一、interface简介
interface(接口)是golang最重要的特性之一,Interface类型可以定义一组方法,但是这些不需要实现。并且interface不能包含任何变量。
简单的说:
interface是方法的集合
interface是一种类型,并且是指针类型
interface的更重要的作用在于多态实现
interface定义
type 接口名称 interface {
method1 (参数列表) 返回值列表
method2 (参数列表) 返回值列表
...
}interface使用
接口的使用不仅仅针对结构体,自定义类型、变量等等都可以实现接口。
如果一个接口没有任何方法,我们称为空接口,由于空接口没有方法,所以任何类型都实现了空接口。
要实现一个接口,必须实现该接口里面的所有方法。
package main
import "fmt"//定义接口type Skills interface {
Running()
Getname() string}
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int}// 实现接口func (p Student) Getname() string{ //实现Getname方法 fmt.Println(p.Name ) return p.Name
}
func (p Student) Running() { // 实现 Running方法
fmt.Printf("%s running",p.Name)
}
func main() { var skill Skills var stu1 Student
stu1.Name = "wd"
stu1.Age = 22
skill = stu1
skill.Running() //调用接口}//wd running多态
上面提到了,go语言中interface是实现多态的一种形式,所谓多态,就是一种事物的多种形态,与python中类的多态是一致的。
同一个interface,不同的类型实现,都可以进行调用,它们都按照统一接口进行操作。
在上面的示例中,我们增加一个Teacher结构体,同样实现接口进行说明:
package main
import "fmt"type Skills interface {
Running()
Getname() string}
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int}
type Teacher struct {
Name string
Salary int}
func (p Student) Getname() string{ //实现Getname方法 fmt.Println(p.Name ) return p.Name
}
func (p Student) Running() { // 实现 Running方法
fmt.Printf("%s running",p.Name)
}
func (p Teacher) Getname() string{ //实现Getname方法 fmt.Println(p.Name ) return p.Name
}
func (p Teacher) Running() { // 实现 Running方法
fmt.Printf("\n%s running",p.Name)
}
func main() { var skill Skills var stu1 Student var t1 Teacher
t1.Name = "wang"
stu1.Name = "wd"
stu1.Age = 22
skill = stu1
skill.Running()
skill = t1
t1.Running()
}//wd running//wang running接口嵌套
go语言中的接口可以嵌套,可以理解我继承,子接口拥有父接口的所有方法,并且想要使用该子接口的话,必须将父接口和子接口的所有方法都实现。
type Skills interface {
Running()
Getname() string}
type Test interface {
sleeping()
Skills //继承Skills}类型转换
由于接口是一般类型,当我们使用接口时候可能不知道它是那个类型实现的,基本数据类型我们有对应的方法进行类型转换,当然接口类型也有类型转换。
当然我们也可以用这个方式来进行类型的判断。
转换方式:
var s intvar x interfacex = s y , ok := x.(int) //将interface 转为int,ok可省略 但是省略以后转换失败会报错,true转换成功,false转换失败, 并采用默认值
示例:
package main
import "fmt"func main() { var x interface{}
s := "WD"
x = s
y,ok := x.(int)
z,ok1 := x.(string)
fmt.Println(y,ok)
fmt.Println(z,ok1)
}//0 false//WD true判断类型示例:
package main
import "fmt"type Student struct {
Name string}
func TestType(items ...interface{}) { for k, v := range items { switch v.(type) { case string:
fmt.Printf("type is string, %d[%v]\n", k, v) case bool:
fmt.Printf("type is bool, %d[%v]\n", k, v) case int:
fmt.Printf("type is int, %d[%v]\n", k, v) case float32, float64:
fmt.Printf("type is float, %d[%v]\n", k, v) case Student:
fmt.Printf("type is Student, %d[%v]\n", k, v) case *Student:
fmt.Printf("type is Student, %d[%p]\n", k, v)
}
}
}
func main() { var stu Student
TestType("WD", 100, stu,3.3)
}//type is string, 0[WD]//type is int, 1[100]//type is Student, 2[{}]//type is float, 3[3.3]二、反射reflect
反射是程序执行时检查其所拥有的结构。尤其是类型的一种能力。这是元编程的一种形式。它同一时候也是造成混淆的重要来源。
每一个语言的反射模型都不同(同一时候很多语言根本不支持反射,python通过hasattr方法实现)
go语言中的反射通过refect包实现,reflect包实现了运行时反射,允许程序操作任意类型的对象。
在介绍反射之前先说明下reflect包中的两个数据类Type和Value。
Type
Type:Type类型用来表示一个go类型。
