一、简介
马三从上一家公司离职了,最近一直在出去面试,忙得很,所以这一篇博客拖到现在才写出来。马三在上家公司工作的时候,曾处理了一个UGUI不规则区域点击的问题,制作过程中也有一些收获和需要注意坑,因此记录成博客与大家分享。众所周知在UGUI中,响应点击通常是依附在一张图片上的,而图片不管美术怎么给你切,导进Unity之后都是一个矩形,如果要做其他形状,最多只能旋转一下,或者自己做一些处理。而为了美术效果,很多时候我们不得不需要特定形状的UI,并且让它们实现精准的响应点击。例如下图就是一个不规则的点击区域。
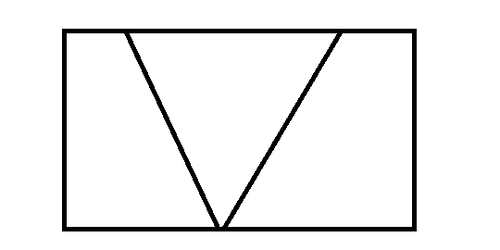
图1:UGUI不规则点击区域示意图
下面是处理了不规则区域点击后的演示效果,当点击按钮的时候,会对点击次数进行累加并且打印到控制台。可以看到进行了不规则区域点击处理以后,对我们原来的普通矩形Sprite的点击不会产生到影响,而不规则区域的表现效果也符合我们的预期。
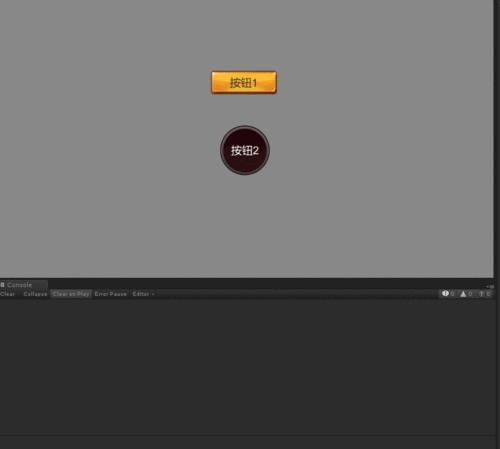
图2:规则区域与不规则区域点击效果对比
二、针对UGUI不规则区域点击的两种处理方法
针对UGUI的不规则区域响应点击,一般来说有两种处理办法:
1.精灵像素检测:该方法是指通过读取精灵(Sprite)在某一点的像素值(RGBA),如果该点的像素值中的Alpha小于一定的阈值(比如0.5)则表示该点处是透明的,即用户点击的位置在精灵边界以外,否则用户点击的位置在精灵边界内部。
2.通过算法计算碰撞区域:通过一定的算法,手动计算出碰撞区域,然后在判断用户是点击在了精灵上面,还是点击在精灵外部。
1.精灵像素检测法
首先来说下精灵像素检测法,因为它实现起来比较简单也好理解。uGUI在处理控件是否被点击的时候,主要是根据IsRaycastLocationValid这个方法的返回值来进行判断的,而这个方法用到的基本原理则是判断指定点对应像素的RGBA数值中的Alpha是否大于某个指定临界值。例如,我们知道半透明通常是指Alpha=0.5,而对一个后缀名为png格式的图片来说半透明或者完全透明的区域理论上不应该被响应的,所以根据这个原理,我们只需要设定一个透明度的临界值,然后对当前鼠标位置对应的像素进行判断就可以了,因此这种方法叫做精灵像素检测。对于上面的这个IsRaycastLocationValid接口,我们可以通过下载UGUI源码或者反编译的方式看到它的实现:
1 public virtual bool IsRaycastLocationValid(Vector2 screenPoint, Camera eventCamera) 2 { 3 //当透明度>=1.0时,表示点击在可响应区域返回true 4 if(this.m_EventAlphaThreshold >= 1f){ 5 return true; 6 } 7 8 //当没有指定精灵时返回true,因为不指定Spirte的时候,Unity将其区域填充为默认的白色,全部区域都是可以响应点击的 9 Sprite overrideSprite = this.overrideSprite;10 if(overrideSprite == null){11 return true;12 }13 14 //坐标系转换 15 Vector2 local;16 RectTransformUtility.ScreenPointToLocalPointInRectangle(base.rectTransform, screenPoint, eventCamera, ref local);17 Rect pixelAdjustedRect = base.GetPixelAdjustedRect ();18 local.x += base.rectTransform.get_pivot ().x * pixelAdjustedRect.get_width ();19 local.y += base.rectTransform.get_pivot ().y * pixelAdjustedRect.get_height ();20 local = this.MapCoordinate(local, pixelAdjustedRect);21 Rect textureRect = overrideSprite.get_textureRect ();22 Vector2 vector = new Vector2(local.x / textureRect.get_width (), local.y / textureRect.get_height ());23 24 //计算屏幕坐标对应的UV坐标25 float num = Mathf.Lerp(textureRect.get_x (), textureRect.get_xMax (), vector.x) / (float)overrideSprite.get_texture().get_width();26 float num2 = Mathf.Lerp(textureRect.get_y (), textureRect.get_yMax (), vector.y) / (float)overrideSprite.get_texture().get_height();27 bool result;28 29 //核心方法:像素检测30 try{31 result = (overrideSprite.get_texture().GetPixelBilinear(num, num2).a >= this.m_EventAlphaThreshold);32 }catch(UnityException ex){33 Debug.LogError("Using clickAlphaThreshold lower than 1 on Image whose sprite texture cannot be read. " + ex.Message + " Also make sure to disable sprite packing for this sprite.", this);34 result = true;35 }36 38 return result;39 }可以看到大概的思路就是经过一系列的坐标转换之后,将一个UV坐标的Alpha值与临界值作比较。