本文首发于个人网站:Spring Boot 2.x实战之定时任务调度
在后端开发中,有些场景是需要使用定时任务的,例如:定时同步一批数据、定时清理一些数据,在Spring Boot中提供了@Scheduled注解就提供了定时调度的功能,对于简单的、单机的调度方案是足够了的。这篇文章准备用实际案例看下@Scheduled的用法。
开发实战
-
新建Spring Boot工程,主pom文件内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>online.javaadu.schedule</groupId> <artifactId>scheduledemo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>scheduledemo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId> <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project> -
新建定时任务组件,使用
@Scheduled注解修饰要调度的方法,在该方法中会打印当前的时间。package online.javaadu.schedule.scheduledemo; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; @Component public class ScheduledTasks { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ScheduledTasks.class); private static final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss"); //第一次执行之前延后10秒钟;后续每隔5秒执行1次 @Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000, initialDelay = 10000) public void reportCurrentTime() { log.info("The time is now {}", dateFormat.format(new Date())); } } -
在ScheduledemoApplication中开启定时调度能力——即开启
@Scheduled注解的定时调度功能,并在系统刚起来的时候打印一行日志,用来体现上一步中的initialDelay的作用。package online.javaadu.schedule.scheduledemo; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; @SpringBootApplication @EnableScheduling public class ScheduledemoApplication { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ScheduledTasks.class); private static final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss"); public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ScheduledemoApplication.class, args); log.info("---The time is now {}", dateFormat.format(new Date())); } } -
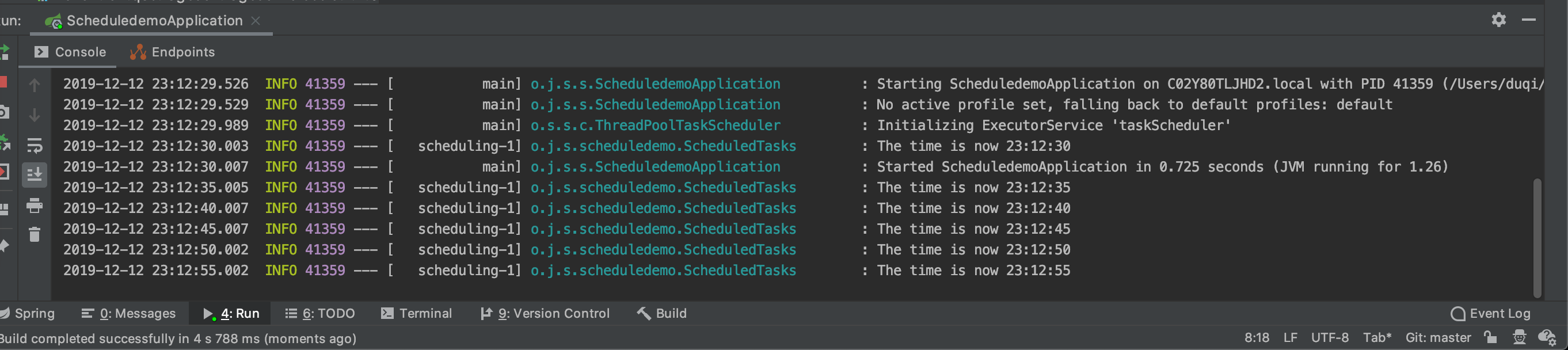
点击运行后,该demo的运行结果如下,可以看出,23:15:35应用启动,过了10秒钟定时调度任务才开始执行,然后是每隔5秒钟打印一次时间。
分析解释
我们一起来看下@Scheduled注解的源码,看看除了上面的例子里提供的案例,该注解还有哪些功能呢?
- cron,可以支持更复杂的时间复杂度
- zone,解析cron表达式的时候解析时区
- fixedDelay(和fixedDelayString),两次调度之间需要加一个固定的延迟
- fixedRate(和fixedRateString),没隔多久需要调度一次
- initialDelay(和initialDelayString),第一次调度之前需要延迟多久
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Repeatable(Schedules.class)
public @interface Scheduled {
/**
* 特殊的cron表达式,如果设置成这个值,则表示将定时调度器关闭,不再调度。
*/
String CRON_DISABLED = ScheduledTaskRegistrar.CRON_DISABLED;
/**
* cron表达式,可以支持复杂的定时调度需求
*/
String cron() default "";
/**
* cron表达式解析的时候,解析依赖的时区
*/
String zone() default "";
/**
* 两次调度触发之间暂停的毫秒数,Long类型
*/
long fixedDelay() default -1;
/**
* 两次调度触发之间暂停的毫秒数,String类型
*/
String fixedDelayString() default "";
/**
* 每隔几毫秒调度一次
*/
long fixedRate() default -1;
/**
* 每隔几毫秒调度一次,String类型
*/
String fixedRateString() default "";
/**
* 第一次执行之前,延迟多少毫秒
*/
long initialDelay() default -1;
/**
* 第一次执行之前,延迟多少毫秒,String类型
*/
String initialDelayString() default "";
}
参考资料
- https://spring.io/guides/gs/scheduling-tasks/
- 《Spring Boot实战》
Spring Boot 2.x系列
本号专注于后端技术、JVM问题排查和优化、Java面试题、个人成长和自我管理等主题,为读者提供一线开发者的工作和成长经验,期待你能在这里有所收获。

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




