一、Contents 内容
1. Image types: gamma emitted, X-rays, ultra-violet, infra-red and, visible images. infra-wave, radio-wave, nuclear magnetic resonance.
图像类型:伽马射线、X 射线、紫外线、红外线和可见光图像。
红外波、无线电波、核磁共振
2. Characteristics of image: energy, frequency and wave-length.
图像特征:能量、频率和波长。
3. Digital image representation: Image sampling and quantification. Image undersampling and image size reduction.
数字图像表示法:图像取样和量化。图像欠采样和缩小图像尺寸。
4. Image resizing and restoration: Nearest-neighbor, bilinear and bicubic interpolation technique for image restoration.
图像大小调整和修复:用于图像复原的最近邻插值、双线性插值和双三次插值技术。
5. Image representation: Mathematical model of the images. Matrixes of binary, intensity, indexed(palette) and RGB(true-color) images.
图像表示法:图像的数学模型。二值、强度、索引(调色板)和 RGB(真彩色)图像矩阵。
二、Digital image processing 数字图像处理
1. Image processing deals with different techniques of transformation existing image to the new image, which has a better quality for man perception or for the subsequent machine processing.
数字图像处理涉及将现有图像转换为新图像的不同技术,新图像对于人类感知或后续机器处理具有更好的质量。
- The serious work in the area of digital image processing(DIP) began when the need for processing lunar images was felt after the space mission.
数字图像处理(DIP)领域的重要工作始于太空任务之后对处理月球图像的需求。 - DIP, originally established to analyze and improve lunar images is rapidly growing into a wealth of new applications, due to the enormous progress made in both algorithm development and computer engineering.
DIP 最初是为分析和改进月球图像而建立的,由于算法开发和计算机工程方面取得的巨大进步,它正迅速发展成为一个丰富的新应用领域。
2. Machine vision is a technique of image processing with the aim of man vision imitation, including learning processes and pattern recognition.
机器视觉是一种以模仿人类视觉为目的的图像处理技术,包括学习过程和模式识别。
3D TV, mobile devices, remote sensing(e.g., meteorological, environmental and military), computer vision (e.g., robotics, autonomous systems and Unman Autonomous Vehicles)
3D电视、移动设备、遥感(例如气象、环境和军事)、计算机视觉(例如机器人、自主系统和无人驾驶车辆)
三、Ranking images by wavelength range 按波长范围排列图像
- Gamma emitered images 伽马射线发射图像
- X-rays images X 射线图像
- Ultraviolet images 紫外线图像
- Visible images 可见图像
- Infrared images 红外图像
- Images in the infrared-wave diapason 红外波段的图像
- Radio-wave images 无线电波图像
- Nuclear magnetic resonance images 核磁共振图像
- Computed Tomography 计算机断层扫描(CT检查)
- Acoustic images 声学图像
四、Examples of gamma ray images 伽马射线图像示例
- Gamma rays are used in nuclear medicine X-ray, Magneto Resonant images MRI, Computed Tomography CT-scan, and Ultrasound images.
伽马射线可用于核医学 X 射线、磁共振成像 MRI、计算机断层扫描 CT 扫描和超声波成像。 - In nuclear medicine, images of bones and skeleton are obtained using a gamma radiation source and a gamma ray detector.
在核医学中,利用伽马辐射源和伽马射线探测器获取骨骼和骨架的图像。 - Astronomical observations allows us to understand the universe beyond the Earth.
天文观测使我们能够了解地球以外的宇宙。 - From the vast distances of the objects we receive only a small amount of radiation.
从遥远的天体中,我们只能接收到少量的辐射。

