一、前言
这篇文章就是从能看到地方去学习Core,没有很深奥,也没有很难懂,现在我们开始吧。
二、构建项目,引发思考
创建项目的步骤真的很简单,你要是不会,我真也没法了,我这是创建的MVC的项目。
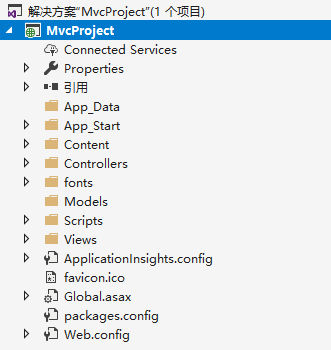

接下来我们开始找不同,这个小学生也会的东西,我相信也难不到大家,这里我们主要说重点的不同:
1. 少了Content和Scripts文件夹,多了wwwroot;
2.少了配置文件web.config,多了appsettings.json;
3.少了App_Start文件夹,多了Program.cs和Startup.cs;
后面确实,实现了前面的功能,接下来引发下我们的思考,带着这些问题我们来学习Core:
配置文件:
1.为什么appsettings.json能默认成为配置文件?
2.怎么读取配置文件?
3.Global.asax如何在core中体现;
DI:
1.为什么全部能按照接口的方式进行注入?
2.怎么替换掉内置的DI?
MVC:
1.Core的请求和MVC的请求有什么不同?
2.Core的认证和授权怎么处理?
怀着这些问题我们来简单结合源码分析下,另外最后我们在上传一个简单的增删改查项目完成我们项目结束。
三、配置文件
GitHub地址:https://github.com/aspnet/MetaPackages/tree/dev/src/Microsoft.AspNetCore
1.为什么appsettings.json能默认成为配置文件?
这个问题看下主要部分在这个地址下面:https://github.com/aspnet/MetaPackages/blob/dev/src/Microsoft.AspNetCore/WebHost.cs,我截取下主要代码;
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateDefaultBuilder(string[] args)
{ var builder = new WebHostBuilder(); if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(builder.GetSetting(WebHostDefaults.ContentRootKey)))
{
builder.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory());
} if (args != null)
{
builder.UseConfiguration(new ConfigurationBuilder().AddCommandLine(args).Build());
}
builder.UseKestrel((builderContext, options) =>
{
options.Configure(builderContext.Configuration.GetSection("Kestrel"));
})
.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, config) =>
{ var env = hostingContext.HostingEnvironment;
config.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true)
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true); if (env.IsDevelopment())
{ var appAssembly = Assembly.Load(new AssemblyName(env.ApplicationName)); if (appAssembly != null)
{
config.AddUserSecrets(appAssembly, optional: true);
}
}
config.AddEnvironmentVariables(); if (args != null)
{
config.AddCommandLine(args);
}
})
.ConfigureLogging((hostingContext, logging) =>
{
logging.AddConfiguration(hostingContext.Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
logging.AddConsole();
logging.AddDebug();
})
.ConfigureServices((hostingContext, services) =>
{ // Fallback
services.PostConfigure<HostFilteringOptions>(options =>
{ if (options.AllowedHosts == null || options.AllowedHosts.Count == 0)
{ // "AllowedHosts": "localhost;127.0.0.1;[::1]"
var hosts = hostingContext.Configuration["AllowedHosts"]?.Split(new[] { ';' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); // Fall back to "*" to disable.
options.AllowedHosts = (hosts?.Length > 0 ? hosts : new[] { "*" });
}
}); // Change notification
services.AddSingleton<IOptionsChangeTokenSource<HostFilteringOptions>>( new ConfigurationChangeTokenSource<HostFilteringOptions>(hostingContext.Configuration));
services.AddTransient<IStartupFilter, HostFilteringStartupFilter>();
})
.UseIISIntegration()
.UseDefaultServiceProvider((context, options) =>
{
options.ValidateScopes = context.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment();
}); return builder;
}View Code
2.怎么读取配置文件?
我主要提供了2种方式,这里前提是引入Microsoft.AspNetCore.All这个dll,这个里面很多我们需要的东西
从appsettings.json增加配置读取,有两种一个是更改配置以后立即生效,一种是重启以后才生效,具体看下代码:

//配置如下
"JwtSettings": { "Issuer": "http://localhost:52588", "Audience": "http://localhost:52588", "SecretKey": "1235455llllll"
}, "UserSetting": { "Name": "wtzzzzz", "Age": 12
} //读取配置
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.Configure<CookiePolicyOptions>(options =>
{ // This lambda determines whether user consent for non-essential cookies is needed for a given request.
options.CheckConsentNeeded = context => true;
options.MinimumSameSitePolicy = SameSiteMode.None;
});
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_1); //读取JWT配置文件
services.Configure<JwtSettingsModel>(Configuration.GetSection("JwtSettings")); //读取User配置文件
services.Configure<UserSettingModel>(Configuration.GetSection("UserSetting"));
} //controller读取 //不支持实时更新
private readonly IOptions<JwtSettingsModel> _jwtConfiguration; //支持实时更新
private readonly IOptionsSnapshot<UserSettingModel> _userConfiguration; public HomeController(IOptions<JwtSettingsModel> jwtConfiguration,IOptionsSnapshot<UserSettingModel> userConfiguration)
{
_jwtConfiguration = jwtConfiguration;
_userConfiguration = userConfiguration;
} public IActionResult Index()
{
ViewBag.Issuer = _jwtConfiguration.Value.Issuer;
ViewBag.Name = _userConfiguration.Value.Name;
ViewBag.PersonName =AppConfigurtaionHelper.GetAppSettings<PersonAppSettingModel>("PersonSetting").Area; return View();
}View Code
从外部引入配置文件,这个时候我们要做一件事情,将你新建的配置文件的属性设置为始终复制,至于这个原理是啥我不懂,有大神可以指点下,剩下的具体看代码吧;