不是所有go类型的Type值都能使用所有方法。请参见每个方法的文档获取使用限制。在调用有分类限定的方法时,应先使用Kind方法获知类型的分类。调用该分类不支持的方法会导致运行时的panic。
获取Type对象的方法:
func TypeOf(i interface{}) Type示例:
package main
import ( "reflect"
"fmt")
func main() {
str := "wd"
res_type := reflect.TypeOf(str)
fmt.Println(res_type) //string}reflect.Type中方法
通用方法:
// 通用方法func (t *rtype) String() string // 获取 t 类型的字符串描述,不要通过 String 来判断两种类型是否一致。func (t *rtype) Name() string // 获取 t 类型在其包中定义的名称,未命名类型则返回空字符串。func (t *rtype) PkgPath() string // 获取 t 类型所在包的名称,未命名类型则返回空字符串。func (t *rtype) Kind() reflect.Kind // 获取 t 类型的类别。func (t *rtype) Size() uintptr // 获取 t 类型的值在分配内存时的大小,功能和 unsafe.SizeOf 一样。func (t *rtype) Align() int // 获取 t 类型的值在分配内存时的字节对齐值。func (t *rtype) FieldAlign() int // 获取 t 类型的值作为结构体字段时的字节对齐值。func (t *rtype) NumMethod() int // 获取 t 类型的方法数量。func (t *rtype) Method() reflect.Method // 根据索引获取 t 类型的方法,如果方法不存在,则 panic。// 如果 t 是一个实际的类型,则返回值的 Type 和 Func 字段会列出接收者。// 如果 t 只是一个接口,则返回值的 Type 不列出接收者,Func 为空值。func (t *rtype) MethodByName(string) (reflect.Method, bool) // 根据名称获取 t 类型的方法。func (t *rtype) Implements(u reflect.Type) bool // 判断 t 类型是否实现了 u 接口。func (t *rtype) ConvertibleTo(u reflect.Type) bool // 判断 t 类型的值可否转换为 u 类型。func (t *rtype) AssignableTo(u reflect.Type) bool // 判断 t 类型的值可否赋值给 u 类型。func (t *rtype) Comparable() bool // 判断 t 类型的值可否进行比较操作
####注意对于:数组、切片、映射、通道、指针、接口 func (t *rtype) Elem() reflect.Type // 获取元素类型、获取指针所指对象类型,获取接口的动态类型
示例:
package main
import ( "fmt"
"reflect")
type Skills interface {
reading()
running()
}
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int}
func (self Student) runing(){
fmt.Printf("%s is running\n",self.Name)
}
func (self Student) reading(){
fmt.Printf("%s is reading\n" ,self.Name)
}
func main() {
stu1 := Student{Name:"wd",Age:22}
inf := new(Skills)
stu_type := reflect.TypeOf(stu1)
inf_type := reflect.TypeOf(inf).Elem() // 特别说明,引用类型需要用Elem()获取指针所指的对象类型
fmt.Println(stu_type.String()) //main.Student
fmt.Println(stu_type.Name()) //Student
fmt.Println(stu_type.PkgPath()) //main
fmt.Println(stu_type.Kind()) //struct
fmt.Println(stu_type.Size()) //24
fmt.Println(inf_type.NumMethod()) //2
fmt.Println(inf_type.Method(0),inf_type.Method(0).Name) // {reading main func() <invalid Value> 0} reading
fmt.Println(inf_type.MethodByName("reading")) //{reading main func() <invalid Value> 0} true}其他方法:
// 数值func (t *rtype) Bits() int // 获取数值类型的位宽,t 必须是整型、浮点型、复数型------------------------------// 数组func (t *rtype) Len() int // 获取数组的元素个数------------------------------// 映射func (t *rtype) Key() reflect.Type // 获取映射的键类型------------------------------// 通道func (t *rtype) ChanDir() reflect.ChanDir // 获取通道的方向------------------------------// 结构体func (t *rtype) NumField() int // 获取字段数量func (t *rtype) Field(int) reflect.StructField // 根据索引获取字段func (t *rtype) FieldByName(string) (reflect.StructField, bool) // 根据名称获取字段func (t *rtype) FieldByNameFunc(match func(string) bool) (reflect.StructField, bool) // 根据指定的匹配函数 math 获取字段func (t *rtype) FieldByIndex(index []int) reflect.StructField // 根据索引链获取嵌套字段------------------------------// 函数func (t *rtype) NumIn() int // 获取函数的参数数量func (t *rtype) In(int) reflect.Type // 根据索引获取函数的参数信息func (t *rtype) NumOut() int // 获取函数的返回值数量func (t *rtype) Out(int) reflect.Type // 根据索引获取函数的返回值信息func (t *rtype) IsVariadic() bool // 判断函数是否具有可变参数。// 如果有可变参数,则 t.In(t.NumIn()-1) 将返回一个切片。
