Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to create trigger in MySQL by using the CREATE TRIGGER statement.
You should follow the introduction to SQL triggers and trigger implementation in MySQL first before going forward with this tutorial.
MySQL trigger syntax
In order to create a trigger you use the CREATE TRIGGER statement. The following illustrates the syntax of the CREATE TRIGGER statement:
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name trigger_time trigger_event ON table_name FOR EACH ROW BEGIN ... END
Let’s examine the syntax above in more detail.
You put the trigger name after the
CREATE TRIGGERstatement. The trigger name should follow the naming convention[trigger time]_[table name]_[trigger event], for examplebefore_employees_update.Trigger activation time can be
BEFOREorAFTER. You must specify the activation time when you define a trigger. You useBEFOREkeyword if you want to process action prior to the change is made on the table andAFTERif you need to process action after the change is made.Trigger event can be
INSERT,UPDATE orDELETE. This event causes trigger to be invoked. A trigger only can be invoked by one event. To define a trigger that is invoked by multiple events, you have to define multiple triggers, one for each event.A trigger must be associated with a specific table. Without a table trigger would not exist therefore you have to specify the table name after the
ONkeyword.The SQL statements are placed between
BEGINandENDblock.The
OLDandNEWkeywords are very handy. TheOLDkeyword refers to the existing record before you change the data and theNEWkeyword refers to the new row after you change the data.
MySQL trigger example
Let’s start creating a trigger in MySQL to audit the changes of the employees table.
First, we have employees table in our MySQL sample database as follows:

Second, we create a new table named employees_audit to keep the changes of the employee records. The following script creates the employee_audit table.
CREATE TABLE employees_audit ( id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, employeeNumber int(11) NOT NULL, lastname varchar(50) NOT NULL, changedon datetime DEFAULT NULL, action varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) )
Third, we create a BEFORE UPDATE trigger to be invoked before a change is made to the employees table.
DELIMITER $$ CREATE TRIGGER before_employee_update BEFORE UPDATE ON employees FOR EACH ROW BEGIN INSERT INTO employees_audit SET action = 'update', employeeNumber = OLD.employeeNumber, lastname = OLD.lastname, changedon = NOW(); END$$ DELIMITER ;
If you take a look at the schema, you will see before_employee_update trigger under the employees table as follows:
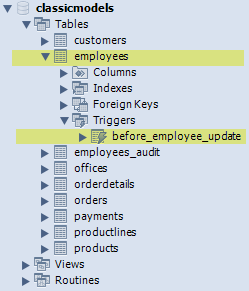
Now it’s time to update an employee record to test if the trigger is really invoked.
UPDATE employees SET lastName = 'Phan' WHERE employeeNumber = 1056
To check if the trigger was invoked by the UPDATE statement, we can query the employees_audit table by using the following query:
SELECT * FROM employees_audit
The following is the output of the query:
![]()
As you see, our trigger was really invoked so that we have a new record in the employees_audit table.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to create a trigger in MySQL. We also shown you how to develop a trigger to audit the changes of the employees table.
Related Tutorials
原文链接:http://outofmemory.cn/mysql/trigger/create-the-first-trigger-in-mysql

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