{ "PersonSetting": { "Area": "China"
}
}//外部的工具类
public class AppConfigurtaionHelper
{ public static T GetAppSettings<T>(string key) where T : class, new()
{
IConfiguration config = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.Add(new JsonConfigurationSource { Path = "/Config/setting.json", ReloadOnChange = true })
.Build(); var appconfig = new ServiceCollection()
.AddOptions()
.Configure<T>(config.GetSection(key))
.BuildServiceProvider()
.GetService<IOptions<T>>()
.Value; return appconfig;
}
}View Code
3.Global.asax如何在core中体现;

public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env,IApplicationLifetime application)
{ if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
} else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
app.UseHsts();
} //类似于Application //开始
application.ApplicationStarted.Register(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("开始了注意");
}); //运行中
application.ApplicationStopping.Register(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("运行中");
}); //结束
application.ApplicationStopped.Register(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("结束了休息下");
});
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseCookiePolicy();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}View Code
IApplicationLifetime这个实现替代在传统应用中Application中生命周期的位置,这个我在上面的代码中已有体现,使用命令的方式运行在控制台就可以看到;
四、DI
针对这个问题,我只能这么说为了为了提高大家,给大家实现一个容器,让大家玩的开心一下,让DI和IOC的思想深入内心,这点有点类似Java操作了,其实早就该这样了,已经让我们变大太懒了,哈哈,借用下蒋神的话,ASP.NET Core的核心是通过一个Server和若干注册的Middleware构成的管道,不论是管道自身的构建,还是Server和Middleware自身的实现,以及构建在这个管道的应用,都需要相应的服务提供支持,ASP.NET Core自身提供了一个DI容器来实现针对服务的注册和消费。换句话说,不只是ASP.NET Core底层框架使用的服务是由这个DI容器来注册和提供,应用级别的服务的注册和提供也需要以来这个DI容器,所以正如本文标题所说的——学习ASP.NET Core,你必须了解无处不在的“依赖注入”。
附上大神的地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/artech/p/dependency-injection-in-asp-net-core.html
不懂DI和IOC的我也附上腾飞大神的地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jesse2013/p/di-in-aspnetcore.html,
腾飞大神博客里面已经将我想要的说2个问题说的很明白了,我这里还是在稍稍说一下吧。
生命周期问题:
Transient: 每一次GetService都会创建一个新的实例
Scoped:每次Http请求只会产生一个实例;
Singleton:整个应用程序生命周期以内只创建一个实例
这个大神博客里面也有介绍,官方也有介绍,大家可以看下https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/fundamentals/dependency-injection?view=aspnetcore-2.1
容器的替换:

public IServiceProvider ConfigureServices(
IServiceCollection services){
services.AddMvc(); // Add other framework services
// Add Autofac
var containerBuilder = new ContainerBuilder();
containerBuilder.RegisterModule<DefaultModule>();
containerBuilder.Populate(services); var container = containerBuilder.Build(); return new AutofacServiceProvider(container);
}View Code
五、MVC
1.Core的请求和MVC的请求有什么不同?
看图说话,主要设计不同主要体现在蒋神说的那句话,Core按照中间件的形式设计,最后全部注入到DI,这个时候我们考虑一个问题,我们想替换任何一个都将变得很容易,但是同样我们又会衍生另外一个问题,当我们服务之间存在依赖的时候,就需要按照顺序进行注入,这个问题需要重视一下,当然微软在设计上也考虑到这点,这里也是简单写个小demo,当你访问网站的时候就会发现网站按照顺序输出来了。MVC还是在IHttpMoudle和IHttpHandle上面做扩展或解耦,整体上本质是不变得,对这块不了解的可以推荐几篇博客给大家看看;推荐大龙龙MVC系列:http://www.cnblogs.com/edisonchou/p/3911558.html



//注册中间件
app.Use(async (context,next)=>
{ await context.Response.WriteAsync("1"); await next.Invoke();
});
app.Use(next =>
{ return (context) =>
{
context.Response.WriteAsync("2"); return next(context);
};
});
app.Run(async (context) =>
{ await context.Response.WriteAsync("3");
});View Code
六、结束
下一篇我们再说,Demo还没时间做好,另外强烈推荐大家去看官方文档:https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/migration/http-modules?view=aspnetcore-2.1,真的比什么都管用!!!


 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频



