本文介绍下Spring中的事件监听,其本质也就是观察者模型(发布/订阅模式),具体的观察者模式参考下文
*********************
Java观察者模式(Observer)
********************
@
Spring事件监听
一、事件监听案例
1.事件类
/**
* 事件类
* @author 波波烤鸭
* @email dengpbs@163.com
*
*/public class MyEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public MyEvent(ApplicationContext source) { super(source);
System.out.println("myEvent 构造方法被执行了...");
}
public void out(String name){
System.out.println("myEvent .... out方法执行了"+name);
}
}2.事件监听类
事件监听器也就是我们的观察者。我们可以创建多个来观察。
/**
* 监听器
* 观察者
* @author 波波烤鸭
* @email dengpbs@163.com
*
*/public class MyListenerA implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent>{ @Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
System.out.println("MyListenerA 监听器触发了..."); // 执行事件中的特定方法
event.out("AAAAA");
}
}/**
* 监听器
* 观察者
* @author 波波烤鸭
* @email dengpbs@163.com
*
*/public class MyListenerB implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent>{ @Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
System.out.println("MyListenerB 监听器触发了..."); // 执行事件中的特定方法
event.out("BBBBB");
}
}3.事件发布者
/**
* 事件发布类
* 实现ApplicationContextAware接口用来感知ApplicationContext对象
* @author 波波烤鸭
* @email dengpbs@163.com
*
*/public class MyPublisher implements ApplicationContextAware{
public ApplicationContext ac; @Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.ac = applicationContext;
} /**
* 发布事件
* 监听该事件的监听者都可以获取消息
* @param event
*/
public void publisherEvent(ApplicationEvent event){
System.out.println("---发布事件---"+event);
ac.publishEvent(event);
}
}4.配置文件中注册
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <bean class="com.dpb.pojo.User" id="user" > <property name="name" value="波波烤鸭"></property> </bean> <!-- 注册事件类 --> <bean class="com.dpb.event.MyEvent"></bean> <!-- 注册监听器 --> <bean class="com.dpb.listener.MyListenerA"></bean> <bean class="com.dpb.listener.MyListenerB"></bean> <!-- 注册发布者类 --> <bean class="com.dpb.publisher.MyPublisher"></bean></beans>
5.测试
@Testpublic void test1() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // 从Spring容器中获取发布者
MyPublisher bean = ac.getBean(MyPublisher.class); // 从Spring容器中获取事件对象
MyEvent event = ac.getBean(MyEvent.class); // 发布者发布事件
bean.publisherEvent(event);
}输出结果
myEvent 构造方法被执行了... ---发布事件---com.dpb.event.MyEvent[source=org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@311d617d: startup date [Wed Mar 06 13:04:57 CST 2019]; root of context hierarchy] MyListenerA 监听器触发了... myEvent .... out方法执行了AAAAA MyListenerB 监听器触发了... myEvent .... out方法执行了BBBBB
小结:通过案例我们实现了事件发生后注册的有此事件的监听者(观察者)监听到了此事件,并做出了响应的处理。
二、Spring中事件监听分析
1. Spring中事件监听的结构
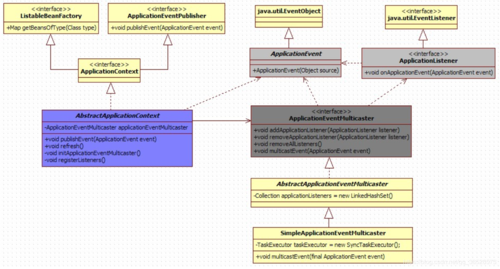
2. 核心角色介绍
2.1 ApplicationEvent
ApplicationEvent是所有事件对象的父类。ApplicationEvent继承自jdk的EventObject,所有的事件都需要继承ApplicationEvent,并且通过source得到事件源。
public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject { /** use serialVersionUID from Spring 1.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7099057708183571937L; /** System time when the event happened */
private final long timestamp; /**
* Create a new ApplicationEvent.
* @param source the object on which the event initially occurred (never {@code null})
*/
public ApplicationEvent(Object source) { super(source); this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
} /**
* Return the system time in milliseconds when the event happened.
