一、多级反馈队列调度算法
多级反馈队列调度算法是进程调度的一种算法,该调度算法可以不用事先知道各种进程所需的执行时间,还可以较好的满足各种类型进程的需要,是目前共认的一种较好的进程调度算法。
那你可能马上就要问了,多级反馈队列调度算法到底是怎么调度的呢?我认为很多算法都可以用一张图+一句话来表达,所以接下来我尽量用图像来使这个算法看起来非常清晰。
一句话:
多级反馈队列调度算法,“多级”在于有多个不同优先级的队列,“反馈”在于如果有进程加入优先级高的队列时立即停止当前任务,转去执行优先级高的队列中进程,上述过程循环调度就形成多级反馈队列调度算法。
一张图:
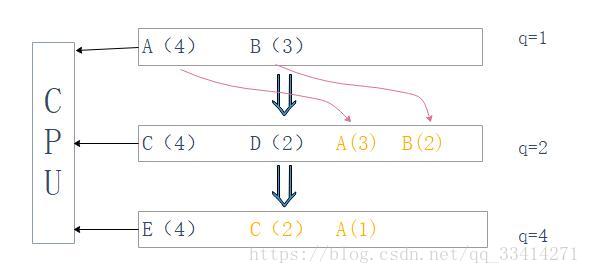
上图是一个调度的示例,进程有A(4),B(3),C(4),D(2),E(4),括号内是需要服务的时间。设第一队列时间片q=1,因为该算法中时间片的规则为:后一个时间片长度为前一个的2倍,所以第二队列时间片q=2,第三队列时间片q=4。
若不能执行完,则放到下一个队列尾部(橙色部分)
到最后一个队列的时候,则执行轮转调度(RR)算法,也就是每次执行一个时间片长度的服务,直到循环执行完所有的进程。
二、Python3实现代码
首先介绍一下程序中使用的结构体
1.“进程/任务”结构体
class Process: def __init__(self,name,arrive_time,serve_time): self.name=name #进程名 self.arrive_time=arrive_time #到达时间 self.serve_time=serve_time #需要服务的时间 self.left_serve_time=serve_time #剩余需要服务的时间 self.finish_time=0 #完成时间 self.cycling_time=0 #周转时间 self.w_cycling_time=0 #带权周转时间
进程的属性有进程名,到达时间,需要服务的时间,剩余需要服务的时间,完成时间,周转时间,带权周转时间。其中周转时间为提交时间与完成时间的间隔;带权周转时间为周转时间/实际运行时间。
2.队列
class Queue: def __init__(self,level,process_list): self.level=level self.process_list=process_list self.q=0 def size(self): return len(self.process_list) def get(self,index): return self.process_list[index] def add(self,process): self.process_list.append(process) def delete(self,index): self.process_list.remove(self.process_list[index])
设置一个队列,初始化方法需要给队列的优先级,以及队列中所包含的进程列表,顺便定义获取队列一些属性的方法。
然后是具体使用的算法程序:
3.多级反馈队列调度算法(RR)
class RR:
def __init__(self,process_list,q):
self.process_list=process_list
self.q=q
def scheduling(self):
process_list.sort(key=lambda x:x.arrive_time)#按照.arrive_time进行排序
len_queue=len(self.process_list) #进程队列的长度
index=int(0) #索引
q=self.q #时间片
running_time=int(0)#已经运行了的时间
#调度的循环
while(True):
#当前进程
current_process=self.process_list[index%len_queue]
#判断当前进程是否已经被完成
if current_process.left_serve_time>0:
#计算完成时间
#还需要服务的时间大于等于时间片,则完成时间+时间片时间 此进程还没结束
#还需要服务的时间小于时间片,则完成时间在原来基础上加上继续服务的时间
if current_process.left_serve_time>=q:
running_time+=q
#print(current_process.name,running_time,index)
current_process.left_serve_time-=q
else :
#print('%s 还需要服务的时间小于当前时间片'%current_process.name)
running_time+=current_process.left_serve_time
current_process.left_serve_time=0
#已完成
if current_process.left_serve_time==0:
#计算完成时间
current_process.finish_time=running_time
#计算周转时间
current_process.cycling_time=current_process.finish_time-current_process.arrive_time
#计算带权周转时间
current_process.w_cycling_time=float(current_process.cycling_time)/current_process.serve_time
#打印
print('%s 进程已完成的进程,详细信息如下:'%current_process.name)
print('进程名称:%s ,完成时间: %d ,周转时间:%d ,带权周转时间: %.2f'%(current_process.name,current_process.finish_time,current_process.cycling_time,current_process.w_cycling_time))
#弹出
self.process_list.remove(current_process)
len_queue=len(self.process_list)
#有进程完成任务后,index先回退,之后再加,以保持指向下一个需要调度的进程
index-=1
#index常规增加
index+=1
#如果队列中没有进程则表示执行完毕
if len(self.process_list)==0:
break
#改变index,避免因为index大于len,导致取模时出错
if index>=len(self.process_list):
