
OAuth 2.0 允许第三方应用程序访问受限的HTTP资源的授权协议,像平常大家使用Github、Google账号来登陆其他系统时使用的就是 OAuth 2.0 授权框架,下图就是使用Github账号登陆Coding系统的授权页面图:

类似使用 OAuth 2.0 授权的还有很多,本文将介绍 OAuth 2.0 相关的概念如:角色、授权类型等知识,以下是我整理一张 OAuth 2.0 授权的脑头,希望对大家了解 OAuth 2.0 授权协议有帮助。

文章将以脑图中的内容展开 OAuth 2.0 协议同时除了 OAuth 2.0 外,还会配合 Spring Security OAuth2 来搭建OAuth2客户端,这也是学习 OAuth 2.0 的目的,直接应用到实际项目中,加深对 OAuth 2.0 和 Spring Security 的理解。
OAuth 2.0 角色
OAuth 2.0 中有四种类型的角色分别为:资源Owner、授权服务、客户端、资源服务,这四个角色负责不同的工作,为了方便理解先给出一张大概的流程图,细节部分后面再分别展开:
OAuth 2.0 大概授权流程

资源 Owner
资源 Owner可以理解为一个用户,如之前提到使用Github登陆Coding中的例子中,用户使用GitHub账号登陆Coding,Coding就需要知道用户在GitHub系统中的的头像、用户名、email等信息,这些账户信息都是属于用户的这样就不难理解资源 Owner了。在Coding请求从GitHub中获取想要的用户信息时也是没那容易的,GitHub为了安全起见,至少要通过用户(资源 Owner)的同意才行。
资源服务器
明白资源 Owner后,相信你已经知道什么是资源服务器,在这个例子中用户账号的信息都存放在GitHub的服务器中,所以这里的资源服务器就是GitHub服务器。GitHub服务器负责保存、保护用户的资源,任何其他第三方系统想到使用这些信息的系统都需要经过资源 Owner授权,同时依照 OAuth 2.0 授权流程进行交互。
客户端
知道资源 Owner和资源服务器后,OAuth中的客户端角色也相对容易理解了,简单的说客户端就是想要获取资源的系统,如例子中的使用GitHub登陆Coding时,Coding就是OAuth中的客户端。客户端主要负责发起授权请求、获取AccessToken、获取用户资源。
授权服务器
有了资源 Owner、资源服务器、客户端还不能完成OAuth授权的,还需要有授权服务器。在OAuth中授权服务器除了负责与用户(资源 Owner)、客房端(Coding)交互外,还要生成AccessToken、验证AccessToken等功能,它是OAuth授权中的非常重要的一环,在例子中授权服务器就是GitHub的服务器。
小结
OAuth中:资源Owner、授权服务、客户端、资源服务有四个角色在使用GitHub登陆Coding的例子中分别表示:
- 资源Owner:GitHub用户
- 授权服务:GitHub服务器
- 客户端:Coding系统
- 资源服务:GitHub服务器
其中授权服务服务器、资源服务器可以单独搭建(鬼知道GitHub怎么搭建的)。在微服务器架构中可单独弄一个授权服务,资源服务服务可以多个如:用户资源、仓库资源等,可根据需求自由分服务。
OAuth2 Endpoint
OAuth2有三个重要的Endpoint其中授权 Endpoint、Token Endpoint结点在授权服务器中,还有一个可选的重定向 Endpoint在客户端中。
- 授权 Endpoint:使用
