介绍
自然语言处理(NLP) 是人工智能方向一个非常重要的研究领域。 自然语言处理在很多智能应用中扮演着非常重要的角色,例如:
automated chat bots,article summarizers,multi-lingual translationopinion identification from data
每一个利用NLP来理解非结构化文本数据的行业,不仅要求准确,而且在获取结果方面也很敏捷。
自然语言处理是一个非常广阔的领域,NLP 的任务包括
text classification,entity detection,machine translation,question answering,concept identification.
在本文中,将介绍一个高级的 NLP 库 - spaCy
内容列表
关于 spaCy 和 安装
Spacy 流水线 和 属性
Tokenization
Pos Tagging
Entity Detection
Dependency Parsing
名词短语
与 NLTK 和 coreNLP 的对比
1.关于 spaCy 和 安装
1.1 关于 Spacy
Spacy 是由 cython 编写。因此它是一个非常快的库。 spaCy 提供简洁的接口用来访问其方法和属性 governed by trained machine (and deep) learning models.
1.2 安装
安装 Spacy
pip install spacy
下载数据和模型
python -m spacy download en
现在,您可以使用 Spacy 了。
2. Spacy 流水线 和 属性
要想使用 Spacy 和 访问其不同的 properties, 需要先创建 pipelines。 通过加载 模型 来创建一个 pipeline。 Spacy 提供了许多不同的 模型 , 模型中包含了 语言的信息- 词汇表,预训练的词向量,语法 和 实体。
下面将加载默认的模型- english-core-web
import spacy nlp = spacy.load(“en”)
nlp 对象将要被用来创建文档,访问语言注释和不同的 nlp 属性。我们通过加载一个 文本文件 来创建一个 document 。这里使用的是从 tripadvisor's 网站上下载下来的 旅馆评论。
document = open(filename).read() document = nlp(document)
现在,document 成为 spacy.english 模型的一部分,同时 document 也有一些 成员属性。可以通过 dir(document) 查看。
dir(document) >> [..., 'user_span_hooks', 'user_token_hooks', 'vector', 'vector_norm', 'vocab']
document 包含大量的文档属性信息,包括 - tokens, token’s reference index, part of speech tags, entities, vectors, sentiment, vocabulary etc. 下面将介绍一下几个属性
2.1 Tokenization
"this is a sentence."-> (tokenization) >> ['this', 'is', 'a', 'sentence', '.']
Spacy 会先将文档 分解成句子,然后再 tokenize 。我们可以使用迭代来遍历整个文档。
# first token of the doc document[0] >> Nice# last token of the doc document[len(document)-5] >> boston # List of sentences of our doc list(document.sents) >> [ Nice place Better than some reviews give it credit for., Overall, the rooms were a bit small but nice., ... Everything was clean, the view was wonderful and it is very well located (the Prudential Center makes shopping and eating easy and the T is nearby for jaunts out and about the city).]
2.2 Part of Speech Tagging (词性标注)
词性标注: word 的 动词/名词/… 属性。这些标注可以作为 文本特征 用到 information filtering, statistical models, 和 rule based parsing 中.
