YAML文件简介
在使用开发工具初始化一个SpringBoot项目之后,我们可以看到在src\main\resources目录下有一个application.properties文件,这个properties文件就是SpringBoot项目的全局配置文件。除了可以使用默认的application.properties文件作为全局配置文件之外,SpringBoot项目还支持另外一种全局配置文件——application.yml
YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language)语言文件,它以.yml作为后缀。相比于传统的xml、properties文件,它的语法更加简洁、可读性更强,它的特点是以数据为中心,更加适合作为项目的配置文件
YAML基本语法
基本语法:
1.定义数据的格式为key: value,表示一对键值对(注意:value与冒号之间一定要有空格)
2.使用缩进表示层级关系
3.缩进时不允许使用Tab键,只允许使用空格
4.缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
5.大小写敏感
示例:
#配置数据库参数 同一层级的元素一定要左侧对齐 spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test username: root password: 123456
支持的数据结构:
1.对象(Map):键值对的集合
示例:
person: name: Allen age: 20
或者使用行内写法:
person: {name: Allen,age: 20}2.数组(List、Set、Array):一组按次序排列的值
示例:
colors: - red - blue - green
行内写法:
colors: [red, blue, green] # 方括号[]可以省略
3.字面量(int、long、boolean、String):单个的、不可再分的值
age: 20city: New York
YAML文件值注入
通过使用@ConfigurationProperties注解,我们可以将YAML配置文件中相关配置的值与javabean进行绑定
新建一个Person类:
public class Address {
private String city; //城市
private Long streetNumber; //街区编号
//省略get/set、toString方法}/**
* 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中
* @ConfigurationProperties:将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定
* prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射
*/@Component@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")public class Person {
private String name; //姓名
private Integer age; //年龄
private Boolean student; //是否是学生
private Date birthday; //生日
private Map<String, Object> scores; //考试分数
private List<String> colors; //喜爱的颜色
private String[] foods; //喜爱的食物
private Address address; //家庭住址
//省略get/set、toString方法}application.yml文件配置:
person: name: Allen age: 20
student: true birthday: 1998/10/20
scores: {math: 90,computer: 85,physics: 75} colors: red, blue, green foods:
- bread
- milk
- hamburger address: city: New York streetNumber: 1005在pom.xml中添加文件处理器依赖:
<!--导入配置文件处理器,导入后配置文件进行绑定就会有提示--><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional></dependency>
单元测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTestpublic class SpringBootYamlApplicationTests { @Autowired
Person person; @Test
public void contextLoads() { System.out.println(person);
}
}运行结果:
Person{name='Allen', age=20, student=true, birthday=Tue Oct 20 00:00:00 CST 1998, scores={math=90, computer=85, physics=75}, colors=[red, blue, green], foods=[bread, milk, hamburger], address=Address{city='New York', streetNumber=1005}}除了使用@ConfigurationProperties进行批量值注入之外,我们还可以使用@Value注解对javabean进行单个值的注入
@Componentpublic class Person {
@Value("${person.name}") private String name; //姓名
@Value("#{10+30/2}") private Integer age; //年龄
@Value("false") private Boolean student; //是否是学生
private Date birthday; //生日
private Map<String, Object> scores; //考试分数
private List<String> colors; //喜爱的颜色
private String[] foods; //喜爱的食物
private Address address; //家庭住址
//省略get/set、toString方法}单元测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTestpublic class SpringBootYamlApplicationTests { @Autowired
Person person; @Test
public void contextLoads() { System.out.println(person);
}
}运行结果:
Person{name='Allen', age=25, student=false, birthday=null, scores=null, colors=null, foods=null, address=null}与@ConfigurationProperties注解相比,@Value既可以注入application.yml中配置的值,也可以注入自定义值
@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较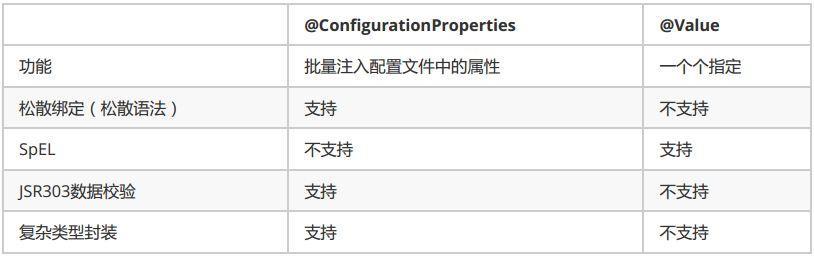
@PropertySource、@ImportResource、@Bean注解详解
1.@PropertySource注解
application.properties是SpringBoot项目默认的全局配置文件,如果我们将项目中的所有配置都写在application.properties文件中,必然会使得文件内容过于庞大,不容易维护。@PropertySource注解可以帮助我们解决这个问题,它可以加载指定的properties配置文件
在resource目录下新建person.properties文件
person.name=Paul person.age=22person.student=trueperson.birthday=1996/08/12person.scores.math=90person.scores.computer=85person.scores.physics=75person.colors=[red, blue, green] person.foods=[bread, milk, hamburger] person.address.city=New York person.address.streetNumber=1005
在Person 类上添加@PropertySource注解
@Component@PropertySource(value={"classpath:person.properties"})@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")public class Person {
private String name; //姓名
private Integer age; //年龄
private Boolean student; //是否是学生
private Date birthday; //生日
private Map<String, Object> scores; //考试分数
private List<String> colors; //喜爱的颜色
private String[] foods; //喜爱的食物
private Address address; //家庭住址
//省略get/set、toString方法}单元测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTestpublic class SpringBootYamlApplicationTests { @Autowired
Person person; @Test
public void contextLoads() { System.out.println(person);
}
}运行结果:
Person{name='Paul', age=22, student=true, birthday=Mon Aug 12 00:00:00 CST 1996, scores={physics=75, math=90, computer=85}, colors=[[red, blue, green]], foods=[[bread, milk, hamburger]], address=Address{city='New York', streetNumber=1005}}2.@ImportResource注解
程序员手动编写的Spring配置文件在SpringBoot项目中并不会被加载生效,要使SpringBoot项目加载Spring配置文件,则必须使用@ImportResource注解,将其标注在项目的启动类上
新建一个User测试类
public class User {
private Long id; private String name;
}编写Spring配置文件spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="user" class="com.yaml.entity.User"></bean></beans>
在启动类上添加@ImportResource注解,使其加载spring.xml文件
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:spring.xml"})@SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringBootYamlApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootYamlApplication.class, args);
}
}单元测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTestpublic class SpringBootYamlApplicationTests {
@Autowired
BeanFactory beanFactory; @Test
public void contextLoads() { boolean flag = beanFactory.containsBean("user");
System.out.println("flag=" + flag);
}
}运行结果:
flag=true
3.@Bean注解
@Bean注解用于给Spring容器中添加组件,这是SpringBoot官方推荐的方式
首先创建一个配置类,使用@Configuration标识
/**
* @Configuration:表示当前类是一个配置类
*/@Configurationpublic class MyAppConfig {
//将方法的返回值添加到容器中,方法名就是容器中这个组件默认的id
@Bean
public User userBean() { return new User();
}
}单元测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTestpublic class SpringBootYamlApplicationTests {
@Autowired
BeanFactory beanFactory; @Test
public void contextLoads() { boolean flag = beanFactory.containsBean("userBean");
System.out.println("flag=" + flag);
}
}运行结果:
flag=true

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