授权 Endpoint去获取资源Owner的授权 - Token Endpoint:客户端获取token
- 重定向 Endpoint:授权服务器使用
重定向 Endpoint返回授权响应给客户端
授权类型
通过四个OAuth角色,应该对OAuth协议有一个大概的认识,不过可能还是一头雾水不知道OAuth中的角色是如何交互的,没关系继续往下看一下授权类型就知道OAuth中的角色是如何完成自己的职责,进一步对OAuth的理解。在OAuth中定义了四种授权类型,分别为:
- 授权码授权
- 客房端凭证授权
- 资源Owner的密码授权
- 隐式的授权
不同的授权类型可以使用在不同的场景中。
授权码授权
这种形式就是我们常见的授权形式(如使用GitHub账号登陆Coding),在整个授权流程中会有资源Owner、授权服务器、客户端三个OAuth角色参与,之所以叫做授权码授权是因为在交互流程中授权服务器会给客房端发放一个code,随后客房端拿着授权服务器发放的code继续进行授权如:请求授权服务器发放AccessToken。

为方便理解再将上图的内容带进真实的场景中,用文字表述一下整个流程:
- A.1、用户访问Coding登陆页(
https://coding.net/login),点击Github登陆按钮; - A.2、Coding服务器将浏览器重定向到Github的授权页(
https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize?client_id=a5ce5a6c7e8c39567ca0&scope=user:email&redirect_uri=https://coding.net/api/oauth/github/callback&response_type=code),同时URL带上client_id和redirect_uri参数; - B.1、用户输入用户名、密码登陆Github;
- B.2、用户点击
授权按钮,同意授权; - C.1、Github授权服务器返回
code; - C.2、Github通过将浏览器重定向到
A.2步骤中传递的redirect_uri地址(https://coding.net/api/oauth/github/callback&response_type=code); - D、Coding拿到code后,调用Github授权服务器API获取AccessToken,由于这一步是在Coding服务器后台做的浏览器中捕获不到,基本就是使用
code访问github的access_token节点获取AccessToken;
以上是大致的授权码授权流程,大部分是客户端与授权服务器的交互,整个过程中有几个参数说明如下:
- client_id:在Github中注册的Appid,用于标记客户端
- redirect_uri:可以理解一个
callback,授权服务器验证完客户端与用户名等信息后将浏览器重定向到此地址并带上code参数 - code:由授权服务器返回的一个凭证,用于获取AccessToken
- state:由客户端传递给授权服务器,授权服务器一般到调用
redirect_uri时原样返回
授权码授权请求
在使用授权码授权的模式中,作为客户端请求授权的的时候都需要按规范请求,以下是使用授权码授权发起授权时所需要的参数 :
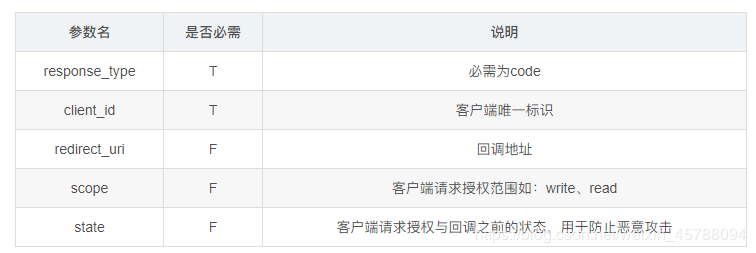
