本章我们介绍链表
前面我们已经介绍了动态数组,栈和队列。
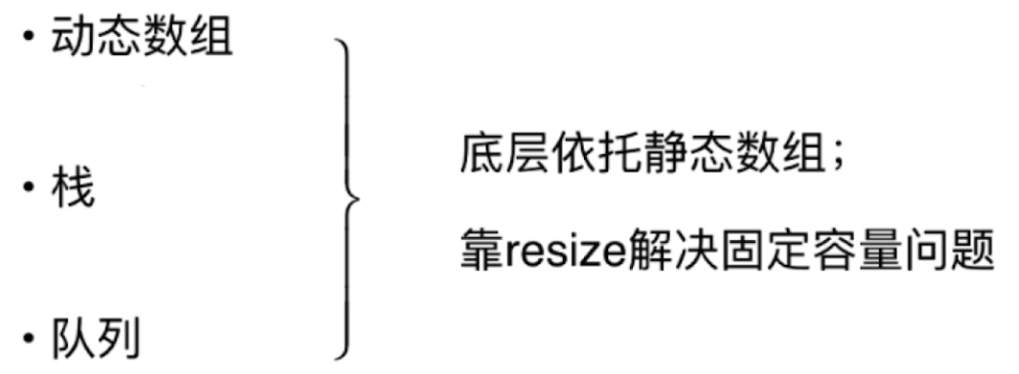
它们的底层依托静态数组;靠resize解决固定容量问题
链表是我们接触的第一个真正的动态数组。
为什么链表很重要
链表是重点,也是难点。它是最简单动态数据结构;后续我们还会学习更多的,比如二分搜索树,平衡二叉树,红黑树,后面很多的动态数据结构都可以在理解链表的基础上学习。
链表可以让我们更深入的理解引用(C++中指针),内存管理等有更深理解。对于更深入的理解递归有好处,树形中递归必须理解。
链表可以辅助组成其他数据结构。
链表Linked List
数据存储在“节点”(Node)中;
class Node{
E e;
Node next;
}车厢和车厢进行连接,使用next进行连接。
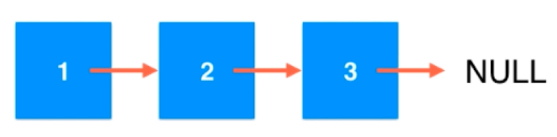
最后一个节点的next指向空,说明这个节点是最后一个节点了。优点:真正的动态,不需要处理固定容量的问题
不像数组一下子必须new出来一片空间,需要考虑空间不够用或浪费。链表是你需要多少个数据,就生成多少个节点将他挂接起来,这就是所谓的动态的意思。
缺点: 丧失了随机访问的能力。不能像数组一样,给定一个索引直接拿出对应元素。底层机制中数组开辟的空间在内存中是连续分布的,我们可以直接寻找索引对应的偏移,直接计算出数据所存储的内存地址,直接用O(1)复杂度拿出。链表靠next连接,每个节点存储地址不同,我们只能通过next顺藤摸瓜找到我们要找的元素。
数组最好用于索引有语意的情况。scores[2] 2是学号,身份证号不能做索引;最大的优点:支持快速查询。
我们在编写动态数组,但是其实这类索引没有语义的情况更适合链表。
链表不适合用于索引有语意的情况。最大的优点:动态
什么时候适合使用数组,什么时候适合使用链表。
链表实现
package cn.mtianyan;public class LinkedList<E> { // private设计,不被用户感知
private class Node{ public E e; public Node next; // c++实现时是指针
public Node(E e, Node next) { this.e = e; this.next = next;
} public Node(E e) { this.e = e; this.next = null;
} public Node() { this(null,null);
} @Override
public String toString() { return "Node[" + "e=" + e + ", next=" + next + ']';
}
}
}上面是我们对于链表节点的设计。注意private设计,以及Node的成员变量Node
应该有一个链表头,声明出LinkedList基本的成员变量。
private Node head; private int size; public LinkedList() {
head = null;
size = 0;
} public LinkedList(Node head, int size) { this.head = head; this.size = size;
} /**
* 从数组创建链表的方法,待完善。
*
* @param e
*/
public LinkedList(E[] e){
} /**
* 获取链表中元素个数
*
* @return
*/
public int getSize(){ return size;
} /**
* 返回链表是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){ return size == 0;
}上面是链表中应该有的成员变量和一些普通方法。
在链表头添加元素是非常方便的,数组在数组尾部添加元素不用挪位会非常方便。数组中有size指向下一个空位置跟踪队尾,链表中有head来标识链表的头部。
node.next = head head = node
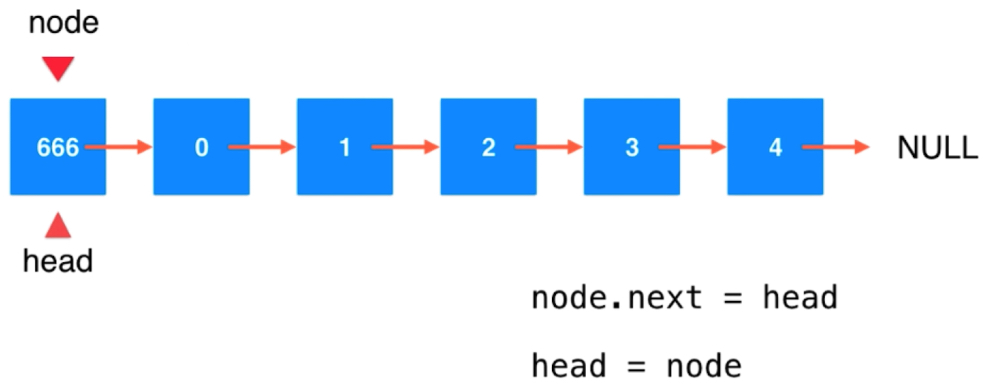
public void addFirst(E e){ // Node node = new Node(e);
// node.next = head;
// head = node;
// 上面三行代码的等价实现
head = new Node(e,head); // 值为e的Node的next是head;head = 这个Node
size++;
}上面有两种等价的实现。
在索引为2的地方添加元素666,要找到之前的节点。关键:找到要添加的节点的前一个节点。前一个节点要特殊处理
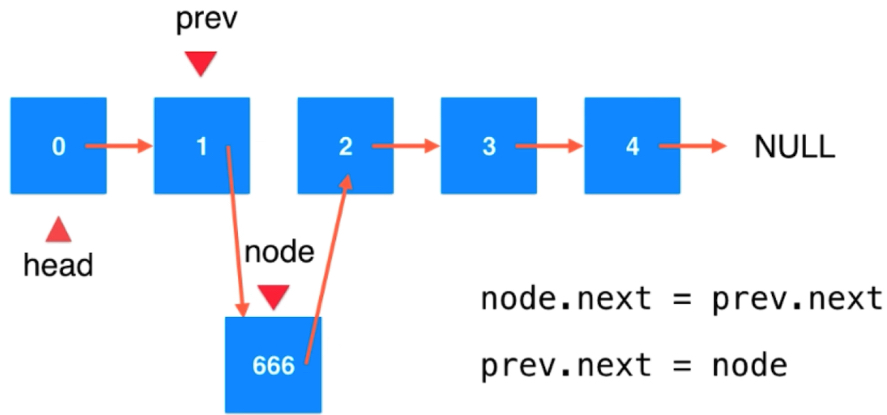
顺序是很重要的,不能颠倒。否则会丢失原本的prev.next。大多时候顺序可以省下一个old的备份临时变量。
/**
* 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
* 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习题用,面试用。
* @param index