五、X-ray Imaging X 射线图像
- The most well-known areas of application of X-ray imaging are radiation medicine, industry, astronomy.
X 射线成像最著名的应用领域是放射医学、工业和天文学。 - X-rays are generated using an X-ray tube, which is a vacuum tube with a cathode and anode.
X 射线是通过 X 射线管产生的,X 射线管是一个带有阴极和阳极的真空管。 - Manufacturers use industrial radiography to check for cracks or flaws in materials.
制造商使用工业射线照相术来检查材料中的裂缝或缺陷。 - Industrial radiography uses x-ray and gamma radiation to show flaws that cannot be detected by the naked eye.
工业射线摄影利用 X 射线和伽马射线来显示肉眼无法发现的缺陷。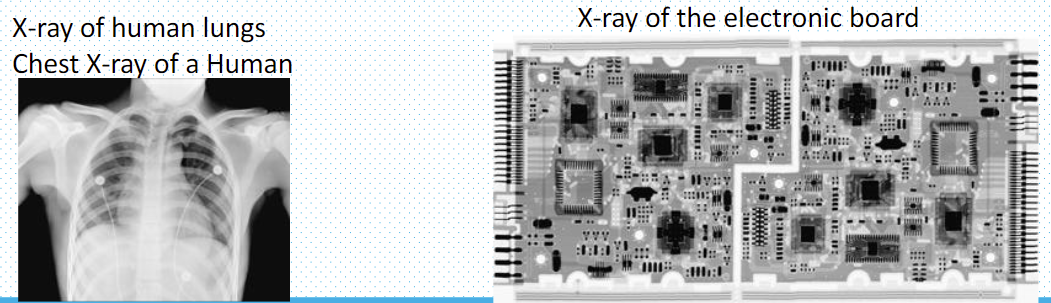
X-ray of human lungs 人体肺部 X 光片
Chest X-ray of a Human 人体胸部 X 光片
X-ray of the electronic board 电子板的 X 光片
六、Imaging in the Ultraviolet Band 紫外波段成像
1. Applications of Ultraviolet “light” include lithography, industrial inspection, microscopy, lasers, biological imaging, and astronomical observations.
紫外线 "光 "的应用包括光刻、工业检测、显微镜、激光、生物成像和天文观测。
2. Fluorescent effect. The ultraviolet light itself is not visible, but when a photon of ultraviolet radiation collides with an electron in an atom of a fluorescent material, it elevates the electron to a higher energy level.
荧光效应。紫外线本身并不可见,但当紫外线光子与荧光材料原子中的电子碰撞时,会将电子提升到更高的能级。
- Tonic water - the quinine in tonic water glows blue.
汤力水–汤力水中的奎宁会发出蓝光。 - Honey - the aromatic molecules in honey can glow green.
蜂蜜–蜂蜜中的芳香分子能发出绿光。 - Turmeric root - the curcumin in turmeric glows yellow.
姜黄根–姜黄中的姜黄素能发出黄色光芒。 - Eggs - a compound in eggshells can glow red.
鸡蛋–蛋壳中的一种化合物能发出红光。
Bees see lines called honey guides on flower petals. 蜜蜂在花瓣上看到称为“蜜线”的线条。
Eggshells can glow red. 蛋壳能发出红光
七、Imaging in the visible and Infrared Bands 可见光和红外波段成像
| Wavelength(μm) 波长 | Characteristics and users 特点和使用者 | |
|---|---|---|
| Violet 紫色 | 0.40-0.44 | A flower of the genus viola 堇菜属的花 |
| indigo 靛青 | 0.44-0.46 | Blueberries 蓝莓 |
| visible blue 可见蓝色 | 0.46-0.50 | Maximum water penetration 最大渗水量 |
| visible green 可见绿色 | 0.50-0.57 | For measuring plant vigor 用于测量植物活力 |
| visible yellow 可见黄色 | 0.57-0.59 | Vegetation discrimination 植被鉴别 |
| orange 橘色 | 0.59-0.62 | Biomass and shoreline mapping 生物量和海岸线测绘 |
| Visible red 可见红色 | 0.62-0.72 | Vegetation discrimination 植被鉴别 |
| Near infrared 近红外 | 0.76-1.00 | Biomass and shoreline mapping 生物量和海岸线测绘 |
| Middle infrared 中红外 | 3.00-8.00 | TV remote control 电视遥控器 |
| Long-wavelength infrared | 8.00-15.00 | Fiber optic cables, infrared astronomy, and meteorology光纤电缆、红外天文学和气象学 |
| Far infrared 远红外 | 15.00-1000 | Fiber optic cables, infrared astronomy, and meteorology光纤电缆、红外天文学和气象学 |
八、Infrared photography 红外摄影
- In infrared photography, image sensor used is sensitive to infrared light.
在红外摄影中,使用的图像传感器对红外光敏感。 - Remote Sensing: Meteorology and climatology, tracking of earth resources, geographical mapping;
遥感: 气象学和气候学、地球资源跟踪、地理测绘; - Prediction of agricultural crops, urban growth and weather, flood, fire control.
预测农作物、城市发展和天气、洪水和火灾控制。
tree photographed in the near-infrared range 在近红外范围内拍摄的树木
A near-infrared photograph 一张近红外线照片
九、Imaging in the Visible and Infrared Bands 可见光和红外波段成像
- Optical scanners take a visual image of the fingerprint using a digital camera.
光学扫描仪使用数码相机拍摄指纹的视觉图像。 - Capacitive scanners use capacitors and thus electrical current to form an image of the fingerprint.
电容式扫描仪利用电容器和电流形成指纹图像。 - Ultrasound fingerprint scanners use high frequency sound waves to penetrate the epidermal(outer) layer of the skin.
超声波指纹扫描仪使用高频声波穿透皮肤表皮(外层)。 - Thermal scanners sense the temperature differences on the contact surface, in between fingerprint ridges and valleys.
热扫描仪能感知接触面上的温差,即指纹脊和指纹谷之间的温差。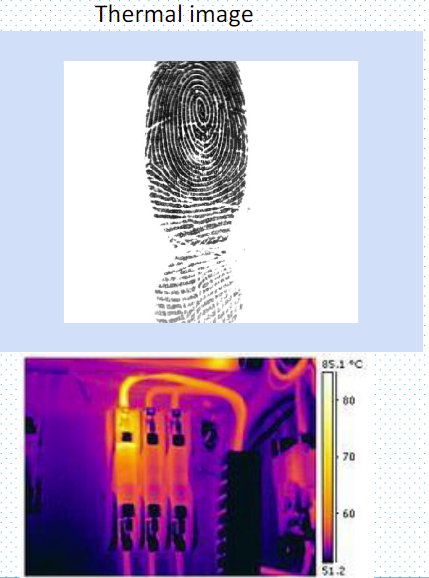
Thermal image 热图像
This thermogram shows excessive heating on a terminal in an industrial electrical fuse block.
该热图显示工业电气保险丝盒中的一个端子发热过度。
十、Multispectral imaging 多光谱成像
A multispectral image captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum(including):
多光谱图像捕捉电磁波谱特定波长范围内的图像数据
- Visible light, 可见光
- Infrared, 红外线
- Ultra-violet. 紫外线
Application: 应用
- Weather forecasting; 天气预报;
- Military target tracking; 军事目标追踪;
- Land mine detection. 地雷探测
Major applications of multispectral imaging from satellites.
卫星多光谱成像的主要应用。
Image of a hurricane satellite using sensors in the visible and infrared band.
使用可见光和红外波段传感器拍摄的飓风卫星图像。
The eye of the hurricane is clearly visible in this image.
在这张图片中,飓风眼清晰可见。
Multispectral image of Hurricane.
飓风的多光谱图像。
十一、Imaging in the Microwave Band 微波波段成像
Application. The dominant application of imaging in the microwave band is radar.
应用。微波波段成像技术的主要应用是雷达。
The unique feature of imaging radar is its ability to collect data independent on weather or lighting conditions.
成像雷达的独特之处在于它能够不受天气或照明条件的影响而收集数据。
Some radar waves can penetrate clouds, and under certain conditions we can see through vegetation, ice, and extremely dry sand.
有些雷达波可以穿透云层,在某些条件下,我们还能看穿植被、冰和极度干燥的沙子。
Automated license plate reading. 车牌自动读取。
十二、Imaging in the radio band 无线电波段成像
| F | Range GHz 范围 | Band width GHz 波段宽度 | Application 应用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | 1-2 | 1 | Mobile satellite communications 移动卫星通信 |
| S | 2-4 | 2 | Mobile communications and space exploration 移动通信和太空探索 |
| C | 4-8 | 4 | Fixed communication satellites 固定通信卫星 |
| X | 8-12.5 | 4.5 | Earth exploration, meteorology 地球探测、气象学 |
| Ku,K,Ka | 12.5-18 | 5.5 | Broadcasting systems 广播系统 |