如使用Github登陆Coding例子中的https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize?client_id=a5ce5a6c7e8c39567ca0&scope=user:email&redirect_uri=https://coding.net/api/oauth/github/callback&response_type=code授权请求URL,就有client_id、redirect_uri参数,至于为啥没有response_type在下猜想是因为Github给省了吧。
授权码授权响应
如果用户同意授权,那授权服务器也会返回标准的OAuth授权响应:
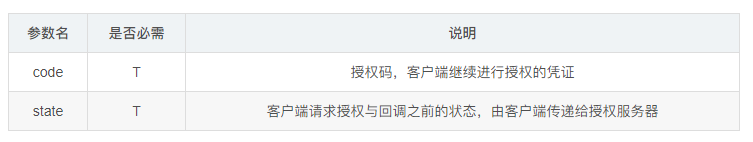
如Coding登陆中的https://coding.net/api/oauth/github/callback&response_type=code,用户同意授权后Github授权服务器回调Coding的回调地址,同时返回code、state参数。
客户端凭证授权
客房端凭证授权授权的过程中只会涉及客户端与授权服务器交互,相比较其他三种授权类型是比较简单的。一般这种授权模式是用于服务之间授权,如在AWS中两台服务器分别为应用服务器(A)和数据服务器(B),A 服务器需要访问 B 服务器就需要通过授权服务器授权,然后才能去访问 B 服务器获取数据。

简单二步就可以完成客房端凭证授权啦,不过在使用客房端凭证授权时客户端是直接访问的授权服务器中获取AccessToken接口。
客户端凭证授权请求
客房端凭证授权中客户端会直接发起获取AccessToken请求授权服务器的AccessTokenEndpoint,请求参数如下:
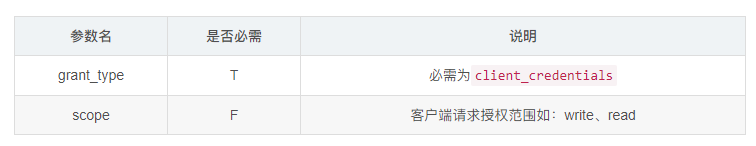
注意: 在OAuth中AccessTokenEndpoint是使用HTTP Basic认证,在请求时还需要携带Authorization请求头,如使用postman测试请求时:

其中的username和password参数对于OAuth协议中的client_id和client_secret,client_id和client_secret都是由授权服务器生成的。
客户端凭证授权响应
授权服务器验证完client_id和client_secret后返回token:
{
"access_token":"2YotnFZFEjr1zCsicMWpAA",
"token_type":"example",
"expires_in":3600,
"example_parameter":"example_value"
}
用户凭证授权
用户凭证授权与客户端凭证授权类似,不同的地方是进行授权时要提供用户名和用户的密码。

基本流程如下:
- A、客户端首先需要知道用户的凭证
- B、使用用户凭证获取AccessToken
- C、授权服务器验证客户端与用户凭证,返回AccessToken
用户凭证授权请求
用户凭证授权请求参数要比客户端凭证授权多username和pwssword参数:

注意: 获取Token时使用HTTP Basic认证,与客户端凭证授权一样。
用户凭证授权响应
用户凭证授权响应与客户端凭证授权差不多:
{
"access_token":"2YotnFZFEjr1zCsicMWpAA",
"token_type":"example",
"expires_in":3600,
"refresh_token":"tGzv3JOkF0XG5Qx2TlKWIA",
"example_parameter":"example_value"
}
隐式授权
隐式授权用于获取AccessToken,但是获取的方式与用户凭证授权和客户端授权不同的是,它是在访问授权Endpoint的时候就会获取AccessToken而不是访问Token Endpoing,而且AccessToken的会作为redirect_uri的Segment返回。