* @param e
*/
public void add(int index,E e){ // index可以取到size,在链表末尾空位置添加元素。
if (index < 0 || index >size){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index");
}
Node prevNode = head; // 因为有了dummyHead,多遍历一次,遍历index次
for (int i = 0; i < index-1; i++) { // 验证。 12 index 1添加,index-1=0一次也不执行,正好是head。符合
// 验证。 1234 index 2添加,index-1=1 运行一次pre指向head下一个也就是2,符合。
prevNode = prevNode.next;
} // Node insertNode = new Node(e);
// insertNode.next = prevNode.next;
// prevNode.next = insertNode;
prevNode.next = new Node(e,prevNode.next); // 后半截是前两句完成任务
size++;
}链表的添加操作时,要找的是前一个节点。而我们之前定义的头结点因为没有前一个节点,需要进行特殊处理,这样不够优雅。而如果我们往前面加一个虚拟的头结点,则可以将我们现在的头结点和其他节点统一起来。
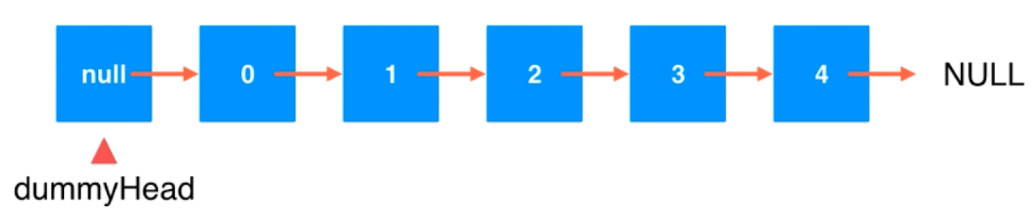
private Node dummyHead;
public LinkedList() {
dummyHead = new Node(null,null);
size = 0;
}虚拟头结点对用户屏蔽不可见。
/**
* 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
* 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习题用,面试用。
* @param index
* @param e
*/
public void add(int index,E e){ // index可以取到size,在链表末尾空位置添加元素。
if (index < 0 || index >size){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index");
}
Node prevNode = dummyHead; // 因为有了dummyHead,多遍历一次,遍历index次
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { // 验证。 12 index 1添加,index-1=0一次也不执行,正好是head。符合
// 验证。 1234 index 2添加,index-1=1 运行一次pre指向head下一个也就是2,符合。
prevNode = prevNode.next;
} // Node insertNode = new Node(e);
// insertNode.next = prevNode.next;
// prevNode.next = insertNode;
prevNode.next = new Node(e,prevNode.next); // 后半截是前两句完成任务
size++;
} /**
* 在链表头添加新元素e
*/
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0,e);
} /**
* 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
*/
public void addLast(E e){
add(size,e);
}添加元素操作时,注意指向,以及循环次数的验证。
/**
* 获得链表的第index(0-based)位置元素
* 链表中不是常用操作,练习用
* @param index
* @return
*/
public E get(int index){ // index不可以取到size,索引从0开始,最多取到size-1
if (index < 0 || index >=size){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index");
}
Node cur = dummyHead.next; // 从索引为0元素开始
// 下面与找index-1个节点保持一致。上面执行了一次。所以从index-1个元素变成了找index个元素。
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
} return cur.e;
} public E getFirst(){ return get(0);
} public E getLast(){ return get(size-1);
}插入时我们要寻找的是index的前一个位置,而get时,我们要找的就是index的当前位置,因此要多找一次,在for循环不变情况下,从虚拟头结点下一个节点开始遍历。