Images of the pulsar 脉冲星图像
- Gamma 伽马
- Optical 光学
- Radio 无线电
十三、Imaging using “sound” finds 利用 "声音 "成像
Application. Ultrasound imaging is used in manufacturing, in medicine.
超声波成像可用于制造和医疗。
The Ultrasound system transmits high-frequency(1 to 5 MHz) sound pulses into the body.
超声波系统向体内发射高频(1 至 5 兆赫)声脉冲。
Application The major applications of imaging in the radio band are in medicine and astronomy.
无线电波段成像的主要应用领域是医学和天文学。
In medicine radio waves are used in magnetic resonance imaging(MRI).
在医学中,无线电波被用于磁共振成像(MRI)。
MRI image of a Knee. 膝关节的核磁共振成像。
Unborn babies are imaged to determine the health of their development.
对未出生的婴儿进行成像,以确定其发育是否健康。
十四、Electromagnetic spectrum 电磁频谱

photon energy(electron-volt) 光子能量(电子伏特)
十五、Converting energy into frequency 将能量转化为频率
- Photon energy 光子能量
E = hv[ev] - Planck’s constant 普朗克常数
h = 4.1358 * 10-15 [ev*s] - Frequency of electromagnetic radiation 电磁辐射频率
v = E / h = E * 2.4179 * 1014 [Hz]
十六、Spectrum of electromagnetic radiation 电磁辐射光谱

