TensorBoard
看得见的训练
一个web应用程序套件,用于检查和了解你的TensorFlow程序运行情况,使用图表展示,可以记录学习率,目标函数等如何变化。
可视化工具带来更好的体验。
mark
如果你要记录下数据,就要使用TensorFlow中的summary操作

mark
summary操作中提供了很多方法,记录标量。
记录激励层的数据分布图
将所有summary合并成一个操作
merged_summary_op = tf.merge_all_summaries()
需要运行op就要放进session.run。如果使用了summary的合并操作。
这时候你只需要run 合并后的op
保存数据
summary.FileWriter把数据写入磁盘供TensorBoard使用
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('/path/to/logs', sess.graph)加载数据
读取summary.Filewriter写到logdir路径下的数据。这里读取的是整个目录,而不是读取某一个指定的文件,因为当TensorFlow程序崩溃的时候,重新启动时会把新的数据写入该目录下新的文件中。
启动TensorBoard

mark
tensorboard -logdir=path/to/logs -host 0.0.0.0
6006
tensorboard使用
首先添加一个参数
logs_path = './example'
在初始化所有变量之后
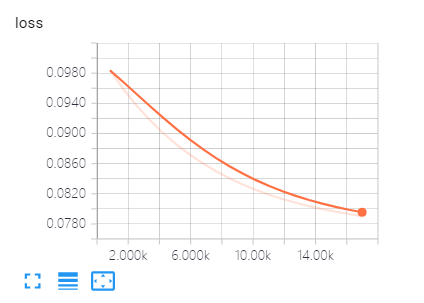
# 创建summary来观察损失值tf.summary.scalar("loss", cost)
merged_summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()将记录的数据写入文件
# op 写把需要记录的数据写入文件 summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logs_path, graph=tf.get_default_graph())
运行
c, summary = sess.run([cost, merged_summary_op], feed_dict={X:train_X, Y:train_Y})
summary_writer.add_summary(summary, epoch * n_samples)tensorboard --logdir=./example --host 0.0.0.0
mark

mark
注意旧版本的TensorBoardy轴不能自适应。
模型的加载与保存
什么是TensorFlow的模型: 网络结构+变量
保存模型: tf.train.Saver() saver.save()
当你观察到网络已经收敛,准确率和损失值不再下降。手动关闭网络的训练。
这时候保存网络结构和变量。先创建一个saver对象。然后调用save方法
加载模型: saver.restore()
重新训练或运用。
saver = tf.train.Saver()
调用saver.save()方法
# Save model weights to disk
save_path = saver.save(sess, model_path)
print("Model saved in file: %s" % save_path)print("Starting 2st session...")# 使用session 启用默认图with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init) # Restore model weights from previously saved model
saver.restore(sess, model_path)
print("Model restored from file: %s" % save_path)第一次训练指定的轮数,然后将模型保存。之后再加载进来进行继续训练。

mark
注意这个tmp目录需要存在。
TensorFlow手写数字识别
TensorFlow版本的手写数字识别
git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow.git