基于这个像素这个思路我们又可以衍生出两种解决方案,一是直接更改临界值,二是在像素检测的思路上进行拓展与重写,定制我们自己的像素检测方法。
先来看下第一种直接更改阈值的方法,Unity在Image组件中为我们暴露出了一条属性alphaHitTestMinimumThreshold。关于它的含义我们可以参考Unity的官方文档:
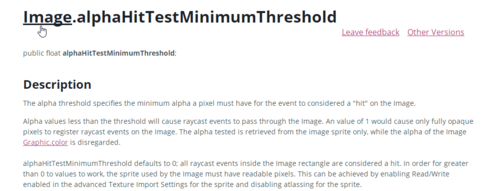
图3:alphaHitTestMinimumThreshold属性文档
大概的意思就是点击的时候会将该像素的Alpah值与该阈值进行比较,Alpha小于该阈值的部分的点击事件会被忽略掉,意思也就是某一像素的Alpha只有大于设定的阈值,你才能接到响应事件。当值为1的时候,表示只有完全不透明的部分才能响应。默认值为0,即一个Image不管透明不透明的部分,都会参与事件的响应。为了能够让alphaHitTestMinimumThreshold这个属性生效和工作,我们需要把Advance选项中的Read/Writeable属性勾选上。
因此我们将alphaHitTestMinimumThreshold值设置为一个合理的范围就可以实现不规则区域的点击了,代码如下:
1 using System.Collections; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using UnityEngine; 4 using UnityEngine.UI; 5 6 /// <summary> 7 /// 不规则区域Button 8 /// </summary> 9 [RequireComponent(typeof(RectTransform))]10 [RequireComponent(typeof(Image))]11 public class IrregulaButton : MonoBehaviour12 {13 [Tooltip("设定Sprite响应的Alpha阈值")]14 [Range(0, 0.5f)]15 public float alpahThreshold = 0.5f;16 17 private void Awake()18 {19 var image = this.GetComponent<Image>();20 if (null != image)21 {22 image.alphaHitTestMinimumThreshold = alpahThreshold;23 }24 }25 }第二种基于像素检测的解决方案是自己重写IsRaycastLocationValid接口里面像素检测方法,将屏幕坐标转换为UI坐标,然后再根据Sprite的类型做一些处理,最后根据x,y坐标取出像素的Alpha值与我们的阈值进行比较,具体代码如下:
using UnityEngine;using UnityEngine.UI;/// <summary>/// 不规则区域图形检测组件/// </summary>[RequireComponent(typeof(RectTransform))]
[RequireComponent(typeof(Image))]public class IrregularRaycastMask : MonoBehaviour, ICanvasRaycastFilter
{ private Image _image; private Sprite _sprite;
[Tooltip("设定Sprite响应的Alpha阈值")]
[Range(0, 0.5f)] public float alpahThreshold = 0.5f; void Start()
{
_image = GetComponent<Image>();
} /// <summary>
/// 重写IsRaycastLocationValid接口 /// </summary>
/// <param name="sp"></param>
/// <param name="eventCamera"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool IsRaycastLocationValid(Vector2 sp, Camera eventCamera)
{
_sprite = _image.sprite; var rectTransform = (RectTransform)transform;
Vector2 localPositionPivotRelative;
RectTransformUtility.ScreenPointToLocalPointInRectangle((RectTransform)transform, sp, eventCamera, out localPositionPivotRelative); // 转换为以屏幕左下角为原点的坐标系