Radiation frequency 辐射频率
十七、Frequency to wavelength conversion 频率到波长的转换
- Electromagnetic radiation frequency 电磁辐射频率
v[Hz] - Light speed 光速
c0 = 3 * 108 - Electromagnetic radiation wavelength 电磁辐射波长
λ = c0 / v = 3 * 108 / v [m]
十八、Spectrum of electromagnetic radiation 电磁辐射光谱

Wavalength 波长
十九、Superposition of three scales 三个尺度的叠加
Superposition of three scales 三个尺度的叠加
二十、Digital Image Acquisition Using Sensors 使用传感器获取数字图像

二十一、Image model 图像模型

二十二、Light level affects image quality 光照度影响图像质量

二十三、Image Sampling and Quantization 图像采样和量化

二十四、Image under-sampling and aliasing 图像采样不足和混叠
Aliasing is an artifact in an image that can appear as a result of reducing an image’s size.
锯齿是图像中的一种伪影,可能是缩小图像尺寸的结果。
When the size of an image is reduced, original pixels are down-sampled.
缩小图像尺寸时,原始像素会被降低采样率。
Aliasing that occurs as a result of size reduction normally appears
因缩小尺寸而出现的混叠现象通常表现为
- as “stair-step” patterns(especially in high contrast images), or
如 "阶梯 "图案(尤其是在高对比度图像中) - as “moire effect” (ripple-effect) patterns.
如 “摩尔效应”(波纹效应)图案。
二十五、The effect of aliased frequencies 混叠频率的影响
- Shannon sampling theorem "If the function is sampled at a rate equal to or greater than twice its highest frequency, it is possible to recover completely the original function."
香农采样定理 “如果函数的采样率等于或大于其最高频率的两倍,就有可能完全恢复原始函数”。 - if the function is undersampled, then a phenomenon called aliasing corrupts the sampled image.
如果函数采样不足,那么一种叫做 "混叠 "的现象就会破坏采样图像。 - The corruption is in the form of additional frequency components being introduced into the sampled function.
损坏的形式是在采样函数中引入额外的频率成分。 - The effect of aliased frequencies can be seen in the form of socalled moire.
混叠频率的影响表现为所谓的摩尔纹。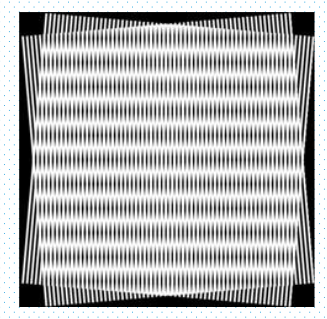
二十六、Aliasing as a result of size reduction 因缩小尺寸而产生的混叠现象



二十七、Degradation of Image 图像质量下降

二十八、Image resizing and restoration 图像大小调整和修复
Nearest-neighbor interpolation technique. 最近邻插值技术
- The output pixel is assigned by the value of the pixel falls within.
输出像素由该像素的数值决定。 - No other pixels are considered.
不考虑其他像素。
Bilinear interpolation technique. 双线性插值技术
- The output pixel is a weighted average of pixels in the nearest 2-by-2 neighborhood.
输出像素是最近的 2×2 邻域像素的加权平均值。
v(x’, y’) = ax + by + cxy + d;
Bicubic interpolation technique. 双三次插值技术
- The output pixel is a weighted average of pixels in the nearest 4-by-4 neighborhood.
输出像素是最近的 4×4 邻域像素的加权平均值。
v(x,y) = ax3 + bx2y + cxy2 + dy3 + e;
二十九、Nearest neighbor technique for image restoration 用于图像修复的最近邻技术