示例:
package main
import ( "fmt"
"reflect")
type Skills interface {
reading()
running()
}
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int}
func (self Student) runing(){
fmt.Printf("%s is running\n",self.Name)
}
func (self Student) reading(){
fmt.Printf("%s is reading\n" ,self.Name)
}
func main() {
stu1 := Student{Name:"wd",Age:22}
stu_type := reflect.TypeOf(stu1)
fmt.Println(stu_type.NumField()) //2
fmt.Println(stu_type.Field(0)) //{Name string 0 [0] false}
fmt.Println(stu_type.FieldByName("Age")) //{{Age int 16 [1] false} true}Value
不是所有go类型值的Value表示都能使用所有方法。请参见每个方法的文档获取使用限制。在调用有分类限定的方法时,应先使用Kind方法获知该值的分类。调用该分类不支持的方法会导致运行时的panic。
Value为go值提供了反射接口,获取Value对象方法:
func ValueOf(i interface{}) Value示例:
str := "wd"val := reflect.ValueOf(str)//wd
reflect.Value方法
注意:以下所有方法中的v是reflect.Value返回的值。
reflect.Value.Kind():获取变量类别,返回常量
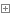
const ( Invalid Kind = iota Bool Int Int8 Int16 Int32 Int64 Uint Uint8 Uint16 Uint32 Uint64 Uintptr Float32 Float64 Complex64 Complex128 Array Chan Func Interface Map Ptr Slice String Struct UnsafePointer )
常量类型
package main
import ("reflect"
"fmt")
func main() {
str := "wd"
val := reflect.ValueOf(str).Kind()
fmt.Println(val)//string}用于获取值方法:
func (v Value) Int() int64 // 获取int类型值,如果 v 值不是有符号整型,则 panic。func (v Value) Uint() uint64 // 获取unit类型的值,如果 v 值不是无符号整型(包括 uintptr),则 panic。func (v Value) Float() float64 // 获取float类型的值,如果 v 值不是浮点型,则 panic。func (v Value) Complex() complex128 // 获取复数类型的值,如果 v 值不是复数型,则 panic。func (v Value) Bool() bool // 获取布尔类型的值,如果 v 值不是布尔型,则 panic。func (v Value) Len() int // 获取 v 值的长度,v 值必须是字符串、数组、切片、映射、通道。func (v Value) Cap() int // 获取 v 值的容量,v 值必须是数值、切片、通道。func (v Value) Index(i int) reflect.Value // 获取 v 值的第 i 个元素,v 值必须是字符串、数组、切片,i 不能超出范围。func (v Value) Bytes() []byte // 获取字节类型的值,如果 v 值不是字节切片,则 panic。func (v Value) Slice(i, j int) reflect.Value // 获取 v 值的切片,切片长度 = j - i,切片容量 = v.Cap() - i。// v 必须是字符串、数值、切片,如果是数组则必须可寻址。i 不能超出范围。func (v Value) Slice3(i, j, k int) reflect.Value // 获取 v 值的切片,切片长度 = j - i,切片容量 = k - i。// i、j、k 不能超出 v 的容量。i <= j <= k。// v 必须是字符串、数值、切片,如果是数组则必须可寻址。i 不能超出范围。func (v Value) MapIndex(key Value) reflect.Value // 根据 key 键获取 v 值的内容,v 值必须是映射。// 如果指定的元素不存在,或 v 值是未初始化的映射,则返回零值(reflect.ValueOf(nil))func (v Value) MapKeys() []reflect.Value // 获取 v 值的所有键的无序列表,v 值必须是映射。// 如果 v 值是未初始化的映射,则返回空列表。func (v Value) OverflowInt(x int64) bool // 判断 x 是否超出 v 值的取值范围,v 值必须是有符号整型。func (v Value) OverflowUint(x uint64) bool // 判断 x 是否超出 v 值的取值范围,v 值必须是无符号整型。func (v Value) OverflowFloat(x float64) bool // 判断 x 是否超出 v 值的取值范围,v 值必须是浮点型。func (v Value) OverflowComplex(x complex128) bool // 判断 x 是否超出 v 值的取值范围,v 值必须是复数型。
设置值方法:
func (v Value) SetInt(x int64) //设置int类型的值func (v Value) SetUint(x uint64) // 设置无符号整型的值func (v Value) SetFloat(x float64) // 设置浮点类型的值func (v Value) SetComplex(x complex128) //设置复数类型的值func (v Value) SetBool(x bool) //设置布尔类型的值func (v Value) SetString(x string) //设置字符串类型的值func (v Value) SetLen(n int) // 设置切片的长度,n 不能超出范围,不能为负数。func (v Value) SetCap(n int) //设置切片的容量func (v Value) SetBytes(x []byte) //设置字节类型的值func (v Value) SetMapIndex(key, val reflect.Value) //设置map的key和value,前提必须是初始化以后,存在覆盖、不存在添加