index=index%len_queue多级反馈队列调度算法用于执行最后一个队列中的进程,如果单独拿出来也是一个完整的算法实现代码,下面的代码中也有相应的测试代码。
4.多级反馈队列调度算法
class MulitlevedFeedbackQueue():
def __init__(self,queue_list,q_first):
self.queue_list=queue_list
self.q_first=q_first
def scheduling(self):
q_list=self.queue_list #当前队列集合
q_first=self.q_first #第一个队列的时间片
for i in range(len(q_list)):
#确定每个队列的时间片
if i==0:
q_list[i].q=q_first
else :
q_list[i].q=q_list[i-1].q*2
#从第一个队列开始执行时间片
#先判断是否是最后一个队列,最后一个队列直接执行RR调度算法
#不是最后一个队列的话,就执行当前队列时间片后判断是否有必要加入到下一个队列的末尾
if i==len(q_list)-1:
print('**************对最后一个队列执行RR调度算法*************')
#print(q_list[i].process_list[])
#最后一个队列重新设置到达时间
for t in range(len(q_list[i].process_list)):
q_list[i].process_list[t].arrive_time=t
rr_last_queue=RR(q_list[i].process_list,q_list[i].q)
rr_last_queue.scheduling()
else:
currentQueue=q_list[i]
index=int(0)
while(True):
if currentQueue.get(index).left_serve_time>q_list[i].q:
currentQueue.get(index).left_serve_time-=q_list[i].q
print('第 %d 队列时间片: %d'%(i,q_list[i].q))
print('进程没有执行完毕,需要添加至下一队列末尾:进程名称:%s '%(currentQueue.get(index).name))
#将当前进程扔到下一个队列的尾部
q_list[i+1].add(currentQueue.get(index))
index+=1
else:
print('服务完成并弹出:',currentQueue.get(index).name)
currentQueue.get(index).left_serve_time=0
currentQueue.delete(index)
if index==currentQueue.size():
break以上是多级反馈队列调度算法,最后一个队列使用第三个代码片中的RR算法,其它的则按照上面算法详情实现。
5.测试程序
'''
测试程序
'''
if __name__=='__main__':
'''产生进程'''
process_list=[]
processA=Process('A',0,4)
processB=Process('B',1,3)
processC=Process('C',2,4)
processD=Process('D',3,2)
processE=Process('E',4,4)
process_list.append(processA),process_list.append(processB),process_list.append(processC)
process_list.append(processD),process_list.append(processE)
'''使用RR调度算法,时间片为1'''
print('#################################################################')
print('---------------------------轮转调度算法--------------------------')
print('#################################################################')
rr=RR(process_list,1)
rr.scheduling()
'''使用多级反馈队列调度算法'''
print()
print('#################################################################')
print('-----------------------测试多级反馈队列调度算法----------------------')
print('#################################################################')
processA=Process('A',0,4)
processB=Process('B',1,3)
processC=Process('C',2,4)
processD=Process('D',3,2)
processE=Process('E',4,4)
process_list0,process_list1,process_list2=[],[],[]
process_list0.append(processA),process_list0.append(processB)
process_list1.append(processC),process_list1.append(processD)
process_list2.append(processE)
#队列
queue_list=[]
queue0=Queue(0,process_list0)
queue1=Queue(1,process_list1)
queue2=Queue(2,process_list2)
queue_list.append(queue0),queue_list.append(queue1),queue_list.append(queue2)
#使用多级反馈队列调度算法,第一队列时间片为1
mfq=MulitlevedFeedbackQueue(queue_list,1)
mfq.scheduling()实现结果: 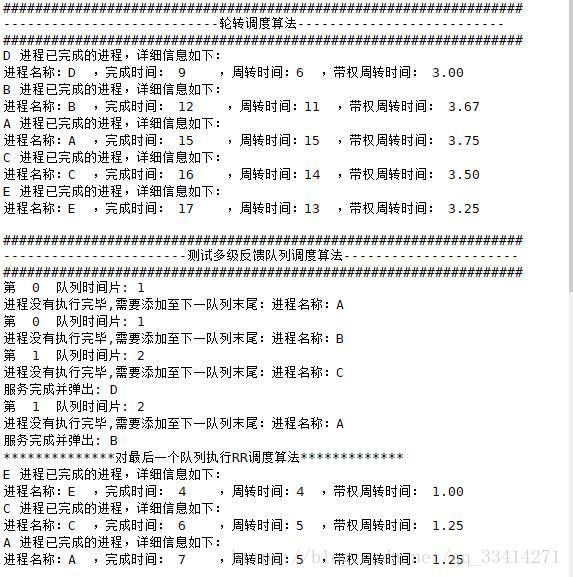



 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