/**
* 修改链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素为e
* 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用
*/
public void set(int index,E e){ // index不可以取到size,索引从0开始,最多取到size-1
if (index < 0 || index >=size){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Illegal index");
}
Node cur = dummyHead.next; // 从索引为0元素开始
// 下面与找index-1个节点保持一致。上面执行了一次。所以从index-1个元素变成了找index个元素。
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.e = e;
} /**
* 查找链表中是否有元素e
*/
public boolean contains(E e){
Node cur = dummyHead.next; while (cur != null){ if (cur.e.equals(e)){ return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
} return false;
} @Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();// Node cur = dummyHead.next;// while (cur != null){// res.append(cur.e +"->");// cur = cur.next;// }// res.append("NULL");
res.append("head: "); for (Node cur=dummyHead.next;cur !=null;cur=cur.next){
res.append(cur.e +"->");
}
res.append("NULL"); return res.toString();
}两种不同的遍历方式是等价的。
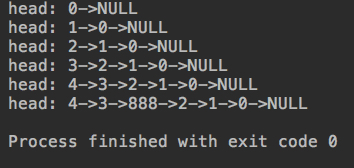
package cn.mtianyan;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
linkedList.addFirst(i);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
linkedList.add(2,888);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}运行结果:
删除元素
删除索引为2位置的元素
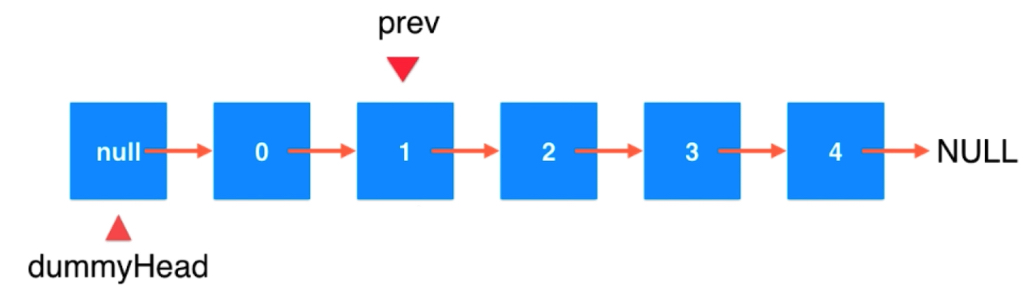
要找到它之前的元素。
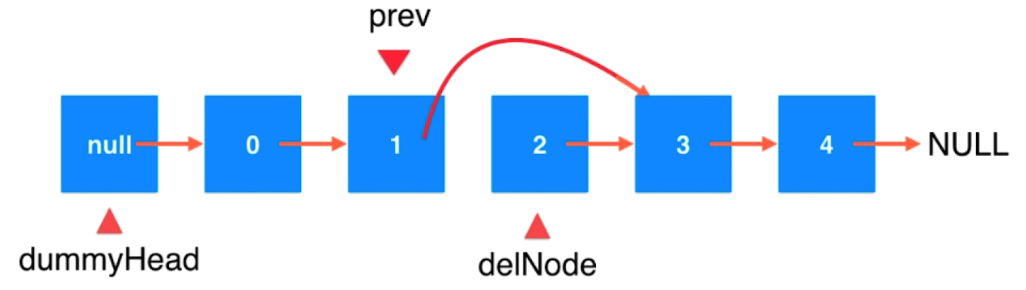
prev.next = delNode.next delNode.next = null
链表元素删除时常见的错误。
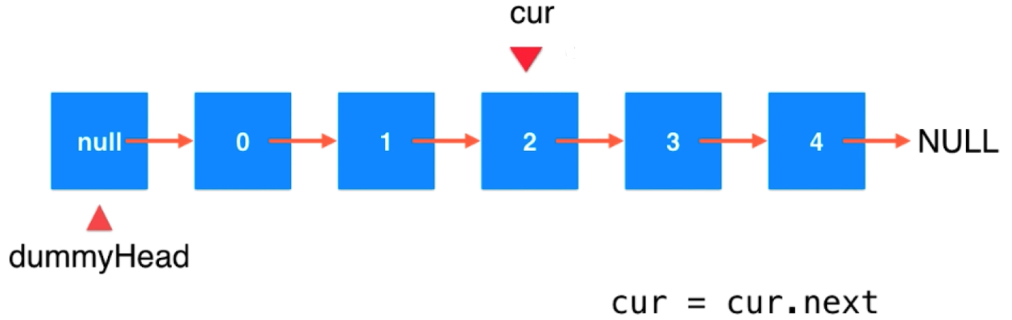
cur 指向cur.next的位置。本质是对于引用概念糊涂,Java中类的对象都是一个引用,理解成一个实际内存的指向。cur = cur.next从原来指的位置,指到下一个位置,但对于链表来说没有发生任何改变。要想改变链表就应该改变节点的next指向。
/**
* 删除链表中指定index位置的元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
public E remove(int index){ if (index < 0 || index >=size){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Illegal index");
}
Node prev = dummyHead; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
prev = prev.next;
}
Node retNode = prev.next;
prev.next = retNode.next;
retNode.next = null;
size--; return retNode.e;
} public E removeFirst(){ return remove(0);
} public E removeLast(){ return remove(size-1);
}linkedList.remove(2); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.removeFirst(); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.removeLast(); System.out.println(linkedList);
运行结果:

链表时间复杂度分析
添加操作:

O(n)是因为往链表尾部添加,要遍历整个链表节点。O(n/2)可以看做操作中间的节点。
删除操作:

修改操作:
set(index e) // O(n/2) = O(n)
查找操作:

get 和 contains 都是O(n/2) find操作是根据元素找index,链表中index没啥用。

看起来,链表的增删改查全都是O(n)级别的,比数组看起来差。链表没有索引,无法像数组一样快速访问。

此时我们能利用的方法复杂度都是O(1)了;链表的改进,比数组节省空间。最基础动态数据结构,对二叉树平衡二叉树的学习都能有辅助作用。
链表实现栈
只对链表头进行操作,也就是只能对一端进行操作,很明显是栈。队列是要对两端都进行操作的。链表头作为栈顶。
Interface Stack<E> implement LinkedListStack<E> int getSize(); boolean isEmpty(); void push(E e); E pop(); E peek();
比较两个栈的性能差异。
package cn.mtianyan;public class LinkedListStack<E> implements Stack<E> { private LinkedList<E> list; public LinkedListStack() {
list = new LinkedList<>();
} @Override
public int getSize() { return list.getSize();
} @Override
public boolean isEmpty() { return list.isEmpty();
} @Override
public void push(E e) {
list.addFirst(e);
} @Override
public E pop() { return list.removeFirst();
} @Override
public E peek() { return list.getFirst();
} @Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("LinkedList Stack :");
res.append(list); return res.toString();
}
} public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListStack stack = new LinkedListStack(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
stack.push(i);
System.out.println(stack);
}
stack.pop();
System.out.println(stack);
}运行结果:

package cn.mtianyan;import java.util.Random;public class mainTwoTest { // 测试使用stack运行opCount个push和pop操作所需要的时间,单位:秒
private static double testStack(Stack<Integer> stack, int opCount){ long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random(); for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
stack.push(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE)); for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
stack.pop(); long endTime = System.nanoTime(); return (endTime - startTime) / 1e9;
} public static void main(String[] args) { int opCount = 100000000;
ArrayStack<Integer> arrayStack = new ArrayStack<>(); double time1 = testStack(arrayStack, opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayStack, time: " + time1 + " s");
LinkedListStack<Integer> linkedListStack = new LinkedListStack<>(); double time2 = testStack(linkedListStack, opCount);
System.out.println("LinkedListStack, time: " + time2 + " s"); // 其实这个时间比较很复杂,因为LinkedListStack中包含更多的new操作
}
}其实这个时间是比较不确定谁大谁小的。
运行结果:
100000000 数据:

10000000 数据:

1000000 数据:

100000 数据:

基本可以看出,数据量小于100万的时候LinkedList比较有优势,数据量大时ArrayList更优。但它们实际是同样级别时间复杂度的,最多相差几倍。
链表实现队列
队列势必会在链表的两端同时操作,一端为O(1)一端为O(n);使用数组时我们也遇到了这个问题,因此我们产生了使用循环队列的方式。

链表中我们为什么对于链表头部的操作都简单一些呢,因为我们有一个标识的head。那么想让尾部也可以操作简单,设置一个tail变量。从两端插入元素都是很容易的。
tail端前一个节点不容易找,得遍历一遍。此时: head添加删除都容易,tail添加容易,删除不易。
因此队列从head端删除元素,从tail端插入元素。head 队首负责出队,tail队尾负责入队。由于没有dummyHead,要注意链表为空的情况
package cn.mtianyan;public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E> { private class Node{ public E e; public Node next; public Node(E e, Node next){ this.e = e; this.next = next;
} public Node(E e){ this(e, null);
} public Node(){ this(null, null);
} @Override
public String toString(){ return e.toString();
}
} private Node head, tail; private int size; public LinkedListQueue(){
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
} @Override
public int getSize(){ return size;
} @Override
public boolean isEmpty(){ return size == 0;
} @Override
public void enqueue(E e){ // 如果队尾为空,说明队列是空的。因为tail一直指向最后一个非空节点。
if(tail == null){
tail = new Node(e);
head = tail;
} else{ // 使用tail.next把新Node挂载上来。
tail.next = new Node(e); // tail后挪
tail = tail.next;
}
size ++;
} @Override
public E dequeue(){ if(isEmpty()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
Node retNode = head;
head = head.next; // head后移
retNode.next = null; // 元素置空
if(head == null) // 如果头结点都没得删了
tail = null;
size --; return retNode.e;
} @Override
public E getFront(){ if(isEmpty()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is empty."); return head.e;
} @Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Queue: front ");
Node cur = head; while(cur != null) {
res.append(cur + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
res.append("NULL tail"); return res.toString();
} public static void main(String[] args){
LinkedListQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedListQueue<>(); for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue); if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}运行结果:

测试性能差异:
package cn.mtianyan;import java.util.Random;public class MainThree { // 测试使用q运行opCount个enqueueu和dequeue操作所需要的时间,单位:秒
private static double testQueue(Queue<Integer> q, int opCount){ long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random(); for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE)); for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.dequeue(); long endTime = System.nanoTime(); return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
} public static void main(String[] args) { int opCount = 100000;
ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue<>(); double time1 = testQueue(arrayQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayQueue, time: " + time1 + " s");
LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue<>(); double time2 = testQueue(loopQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("LoopQueue, time: " + time2 + " s");
LinkedListQueue<Integer> linkedListQueue = new LinkedListQueue<>(); double time3 = testQueue(linkedListQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("LinkedListQueue, time: " + time3 + " s");
}
}运行结果:

作者:天涯明月笙
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/d89021b37d86


 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