mark
0-9数字 (28,28)
tensorflow/tensorflow/examples/tutorials/mnist
全连接网络
tensorflow_code/examples/tutorials/mnist/fully_connected_feed.py:
if __name__ == '__main__': parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
实例化出一个接受命令行参数的参数解析器对象。
parser.add_argument( '--learning_rate', type=float, default=0.01, help='Initial learning rate.' )
设置学习率(默认为0.01)
parser.add_argument( '--max_steps', type=int, default=2000, help='Number of steps to run trainer.' )
设置总共训练的步数: 默认是2000步
parser.add_argument( '--hidden1', type=int, default=128, help='Number of units in hidden layer 1.' )
第一个隐藏层总共有多少个神经元。默认是128个神经元
parser.add_argument( '--hidden2', type=int, default=32, help='Number of units in hidden layer 2.' )
设置第二个隐藏层有多少个神经元。默认是32个神经元
parser.add_argument( '--batch_size', type=int, default=100, help='Batch size. Must divide evenly into the dataset sizes.' )
设置batch_size的大小。每个batch默认是100个。
parser.add_argument( '--input_data_dir',
type=str,
default=os.path.join(os.getenv('TEST_TMPDIR', '/tmp'), 'tensorflow/mnist/input_data'),
help='Directory to put the input data.'
)设置mnist数据的保存路径
parser.add_argument( '--log_dir',
type=str,
default=os.path.join(os.getenv('TEST_TMPDIR', '/tmp'), 'tensorflow/mnist/logs/fully_connected_feed'),
help='Directory to put the log data.'
)设置日志保存路径
parser.add_argument( '--fake_data', default=False, help='If true, uses fake data for unit testing.', action='store_true' )
FLAGS, unparsed = parser.parse_known_args()
解析命令行中输入的参数,如果没有指定参数全部都用代码里设置的默认值
tf.app.run(main=main, argv=[sys.argv[0]] + unparsed)
调用自己定义的main函数,将解析之后的参数传进去。
def main(_): if tf.gfile.Exists(FLAGS.log_dir): tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(FLAGS.log_dir) tf.gfile.MakeDirs(FLAGS.log_dir) run_training()
判断了一下这个log_dir是否存在,如果存在就删除掉。不存在就重新建立一个log_dir,接着开始训练run_training。
def run_training(): """Train MNIST for a number of steps.""" # Get the sets of images and labels for training, validation, and # test on MNIST. # 读取训练数据(做了一层封装) data_sets = input_data.read_data_sets(FLAGS.input_data_dir, FLAGS.fake_data) # Tell TensorFlow that the model will be built into the default Graph. # 使用默认图(图中的所有op描述了数据是怎样计算的过程) with tf.Graph().as_default(): # Generate placeholders for the images and labels. # 创建两个占位符。一个是x, 一个是它对应的标签 images_placeholder, labels_placeholder = placeholder_inputs( FLAGS.batch_size)
这里将创建占位符封装进了一个方法placeholder_inputs中
# 创建占位符的函数def placeholder_inputs(batch_size): """Generate placeholder variables to represent the input tensors. These placeholders are used as inputs by the rest of the model building code and will be fed from the downloaded data in the .run() loop, below. Args: batch_size: The batch size will be baked into both placeholders. Returns: images_placeholder: Images placeholder. labels_placeholder: Labels placeholder. """ # Note that the shapes of the placeholders match the shapes of the full # image and label tensors, except the first dimension is now batch_size # rather than the full size of the train or test data sets. # 创建占位符, 使用float32类型, shape为batchsizes和IMAGE_PIXELS images_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, mnist.IMAGE_PIXELS)) # 创建占位符,然后返回占位符 labels_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(batch_size)) # 返回占位符 return images_placeholder, labels_placeholder
# 创建网络结构 logits = mnist.inference(images_placeholder, FLAGS.hidden1, FLAGS.hidden2)
将网络结构创建封装到inference方法中。就像我们之前创建全连接网络一样,第一层输入层,第二层隐藏层,第三层隐藏层。
指定网络的隐藏层的神经元个数,过完网络之后就会有一个预测结果。
def inference(images, hidden1_units, hidden2_units):
"""Build the MNIST model up to where it may be used for inference.
Args:
images: Images placeholder, from inputs().
hidden1_units: Size of the first hidden layer.
hidden2_units: Size of the second hidden layer.
Returns:
softmax_linear: Output tensor with the computed logits.
"""
# Hidden 1 第一个隐藏层,创建了一个w和一个b偏置
with tf.name_scope('hidden1'):
weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([IMAGE_PIXELS, hidden1_units],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(float(IMAGE_PIXELS))),
name='weights')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([hidden1_units]),
name='biases')
hidden1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(images, weights) + biases) # Hidden 2
with tf.name_scope('hidden2'):
weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([hidden1_units, hidden2_units],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(float(hidden1_units))),
name='weights')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([hidden2_units]),
name='biases')
hidden2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(hidden1, weights) + biases)使用truncated_normal初始化函数初始化了w的形状。均值,方差。
使用Variable创建了biases偏置。使用wx+b线性部分经过relu函数创建了隐藏层1
第二个隐藏层:
依然w和b线性组合然后过relu函数。
# Linear
with tf.name_scope('softmax_linear'):
weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([hidden2_units, NUM_CLASSES],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(float(hidden2_units))),
name='weights')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([NUM_CLASSES]),
name='biases')
logits = tf.matmul(hidden2, weights) + biases return logits最后一层还是w和b。它的输出总共有NUM_CLASSES。第二个隐藏层的输出乘以权重+偏置。
计算loss的函数
# Add to the Graph the Ops for loss calculation. # 损失函数 loss = mnist.loss(logits, labels_placeholder)
将网络的预测值与真实标签输入loss函数