三十、Bilinear interpolation technique for image restoration 用于图像复原的双线性插值技术

三十一、Bicubic interpolation technique for the image restoration 用于图像修复的双三次插值技术

三十二、Images is Matlab
- Binary images are represented as a logical array of 0’s and 1’s.
二进制图像是由 0 和 1 组成的逻辑数组。 - Intensity (grayscale) are represented by an array of class.
强度(灰度)由类数组表示。
uint 8, uint 16, double. - Indexed (palette) images is represented by an array of class.
索引(调色板)图像由类数组表示。
uint 8, uint 16, double.
The color-map is always an m-by-3 array of class.
颜色映射总是一个 m×3 的类数组。
double. - RGB (true-color) images are represented by an m * n * 3 array of class.
RGB(真彩色)图像由一个 m * n * 3 的类数组表示。
uint 8, uint 16, double.
三十三、The grayscale (intensity) images 灰度(强度)图像
- A grayscale image is a data matrix, which values represent intensities within the range[0, 255], [0.1].
灰度图像是一个数据矩阵,其值代表[0, 255]、[0.1]范围内的强度。 - Grayscale image is a single matrix, with each element of the matrix corresponding to one image pixel.
灰度图像是一个单独的矩阵,矩阵的每个元素对应一个图像像素。 - The matrix may be of class double, uint 8, or uint16.
矩阵可以是 double、uint 8 或 uint16 类型。 - The grayscale images are rarely saved with a colormap.
灰度图像很少使用色谱图保存。
三十四、An intensity(gray-scale) image 强度(灰度)图像

三十五、RGB(true-color) image RGB(真彩色)图像
- An RGB image, is stored in MATLAB as an m * n * 3 data array that defines red, green, and blue color components for each individual pixel.
RGB 图像在 MATLAB 中存储为 m * n * 3 数据数组,定义了每个像素的红、绿、蓝色彩分量。 - RGB images do not use a palette. RGB 图像不使用调色板。
- The color of each pixel is determined by the combination of the red, green, and blue intensities stored in each color.
每个像素的颜色是由存储在每个颜色中的红、绿、蓝三色强度的组合决定的。
Graphics file formats store RGB images as 24-bit images, where
图形文件格式将 RGB 图像存储为 24 位图像,其中 - red components are 8 bits 红色组件为 8 位
- green components are 8 bits 绿色组件为8位
- blue components are 8 bits. 蓝色组件为8位
The yields a potential of 16 million colors.
可产生 1,600 万种色彩。
The precision with which a real-life image can be replicated has led to the commonly used term true-color image.
由于可以精确地复制现实生活中的图像,因此人们通常使用 "真彩色图像 "这一术语。
三十六、RGB(true-color) images RGB(真彩色)图像

三十七、Binary image 二进制图像
- In a binary image, each pixel is represented by discrete values [0, 1].
在二值图像中,每个像素用离散值 [0, 1] 表示。 - Essentially, these two values correspond to on and off.
从本质上讲,这两个值分别对应开启和关闭。 - A binary image is stored as a logical array of 0’s (off pixels) and 1’s (on pixels)
二进制图像以 0(关闭像素)和 1(打开像素)的逻辑数组形式存储
三十八、Binary & contour image 二值图像和轮廓图像

三十九、An indexed image
An indexed image consists of
索引图像包括
- a data matrix 数据矩阵
- a color-map matrix, map. 一个颜色映射矩阵,map.
The data matrix can be of class uint 8, uint 16, or double.
数据矩阵可以是 uint 8、uint 16 或 double 类。
The color-map matrix is an m-by-3 array of class double containing floating-point values in the range [0, 1].
颜色映射矩阵是一个 m×3 的 double 类数组,包含范围为 [0, 1] 的浮点数值。
Each row of map specifies the red, green, and blue components of a single color.
每行映射指定一种颜色的红色、绿色和蓝色成分。
An indexed image uses direct mapping of pixel values to color-map values.
索引图像使用像素值到颜色图值的直接映射。
The color of each image pixel is determined by using the corresponding value of element data matrix as an index into map.
每个图像像素的颜色是通过使用元素数据矩阵的相应值作为映射索引来确定的。
四十、References 参考文献
-
Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard E. Woods “Digital Image Processing”, Third Edition. University of Tennessee
-
Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard E. Woods, Steven Eddins “Digital Image Processing using Matlab”,
四十一、The common questions underlying these areas are 这些领域所涉及的共同问题是
-
How do we describe or characterize images? 我们如何描述或描述图像的特征?
-
What mathematical methods do we want to use on an image? 我们想在图像上使用什么数学方法?
-
How do we implement these algorithms? 我们如何实现这些算法?
-
How do we evaluate the quality of the processed images? 如何评估处理后图像的质量?






 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