- A.1、A.2、浏览器访问支持隐式授权的服务器的授权Endpoint;
- B.1、用户输入账号密码;
- B.2、用户点击
授权按钮,同意授权; - C、授权服务器使用
redirect_uri返回AccessToken; - D、授权服务器将浏览器重定向到
redirect_uri,并携带AccessToken如:http://example.com/cb#access_token=2YotnFZFEjr1zCsicMWpAA&state=xyz&token_type=example&expires_in=3600; - D、
redirect_uri的地址是指向一个Web资源客户端 - E、
Web资源客户端返回一段脚本 - F、浏览器执行脚本
- D、客户端获得AccessToken
隐式授权不太好理解,但是仔细比较客户端凭证授权和用户凭证授权会发现隐式授权不需要知道用户凭证或客户端凭证,这样做相对更安全。
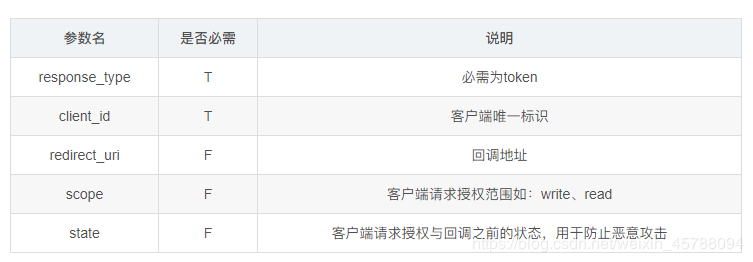
隐式授权请求
再使用隐式授权时,所需要请求参数如下:
隐式授权响应
隐式授权响应参数是通过redirect_uri回调返回的,如http://example.com/cb#access_token=2YotnFZFEjr1zCsicMWpAA &state=xyz&token_type=example&expires_in=3600就是隐式授权响应参数,其中需要注意的是响应的参数是使用Segment的形式的,而不是普通的URL参数。
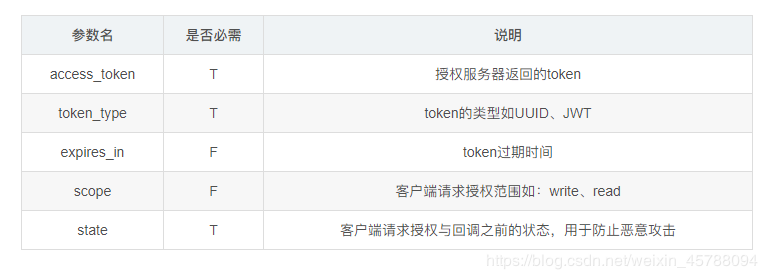
OAuth2 客户端
前面提到过OAuth协议中有四个角色,这一节使用Spring Boot实现一个登陆GitHub的OAuthClient,要使用OAuth2协议登陆GitHub首先要云GitHub里面申请:
申请 OAuth App
填写必需的信息
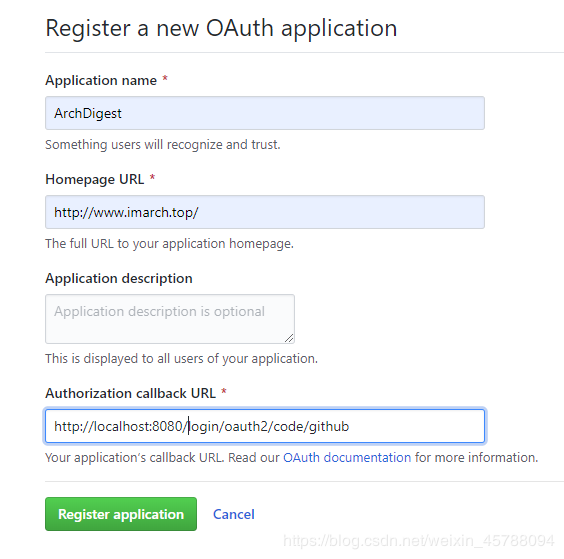
上图中的Authorization callback URL就是redirect_uri用户同意授权后GitHub会将浏览器重定向到该地址,因此先要在本地的OAuth客户端服务中添加一个接口响应GitHub的重定向请求。
配置OAuthClient
熟悉OAuth2协议后,我们在使用 Spring Security OAuth2 配置一个GitHub授权客户端,使用认证码授权流程(可以先去看一遍认证码授权流程图),示例工程依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
Spring Security OAuth2 默认集成了Github、Goolge等常用的授权服务器,因为这些常用的授权服务的配置信息都是公开的,Spring Security OAuth2 已经帮我们配置了,开发都只需要指定必需的信息就行如:clientId、clientSecret。
Spring Security OAuth2使用Registration作为客户端的的配置实体:
public static class Registration {
//授权服务器提供者名称
private String provider;
//客户端id
private String clientId;
//客户端凭证
private String clientSecret;
....