def loss(logits, labels): """Calculates the loss from the logits and the labels. Args: logits: Logits tensor, float - [batch_size, NUM_CLASSES]. labels: Labels tensor, int32 - [batch_size]. Returns: loss: Loss tensor of type float. """ labels = tf.to_int64(labels) cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( labels=labels, logits=logits, name='xentropy') return tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='xentropy_mean')
数据对应的真实标签类型转换。
使用sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits进行损失值的计算。
将softmax和crossentropy整合成了一个函数。sparse把标签做了稀疏矩阵的转换。
reduce_mean 求累积均值。
train中丢入loss和learning_rate
def training(loss, learning_rate):
"""Sets up the training Ops.
Creates a summarizer to track the loss over time in TensorBoard.
Creates an optimizer and applies the gradients to all trainable variables.
The Op returned by this function is what must be passed to the
`sess.run()` call to cause the model to train.
Args:
loss: Loss tensor, from loss().
learning_rate: The learning rate to use for gradient descent.
Returns:
train_op: The Op for training.
"""
# Add a scalar summary for the snapshot loss.
tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) # Create the gradient descent optimizer with the given learning rate.
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate) # Create a variable to track the global step.
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) # Use the optimizer to apply the gradients that minimize the loss
# (and also increment the global step counter) as a single training step.
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step=global_step) return train_op训练返回的是一个train_op
写入loss的变化值。
GradientDescentOptimizer 梯度下降算法。传入学习率
最小化损失值,传入当前的步数。
验证
# Add the Op to compare the logits to the labels during evaluation. eval_correct = mnist.evaluation(logits, labels_placeholder)
把网络的预测结果和真实标签丢进去做评估验证
def evaluation(logits, labels): """Evaluate the quality of the logits at predicting the label. Args: logits: Logits tensor, float - [batch_size, NUM_CLASSES]. labels: Labels tensor, int32 - [batch_size], with values in the range [0, NUM_CLASSES). Returns: A scalar int32 tensor with the number of examples (out of batch_size) that were predicted correctly. """ # For a classifier model, we can use the in_top_k Op. # It returns a bool tensor with shape [batch_size] that is true for # the examples where the label is in the top k (here k=1) # of all logits for that example. correct = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, labels, 1) # Return the number of true entries. return tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, tf.int32))
summary = tf.summary.merge_all()
将所有的写入到log的op合并
# Add the variable initializer Op. init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # Create a saver for writing training checkpoints. saver = tf.train.Saver()
初始化全局变量 & 场景一个保存模型的saver变量
# Create a session for running Ops on the Graph. sess = tf.Session() # Instantiate a SummaryWriter to output summaries and the Graph. summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.log_dir, sess.graph)
创建会话,以及将TensorBoard需要的数据写入到磁盘里
网络在运行之前需要初始化一下全局变量
sess.run(init) # Start the training loop. for step in xrange(FLAGS.max_steps): start_time = time.time()
首先记录了一下每一步的开始时间。
feed_dict = fill_feed_dict(data_sets.train, images_placeholder, labels_placeholder)
回填了数据。
def fill_feed_dict(data_set, images_pl, labels_pl):
"""Fills the feed_dict for training the given step.
A feed_dict takes the form of:
feed_dict = {
<placeholder>: <tensor of values to be passed for placeholder>,
....
}
Args:
data_set: The set of images and labels, from input_data.read_data_sets()
images_pl: The images placeholder, from placeholder_inputs().
labels_pl: The labels placeholder, from placeholder_inputs().
Returns:
feed_dict: The feed dictionary mapping from placeholders to values.
"""
# Create the feed_dict for the placeholders filled with the next
# `batch size` examples.
images_feed, labels_feed = data_set.next_batch(FLAGS.batch_size,
FLAGS.fake_data)
feed_dict = {
images_pl: images_feed,
labels_pl: labels_feed,
} return feed_dict首先从数据集里拿一个batch的数据,把这个batch的数据填充到placeholder里面去。
我们之前是吧feed_dict直接写在sess.run里面。这里当做一个函数的返回值。
调用sess.run方法
_, loss_value = sess.run([train_op, loss], feed_dict=feed_dict) duration = time.time() - start_time
训练的op和计算loss的op
忽略了train的返回值,只拿到了loss的返回值。duration计算了这一步所用的时间。
每隔100步打印一下网络的信息
# Write the summaries and print an overview fairly often.
if step % 100 == 0: # Print status to stdout.
print('Step %d: loss = %.2f (%.3f sec)' % (step, loss_value, duration)) # Update the events file.
summary_str = sess.run(summary, feed_dict=feed_dict)
summary_writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
summary_writer.flush()下面三行是将这些数据写入到磁盘,方便我们之后TensorBoard查看。
# Save a checkpoint and evaluate the model periodically. if (step + 1) % 1000 == 0 or (step + 1) == FLAGS.max_steps: checkpoint_file = os.path.join(FLAGS.log_dir, 'model.ckpt') saver.save(sess, checkpoint_file, global_step=step)
每隔多少步保存一个模型。
# Evaluate against the training set.
print('Training Data Eval:')
do_eval(sess,
eval_correct,
images_placeholder,
labels_placeholder,
data_sets.train) # Evaluate against the validation set.
print('Validation Data Eval:')
do_eval(sess,
eval_correct,
images_placeholder,
labels_placeholder,
data_sets.validation) # Evaluate against the test set.
print('Test Data Eval:')
do_eval(sess,
eval_correct,
images_placeholder,
labels_placeholder,
data_sets.test)do_eval计算当前的准确率是多少,训练,验证,测试集上准确率。
全连接网络。

mark
作者:天涯明月笙
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/089f0f28408c
來源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




