前面我们对于 ListView 的操作讲过 [Flutter 滑动删除最佳实践],那现在我们来了解一下 ListView 的拖拽排序。
效果如下:
ReorderableListView
想要达到如上效果,需使用该类,官网简介:
A list whose items the user can interactively reorder by dragging.
This class is appropriate for views with a small number of children because constructing the List[1] requires doing work for every child that could possibly be displayed in the list view instead of just those children that are actually visible.
All children[2] must have a key.
简单翻译如下:
用户可以通过拖动来重新排序的列表。
该类适用于少量 children 的页面,因为构造列表需要为每一个 children 执行操作,而不只是可见的 children。
所有的 children 都必须有一个 key。
构造函数
按照惯例,查看构造函数:
ReorderableListView({
this.header,
@required this.children,
@required this.onReorder,
this.scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
this.padding,
this.reverse = false,
}) : assert(scrollDirection != null),
assert(onReorder != null),
assert(children != null),
assert(
children.every((Widget w) => w.key != null),
'All children of this widget must have a key.',
);
了解一下各个参数:
•header:是一个不参与拖动排序的 Widget•children:不用多说,列表项•onReorder:见名知意,重新排序后的回调•scrollDirection:方向
剩下两个就不多说了,都应该了解。
简单使用
既然看完了构造函数,那我们就可以分分钟写一个 Demo 出来:
class _ReorderableListViewPageState extends State<ReorderableListViewPage> {
List<Color> _data = [
Colors.blue,
Colors.pinkAccent,
Colors.deepPurple,
Colors.orangeAccent
];
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('ReorderableListViewPage'),
),
body: ReorderableListView(
header: Container(
height: 50,
),
children: _data
.map((s) => Card(
color: s,
key: Key(s.toString()),
child: Container(
width: 300,
height: 100,
),
))
.toList(),
onReorder: (int oldIndex, int newIndex) {
print("$oldIndex --- $newIndex");
}),
);
}
}
1.首先我们定义好一组颜色的列表2.然后在 build 方法中返回 ReorderableListView3.ReorderableListView 中的 children 为用颜色定义好的 Card4.在 onReorder 回调中打印两个参数 oldIndex & newIndex
运行一下,看一下打印的 log:
可以看到确实是能打印出新旧两个 index, 但是这里有一个很明显的问题,
我们大家都知道数组的下标是从 0 开始,可以看到 第一次是 从 0 到 3,第二次是从 0 到 4,
但是讲道理明明应该是 从 0 到 2,从 0 到 3。
那为什么我前两次移动后的 newIndex 都 +1 了呢?
我们这里也不去深究,
既然我们要移动,那肯定也会对源数据进行操作,不然移动也都是假的。
所以,基于这样的一个 newIndex,我们只需要这样:
setState(() {
if(oldIndex < newIndex) {
newIndex -= 1;
}
var temp = _data.removeAt(oldIndex);
_data.insert(newIndex, temp);
});
1.先判断是向上还是向下拖拽2.如果是向下拖拽,那么 newIndex 会多加一个,我们把它减掉3.然后我们删除旧数据并保存它4.最后在新的 index 上插入
ListView 的拖拽排序和删除
既然前面说到了 ListView 的删除,那这里也必须把它俩组合起来了:
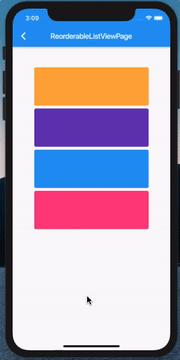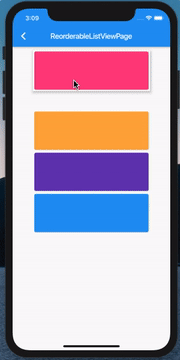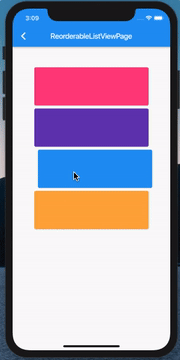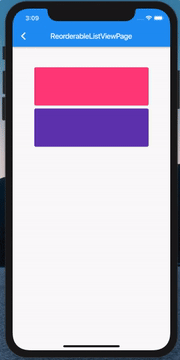
其实代码非常简单,当然这也得益于 Flutter 一切皆 Widget,我们只需要在 Card 上包裹一个 Dismissible 就ok了:
children: _data
.map((s) => Dismissible(
key: Key("dismiss $s"),
child: Card(
color: s,
key: Key(s.toString()),
child: Container(
width: 300,
height: 100,
),
),
))
.toList(),
总结
在 Flutter 当中,我们可以封装很多的 Widget 来为我们日后的开发来节省时间,
当然,也不要忘记 Flutter 当中的 [Widget 测试]


 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