下面是之前注册好的 GitHub OAuth App 的信息:
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.github.clientId=5fefca2daccf85bede32
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.github.clientSecret=01dde7a7239bd18bd8a83de67f99dde864fb6524``
配置redirect_uri
Spring Security OAuth2内置了一个redirect_uri模板:{baseUrl}/login/oauth2/code/{registrationId},其中的registrationId是在从配置中提取出来的:
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.[registrationId].clientId=xxxxx
如在上面的GitHub客户端的配置中,因为指定的registrationId是github,所以重定向uri地址就是:
{baseUrl}/login/oauth2/code/github
启动服务器
OAuth2客户端和重定向Uri配置好后,将服务器启动,然后打开浏览器进入:http://localhost:8080/。第一次打开因为没有认证会将浏览器重客向到GitHub的授权Endpoint:
常用授权服务器(CommonOAuth2Provider)
Spring Security OAuth2内置了一些常用的授权服务器的配置,这些配置都在CommonOAuth2Provider中:
public enum CommonOAuth2Provider {
GOOGLE {
@Override
public Builder getBuilder(String registrationId) {
ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBuilder(registrationId,
ClientAuthenticationMethod.BASIC, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL);
builder.scope("openid", "profile", "email");
builder.authorizationUri("https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/auth");
builder.tokenUri("https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token");
builder.jwkSetUri("https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/certs");
builder.userInfoUri("https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/userinfo");
builder.userNameAttributeName(IdTokenClaimNames.SUB);
builder.clientName("Google");
return builder;
}
},
GITHUB {
@Override
public Builder getBuilder(String registrationId) {
ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBuilder(registrationId,
ClientAuthenticationMethod.BASIC, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL);
builder.scope("read:user");
builder.authorizationUri("https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize");
builder.tokenUri("https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token");
builder.userInfoUri("https://api.github.com/user");
builder.userNameAttributeName("id");
builder.clientName("GitHub");
return builder;
}
},
FACEBOOK {
@Override
public Builder getBuilder(String registrationId) {
ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBuilder(registrationId,
ClientAuthenticationMethod.POST, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL);
builder.scope("public_profile", "email");
builder.authorizationUri("https://www.facebook.com/v2.8/dialog/oauth");
builder.tokenUri("https://graph.facebook.com/v2.8/oauth/access_token");
builder.userInfoUri("https://graph.facebook.com/me?fields=id,name,email");
builder.userNameAttributeName("id");
builder.clientName("Facebook");
return builder;
}
},
OKTA {
@Override
public Builder getBuilder(String registrationId) {
ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBuilder(registrationId,
ClientAuthenticationMethod.BASIC, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL);
builder.scope("openid", "profile", "email");
builder.userNameAttributeName(IdTokenClaimNames.SUB);
builder.clientName("Okta");
return builder;
}
};
private static final String DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL = "{baseUrl}/{action}/oauth2/code/{registrationId}";
}
CommonOAuth2Provider中有四个授权服务器配置:OKTA、FACEBOOK 、GITHUB 、GOOGLE。在OAuth2协议中的配置项redirect_uri、Token Endpoint、授权 Endpoint、scope都会在这里配置:
GITHUB {
@Override
public Builder getBuilder(String registrationId) {
ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBuilder(registrationId,
ClientAuthenticationMethod.BASIC, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL);
builder.scope("read:user");
builder.authorizationUri("https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize");
builder.tokenUri("https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token");
builder.userInfoUri("https://api.github.com/user");
builder.userNameAttributeName("id");
builder.clientName("GitHub");
return builder;
}
}
重定向Uri拦截
脑瓜子有点蒙了,感觉自己就配置了clientid和clientSecret一个OAuth2客户端就完成了,其中的一些原由还没搞明白啊。。。,最好奇的是重定向Uri是怎么被处理的。
Spring Security OAuth2 是基于 Spring Security 的,之前看过Spring Security文章,知道它的处理原理是基于过滤器的,如果你不知道的话推荐看这篇文章:《Spring Security 架构》。在源码中找了一下,发现一个可疑的Security 过滤器:
- OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter:处理OAuth2授权的过滤器
这个 Security 过滤器有个常量:
public static final String DEFAULT_FILTER_PROCESSES_URI = "/login/oauth2/code/*";
是一个匹配器,之前提到过Spring Security OAuth2中有一个默认的redirect_uri模板:{baseUrl}/{action}/oauth2/code/{registrationId},/login/oauth2/code/*正好能与redirect_uri模板匹配成功,所以OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter会在用户同意授权后执行,它的构造方法如下:
public OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter(ClientRegistrationRepository clientRegistrationRepository,
OAuth2AuthorizedClientService authorizedClientService) {
this(clientRegistrationRepository, authorizedClientService, DEFAULT_FILTER_PROCESSES_URI);
}
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter 主要将授权服务器返回的code拿出来,然后通过AuthenticationManager 来认证(获取AccessToken),下来是移除部分代码后的源代码:
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
MultiValueMap<String, String> params = OAuth2AuthorizationResponseUtils.toMultiMap(request.getParameterMap());
//检查没code与state
if (!OAuth2AuthorizationResponseUtils.isAuthorizationResponse(params)) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(OAuth2ErrorCodes.INVALID_REQUEST);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
//获取 OAuth2AuthorizationRequest
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest =
this.authorizationRequestRepository.removeAuthorizationRequest(request, response);
if (authorizationRequest == null) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_NOT_FOUND_ERROR_CODE);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
//取出 ClientRegistration
String registrationId = authorizationRequest.getAttribute(OAuth2ParameterNames.REGISTRATION_ID);
ClientRegistration clientRegistration = this.clientRegistrationRepository.findByRegistrationId(registrationId);
if (clientRegistration == null) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(CLIENT_REGISTRATION_NOT_FOUND_ERROR_CODE,
"Client Registration not found with Id: " + registrationId, null);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
String redirectUri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(UrlUtils.buildFullRequestUrl(request))
.replaceQuery(null)
.build()
.toUriString();
//认证、获取AccessToken
OAuth2AuthorizationResponse authorizationResponse = OAuth2AuthorizationResponseUtils.convert(params, redirectUri);
Object authenticationDetails = this.authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request);
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authenticationRequest = new OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken(
clientRegistration, new OAuth2AuthorizationExchange(authorizationRequest, authorizationResponse));
authenticationRequest.setDetails(authenticationDetails);
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authenticationResult =
(OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken) this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authenticationRequest);
...
return oauth2Authentication;
}
获取AccessToken
前面提到OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter是使用 AuthenticationManager 来进行OAuth2认证的,一般情况下在 Spring Security 中的 AuthenticationManager 都是使用的 ProviderManager 来进行认证的,所以对应在 Spring Security OAuth2 中有一个 OAuth2LoginAuthenticationProvider 用于获取AccessToken:
public class OAuth2LoginAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
private final OAuth2AccessTokenResponseClient<OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantRequest> accessTokenResponseClient;
private final OAuth2UserService<OAuth2UserRequest, OAuth2User> userService;
private GrantedAuthoritiesMapper authoritiesMapper = (authorities -> authorities);
....
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authorizationCodeAuthentication =
(OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken) authentication;
// Section 3.1.2.1 Authentication Request - https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#AuthRequest
// scope
// REQUIRED. OpenID Connect requests MUST contain the "openid" scope value.
if (authorizationCodeAuthentication.getAuthorizationExchange()
.getAuthorizationRequest().getScopes().contains("openid")) {
// This is an OpenID Connect Authentication Request so return null
// and let OidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider handle it instead
return null;
}
OAuth2AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse;
try {
OAuth2AuthorizationExchangeValidator.validate(
authorizationCodeAuthentication.getAuthorizationExchange());
//访问GitHub TokenEndpoint获取Token
accessTokenResponse = this.accessTokenResponseClient.getTokenResponse(
new OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantRequest(
authorizationCodeAuthentication.getClientRegistration(),
authorizationCodeAuthentication.getAuthorizationExchange()));
} catch (OAuth2AuthorizationException ex) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = ex.getError();
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
...
return authenticationResult;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
}

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