其他方法:
##########结构体相关:func (v Value) NumField() int // 获取结构体字段(成员)数量func (v Value) Field(i int) reflect.Value //根据索引获取结构体字段func (v Value) FieldByIndex(index []int) reflect.Value // 根据索引链获取结构体嵌套字段func (v Value) FieldByName(string) reflect.Value // 根据名称获取结构体的字段,不存在返回reflect.ValueOf(nil)func (v Value) FieldByNameFunc(match func(string) bool) Value // 根据匹配函数 match 获取字段,如果没有匹配的字段,则返回零值(reflect.ValueOf(nil))########通道相关:func (v Value) Send(x reflect.Value)// 发送数据(会阻塞),v 值必须是可写通道。func (v Value) Recv() (x reflect.Value, ok bool) // 接收数据(会阻塞),v 值必须是可读通道。func (v Value) TrySend(x reflect.Value) bool // 尝试发送数据(不会阻塞),v 值必须是可写通道。func (v Value) TryRecv() (x reflect.Value, ok bool) // 尝试接收数据(不会阻塞),v 值必须是可读通道。func (v Value) Close() // 关闭通道########函数相关func (v Value) Call(in []Value) (r []Value) // 通过参数列表 in 调用 v 值所代表的函数(或方法)。函数的返回值存入 r 中返回。// 要传入多少参数就在 in 中存入多少元素。// Call 即可以调用定参函数(参数数量固定),也可以调用变参函数(参数数量可变)。func (v Value) CallSlice(in []Value) []Value // 调用变参函数
示例一:获取和设置普通类型的值
package main
import ( "reflect"
"fmt")
func main() {
str := "wd"
age := 11
fmt.Println(reflect.ValueOf(str).String()) //获取str的值,结果wd
fmt.Println(reflect.ValueOf(age).Int()) //获取age的值,结果age
str2 := reflect.ValueOf(&str) //获取Value类型
str2.Elem().SetString("jack") //设置值
fmt.Println(str2.Elem(),age) //jack 11}示例二:简单结构体操作
package main
import ( "fmt"
"reflect")
type Skills interface {
reading()
running()
}
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int}
func (self Student) runing(){
fmt.Printf("%s is running\n",self.Name)
}
func (self Student) reading(){
fmt.Printf("%s is reading\n" ,self.Name)
}
func main() {
stu1 := Student{Name:"wd",Age:22}
stu_val := reflect.ValueOf(stu1) //获取Value类型
fmt.Println(stu_val.NumField()) //2
fmt.Println(stu_val.Field(0),stu_val.Field(1)) //wd 22
fmt.Println(stu_val.FieldByName("Age")) //22
stu_val2 := reflect.ValueOf(&stu1).Elem()
stu_val2.FieldByName("Age").SetInt(33) //设置字段值 ,结果33 fmt.Println(stu1.Age)
}示例三:通过反射调用结构体中的方法,通过reflect.Value.Method(i int).Call()或者reflect.Value.MethodByName(name string).Call()实现
package main
import ( "fmt"
"reflect")
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int}
func (this *Student) SetName(name string) { this.Name = name
fmt.Printf("set name %s\n",this.Name )
}
func (this *Student) SetAge(age int) { this.Age = age
fmt.Printf("set age %d\n",age )
}
func (this *Student) String() string {
fmt.Printf("this is %s\n",this.Name) return this.Name
}
func main() {
stu1 := &Student{Name:"wd",Age:22}
val := reflect.ValueOf(stu1) //获取Value类型,也可以使用reflect.ValueOf(&stu1).Elem()
val.MethodByName("String").Call(nil) //调用String方法
params := make([]reflect.Value, 1) params[0] = reflect.ValueOf(18)
val.MethodByName("SetAge").Call(params) //通过名称调用方法
params[0] = reflect.ValueOf("jack")
val.Method(1).Call(params) //通过方法索引调用
fmt.Println(stu1.Name,stu1.Age)
}//this is wd//set age 18//set name jack//jack 18



 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




