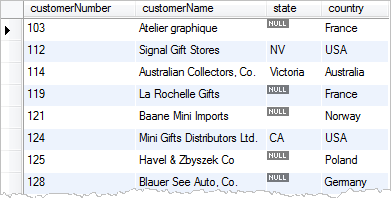
Let’s take a look at the data in the customers table in the sample database.
In the customers table, many customers do not have state data in the state column therefore when we select customers, the state column displays NULL values, which is not meaningful for the reporting purpose. See the following query:
SELECT customerNumber, customerName, state, country FROM customers;
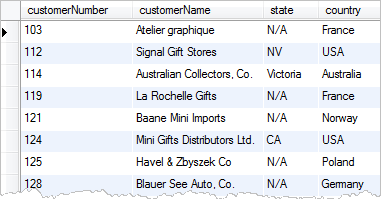
We can improve the output by using the IF function to return N/A if the state is NULL as the following query:
SELECT customerNumber, customerName, IF(state IS NULL,'N/A',state) state, country FROM customers;
MySQL IF function with aggregate functions
MySQL SUM IF – Combining the IF function with the SUM function
The IF function is useful when it combines with an aggregate function. Suppose if you want to know how many shipped and cancelled orders all time, you can use the IF function with the SUM aggregate function as following:
SELECT SUM(IF(status = 'Shipped',1,0)) AS Shipped, SUM(IF(status = 'Cancelled',1,0)) AS Cancelled FROM orders;
![]()
In the query above, if the orderstatusis shipped or cancelled, the IF function returns 1 otherwise it returns 0. The SUM function calculates the total number of shipped and cancelled orders based on the returned value of the IFfunction.
MySQL COUNT IF – Combining the IF function with the COUNT function
First, we select all order’s status in the orders table by using the following query:
SELECT DISTINCT status FROM orders ORDER BY status;
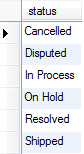
Second, we can get the number of orders in each status by combining the IF function with the COUNT function. Because the COUNT function does not count NULL values, the IF function returns NULL if the status is not in the selected status, otherwise it returns 1. See the following query:
SELECT COUNT(IF(status = 'Cancelled',1,NULL)) Cancelled, COUNT(IF(status = 'Disputed',1,NULL)) Disputed, COUNT(IF(status = 'In Process',1,NULL)) 'In Process', COUNT(IF(status = 'On Hold',1,NULL)) 'On Hold', COUNT(IF(status = 'Resolved',1,NULL)) 'Resolved', COUNT(IF(status = 'Shipped',1,NULL)) 'Shipped' FROM orders;
![]()
Of course, you can achieve the similar result using the GROUP BY clause and the COUNT function without using the IF function as the following query:
SELECT status, COUNT(STATUS) FROM orders GROUP BY status
In this tutorial, we have introduced you to the MySQL IF function which helps you write query with condition embedded in SELECT clause.
Reference
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/control-flow-functions.html#function_if – MySQL IF function

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