var localPosition = new Vector2(localPositionPivotRelative.x + rectTransform.pivot.x * rectTransform.rect.width,
localPositionPivotRelative.y + rectTransform.pivot.y * rectTransform.rect.height); var spriteRect = _sprite.textureRect; var maskRect = rectTransform.rect; var x = 0; var y = 0; // 转换为纹理空间坐标
switch (_image.type)
{ case Image.Type.Sliced:
{ var border = _sprite.border; // x 轴裁剪
if (localPosition.x < border.x)
{
x = Mathf.FloorToInt(spriteRect.x + localPosition.x);
} else if (localPosition.x > maskRect.width - border.z)
{
x = Mathf.FloorToInt(spriteRect.x + spriteRect.width - (maskRect.width - localPosition.x));
} else
{
x = Mathf.FloorToInt(spriteRect.x + border.x +
((localPosition.x - border.x) /
(maskRect.width - border.x - border.z)) *
(spriteRect.width - border.x - border.z));
} // y 轴裁剪
if (localPosition.y < border.y)
{
y = Mathf.FloorToInt(spriteRect.y + localPosition.y);
} else if (localPosition.y > maskRect.height - border.w)
{
y = Mathf.FloorToInt(spriteRect.y + spriteRect.height - (maskRect.height - localPosition.y));
} else
{
y = Mathf.FloorToInt(spriteRect.y + border.y +
((localPosition.y - border.y) /
(maskRect.height - border.y - border.w)) *
(spriteRect.height - border.y - border.w));
}
} break; case Image.Type.Simple: default:
{ // 转换为统一UV空间
x = Mathf.FloorToInt(spriteRect.x + spriteRect.width * localPosition.x / maskRect.width);
y = Mathf.FloorToInt(spriteRect.y + spriteRect.height * localPosition.y / maskRect.height);
} break;
} // 如果texture导入过程报错,则删除组件
try
{ return _sprite.texture.GetPixel(x, y).a > alpahThreshold;
} catch (UnityException e)
{
Debug.LogError("Mask texture not readable, set your sprite to Texture Type 'Advanced' and check 'Read/Write Enabled'" + e.Message);
Destroy(this); return false;
}
}
}最后为了验证我们的组件是否生效,可以在按钮上挂载一个ButtonClickCounter 脚本,当接收到点击事件的时候,记录点击次数并打印到控制台方便观察,具体代码如下:
1 using System.Collections; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using UnityEngine; 4 using UnityEngine.UI; 5 6 /// <summary> 7 /// 按钮点击次数计数器 8 /// </summary> 9 public class ButtonClickCounter : MonoBehaviour10 {11 private int count = 0;12 private string btnName;13 14 void Start()15 {16 var text = this.transform.Find("Text").GetComponent<Text>();17 btnName = text.text;18 }19 20 21 public void Click()22 {23 count++;24 Debug.Log(string.Format("{0}点击了{1}次!", btnName, count));25 }26 }我们只要简单地直接把组件挂载到Image上面便可以生效了,具体截图如下:
图4:不规则区域检测组件使用
2.通过算法计算碰撞区域法
对于这种实现不规则碰撞区域的方法,马三并没有进行深入地研究,因为马三觉得挑选一个可靠的检测碰撞算法不是很容易,既要考虑到它的精准性又要考虑当图形复杂以后的计算效率,因此从易用性上面来讲,不如第一种实现方案好。关于这种方法的实现和原理,马三也是从网上搜集的一些资料进行整理的,感兴趣的读者可以深入研究一下哈,下面很多内容都是马三搜集整理网上大神的文章的资料得来的,其中给出了许多链接,大家可以直接参看链接里面的内容。
该方法是指给精灵(Sprite)添加一个多边形碰撞器(Rolygon Collider)组件,利用该组件来标记精灵的边界,这样通过比较鼠标位置和边界可以判断点击是否发生在精灵内部。关于这个算法与实现,PayneQin大神已经在他的博客中做了很详细的解析和说明,大家可以直接去看他的博客。知乎上关于判断一个点是否在多边形内部也有很多算法地讨论,具体可以看这里。其中这篇文献提供了判断一个点是否在任意多边形内部的两种方法,分别为Corssing Number和Winding Number。这两种方法在理论层面的相关细节请大家自行阅读这篇文章,PayneQin大神选择的是前者实现,其基本思想是计算从该点引出的射线与多边形边界相交的次数,当其为奇数时表示该点在多边形内部,当其为偶数时表示在多边形外部。马三在网上找到了相关的实现(偷懒):
1 bool ContainsPoint2(Vector2[] polyPoints,Vector2 p) 2 { 3 //统计射线和多边形交叉次数 4 int cn = 0; 5 6 //遍历多边形顶点数组中的每条边 7 for(int i=0; i<polyPoints.Length-1; i++)
8 { 9 //正常情况下这一步骤可以忽略这里是为了统一坐标系10 polyPoints [i].x += transform.GetComponent<RectTransform> ().position.x;11 polyPoints [i].y += transform.GetComponent<RectTransform> ().position.y;12 13 //从当前位置发射向上向下两条射线14 if(((polyPoints [i].y <= p.y) && (polyPoints [i + 1].y > p.y))
15 || ((polyPoints [i].y > p.y) && (polyPoints [i + 1].y <= p.y)))16 {17 //compute the actual edge-ray intersect x-coordinate18 float vt = (float)(p.y - polyPoints [i].y) / (polyPoints [i + 1].y - polyPoints [i].y);19 20 //p.x < intersect21 if(p.x < polyPoints [i].x + vt * (polyPoints [i + 1].x - polyPoints [i].x))22 ++cn;23 }24 }25 26 //实际测试发现cn为0的情况即为宣雨松算法中存在的问题27 //所以在这里进行屏蔽直接返回false这样就可以让透明区域不再响应28 if(cn == 0)29 return false;30 31 //返回true表示在多边形外部否则表示在多边形内部32 return cn % 2 == 0;33 }基于上面算法制作的多边形碰撞器实现的不规则按钮,以正五边形举例(PayneQin大神实现,马三只是搬运工):
1 /* 2 * 基于多边形碰撞器实现的不规则按钮
3 * 作者:PayneQin 4 * 日期:2016年7月9日 5 */ 6 7 using UnityEngine; 8 using System.Collections; 9 using UnityEngine.UI;10 using UnityEngine.EventSystems;11 12 public class UnregularButtonWithCollider : MonoBehaviour,IPointerClickHandler13 {14 /// <summary>15 /// 多边形碰撞器16 /// </summary>17 PolygonCollider2D polygonCollider;18 19 void Start()20 {21 //获取多边形碰撞器22 polygonCollider = transform.GetComponent<PolygonCollider2D>();23 }24 25 26 public void OnPointerClick(PointerEventData eventData)27 {28 //对2D屏幕坐标系进行转换29 Vector2 local;30 local.x = eventData.position.x - (float)Screen.width / 2.0f;31 local.y = eventData.position.y - (float)Screen.height / 2.0f;32 if(ContainsPoint(polygonCollider.points,local))33 {34 35 Debug.Log ("这是一个正五边形!");36 }37 38 }39 40 /// <summary>41 /// 判断指定点是否在给定的任意多边形内42 /// </summary>43 bool ContainsPoint(Vector2[] polyPoints,Vector2 p)44 {45 //统计射线和多边形交叉次数46 int cn = 0;47 48 //遍历多边形顶点数组中的每条边49 for(int i=0; i<polyPoints.Length-1; i++)