# get all tagsall_tags = {w.pos: w.pos_ for w in document}
>> {83: 'ADJ', 91: 'NOUN', 84: 'ADP', 89: 'DET', 99: 'VERB', 94: 'PRON', 96: 'PUNCT', 85: 'ADV', 88: 'CCONJ', 95: 'PROPN', 102: 'SPACE', 93: 'PART', 98: 'SYM', 92: 'NUM', 100: 'X', 90: 'INTJ'}# all tags of first sentence of our document for word in list(document.sents)[0]:
print(word, word.tag_)
>> (Nice, 'JJ') (place, 'NN') (Better, 'JJR') (than, 'IN') (some, 'DT') (reviews, 'NNS') (give, 'VBP') (it, 'PRP') (credit, 'NN') (for, 'IN') (., '.')下面代码创建一个 文本处理 操作,去掉噪声词。
#define some parameters noisy_pos_tags = ["PROP"]
min_token_length = 2#Function to check if the token is a noise or not def isNoise(token):
is_noise = False
if token.pos_ in noisy_pos_tags:
is_noise = True
elif token.is_stop == True:
is_noise = True
elif len(token.string) <= min_token_length:
is_noise = True
return is_noise
def cleanup(token, lower = True):
if lower:
token = token.lower() return token.strip()# top unigrams used in the reviews from collections import Counter
cleaned_list = [cleanup(word.string) for word in document if not isNoise(word)]
Counter(cleaned_list) .most_common(5)
>> [('hotel', 683), ('room', 652), ('great', 300), ('sheraton', 285), ('location', 271)]2.3 Entity Detection (实体检测)
Spacy 包含了一个快速的 实体识别模型,它可以识别出文档中的 实体短语。有多种类型的实体,例如 - 人物,地点,组织,日期,数字。可以通过 document 的 ents 属性来访问这些实体。
下面代码用来 找出 当前文档中的所有 命名实体。
labels = set([w.label_ for w in document.ents]) for label in labels: entities = [cleanup(e.string, lower=False) for e in document.ents if label==e.label_] entities = list(set(entities)) print label,entities
2.4 Dependency Parsing
spacy 一个非常强大的特性就是 十分快速和准确的语法解析树的构建,通过一个简单的 API 即可完成。这个 parser 也可以用作句子边界检测和短语切分。通过 “.children” , “.root”, “.ancestor” 即可访问。
# extract all review sentences that contains the term - hotelhotel = [sent for sent in document.sents if 'hotel' in sent.string.lower()]# create dependency treesentence = hotel[2] for word in sentence: print(word, ': ', str(list(word.children))) >> A : [] cab : [A, from] from : [airport, to] the : [] airport : [the] to : [hotel] the : [] hotel : [the] can : [] be : [cab, can, cheaper, .] cheaper : [than] than : [shuttles] the : [] shuttles : [the, depending] depending : [time] what : [] time : [what, of] of : [day] the : [] day : [the, go] you : [] go : [you] . : []
下面代码所作的工作是:解析所有 包含 “hotel” 句子的依赖树,看看都用了什么样的形容词来描述 “hotel”。下面创建了一个自定义函数来解析依赖树和抽取相关的词性标签。
# check all adjectives used with a word def pos_words (document, token, pos_tag): sentences = [sent for sent in document.sents if token in sent.string] pwrds = [] for sent in sentences: for word in sent: if token in word.string: pwrds.extend([child.string.strip() for child in word.children if child.pos_ == pos_tag] ) return Counter(pwrds).most_common(10) pos_words(document, 'hotel', "ADJ") >> [(u'other', 20), (u'great', 10), (u'good', 7), (u'better', 6), (u'nice', 6), (u'different', 5), (u'many', 5), (u'best', 4), (u'my', 4), (u'wonderful', 3)]
2.5 Noun Phrases (名词短语)
Dependency trees 也可以用来生成名词短语。
# Generate Noun Phrases doc = nlp(u'I love data science on analytics vidhya') for np in doc.noun_chunks: print(np.text, np.root.dep_, np.root.head.text) >> I nsubj love data science dobj love analytics pobj on
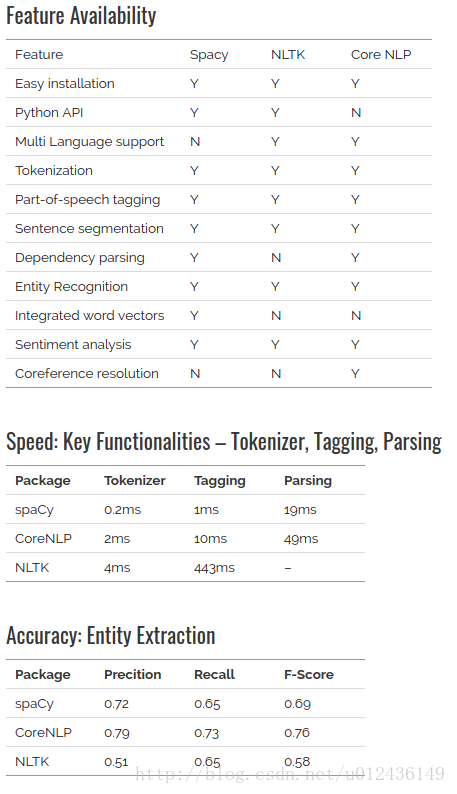
3.与CNTK和core NLP 的对比

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