*/
public final long getTimestamp() { return this.timestamp;
}
}实现类: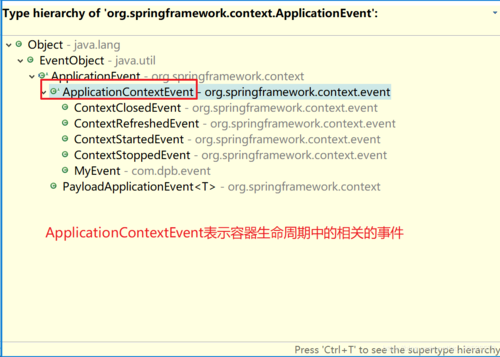
2.2 ApplicationListener
ApplicationListener事件监听器,也就是观察者。继承自jdk的EventListener,该类中只有一个方法onApplicationEvent。当监听的事件发生后该方法会被执行。
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener { /**
* Handle an application event.
* @param event the event to respond to
*/
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
}实现类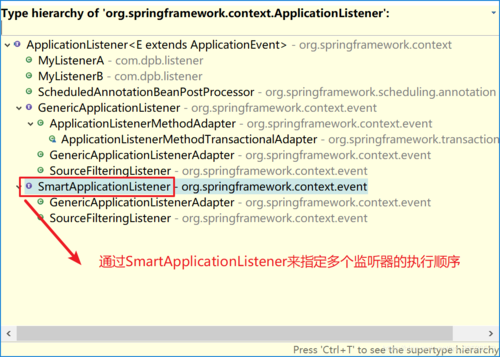
2.3 ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext是Spring中的核心容器,在事件监听中ApplicationContext可以作为事件的发布者,也就是事件源。因为ApplicationContext继承自ApplicationEventPublisher。在ApplicationEventPublisher中定义了事件发布的方法
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher { /**
* Notify all <strong>matching</strong> listeners registered with this
* application of an application event. Events may be framework events
* (such as RequestHandledEvent) or application-specific events.
* @param event the event to publish
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.RequestHandledEvent
*/
void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event); /**
* Notify all <strong>matching</strong> listeners registered with this
* application of an event.
* <p>If the specified {@code event} is not an {@link ApplicationEvent},
* it is wrapped in a {@link PayloadApplicationEvent}.
* @param event the event to publish
* @since 4.2
* @see PayloadApplicationEvent
*/
void publishEvent(Object event);
}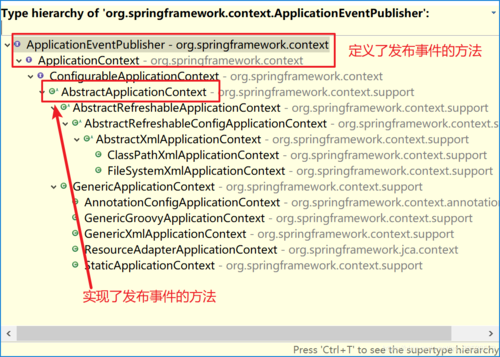 具体发布消息的方法实现:AbstractApplicationContext中
具体发布消息的方法实现:AbstractApplicationContext中
protected void publishEvent(Object event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null"); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);
} // Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent; if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
} else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<Object>(this, event); if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
} // Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) { this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
} else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
} // Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) { if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
} else { this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);这行代码的作用是获取ApplicationEventMulticaster来广播事件给所有的监听器。
2.4 ApplicationEventMulticaster
事件广播器,它的作用是把Applicationcontext发布的Event广播给所有的监听器.
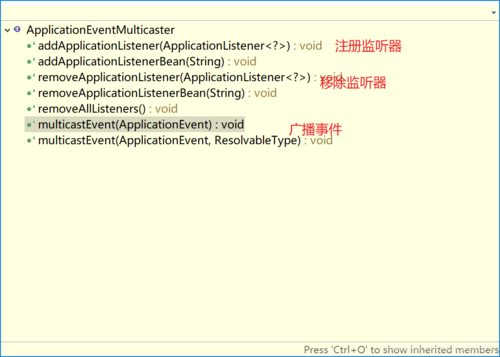 具体的注册监听是在AbstractApplicationContext中实现的。
具体的注册监听是在AbstractApplicationContext中实现的。
@Overridepublic void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
Assert.notNull(listener, "ApplicationListener must not be null"); if (this.applicationEventMulticaster != null) { this.applicationEventMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
} else { this.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
}三、总结
Spring中的事件监听使用的是观察者模式
所有事件需要继承ApplicationEvent父类
所有的监听器需要实现ApplicationListener接口
事件发布需要通过ApplicationContext中的publisherEvent方法实现
监听器的注册是ApplicationEventMulticaster提供的,但我们并不需要实现。
作者:ゞ .邓澎波

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频