50 {51 //正常情况下这一步骤可以忽略这里是为了统一坐标系52 polyPoints [i].x += transform.GetComponent<RectTransform> ().position.x;53 polyPoints [i].y += transform.GetComponent<RectTransform> ().position.y;54 55 //从当前位置发射向上向下两条射线56 if(((polyPoints [i].y <= p.y) && (polyPoints [i + 1].y > p.y))
57 || ((polyPoints [i].y > p.y) && (polyPoints [i + 1].y <= p.y)))58 {59 //compute the actual edge-ray intersect x-coordinate60 float vt = (float)(p.y - polyPoints [i].y) / (polyPoints [i + 1].y - polyPoints [i].y);61 62 //p.x < intersect63 if(p.x < polyPoints [i].x + vt * (polyPoints [i + 1].x - polyPoints [i].x))64 ++cn;65 }66 67 }68 69 //实际测试发现cn为0的情况即为宣雨松算法中存在的问题70 //所以在这里进行屏蔽直接返回false这样就可以让透明区域不再响应71 if(cn == 0)72 return false;73 74 //返回true表示在多边形外部否则表示在多边形内部75 return cn % 2 == 0;76 }三、需要注意的坑
在像素检测法实现UGUI不规则碰撞区域的过程中,马三也遇到了很多需要注意的问题,在这里和大家分享一下:
1.图片需要开启Read/Writeable属性
如果选择使用像素检测法实现的话,需要注意开启Texture的Read/Writeable属性(我们需要读写该Texture的像素值),而且他必须是Advance类型。这样这张图片就不能打进我们的图集里面了,必须以散图的形式存在于工程当中,不利于统一管理。而且开启了Read/Writeable属性属性的话,在程序运行的时候,它会在内存中多复制出来一份,必然会影响到游戏的运行效率。所以尽量还是减少游戏中这种不规则UI的出现。
2.像素检测有偏移,不准确的问题
马三在实际操作的过程中,发现实际点击的时候经常会有偏移(经常偏下一些),有的透明的地方可以点击,而明明是不透明的地方却不能点击。刚开始马三还以为是图片格式或者是图片本身有什么问题,反反复复确认了好多次。直到后来马三在unity论坛上找到了这篇文章,才找到问题的症结所在。
对于如下图所示的这种周围有空白区域的图片,我们需要在Unity图片导入设置的时候,将Mesh Type格式设置为Full Rect,而unity导入时默认帮我们设置的是Tight模式。
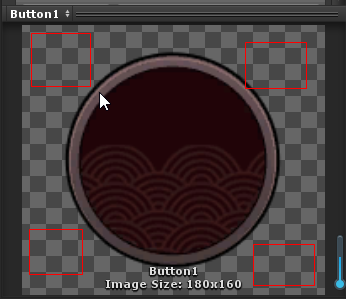
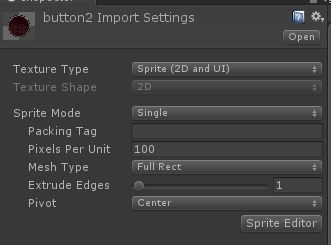
图5:周围有空白的图片 图6:正确的导入设置
那么,它们有什么区别呢?关于它们的区别,Unity官方是这样解释的:
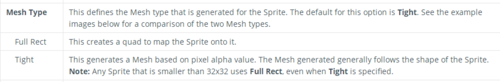
图7:Full Rect和Tight两种Mesh Type的官方解释
总的来说就是,用Tight模式的话,如果你的图片周围有空白像素,它会帮你压缩掉减小面积,以减少DrawCall,但是会增加Sprite的面数。如果用Full Rect模式不会压缩,也不会增加面数,直接创建一个quab,然后把图片扔上去。如果尺寸小于32x32的话,Unity默认使用Full Rect格式导入,否则使用Tight格式导入。因此如果我们不对Mesh Type进行设置的话,原来的一些空白区域就相当于裁剪掉了,这样相对于左下角的坐标来说,一些像素坐标就发生了偏移,而我们使用的是像素检测方法,必然也会导致偏移误差。
四、总结
通过本篇博客,马三和大家一起学习了如何在Unity中实现UGUI不规则区域的点击,希望本篇博客能为大家的工作过程中带来一些帮助与启发。
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/qinyuanpei/article/details/51868638
https://blog.csdn.net/shenmifangke/article/details/53504036
https://www.zhihu.com/question/26551754?f3fb8ead20=b6b9d1289bcc893ff2fa0abd1e65fc52
原文出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/msxh/p/9283266.html


 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




