集合: 集合的概念;体系结构;实际应用
通过案例为大家展示集合中类和接口的使用。
生活中的集合: 人或事物聚集到一起; 数学中的集合: 具有某种特性的事物的整体
Java: Java中的集合是工具类,可以存储任意数量的具有共同属性的对象。
超市购物的购物车就是容器: 存储商品的信息,数组也可以,为什么要使用集合?
疑问: 为什么使用集合,而不用数组呢?
问题: 存储20名学生的学生信息。20是不变的,就是这么多。
问题: 存储商品信息。不知道自己要买多少商品。
数组用于固定长度的数据场景,集合更适合数据动态变化的场景。
集合应用场景: 无法预测存储数据的数量;同时存储具有一对一关系的数据(商品信息&详情);需要进行数据的增删;数据重复问题
Set不允许插入重复数据。
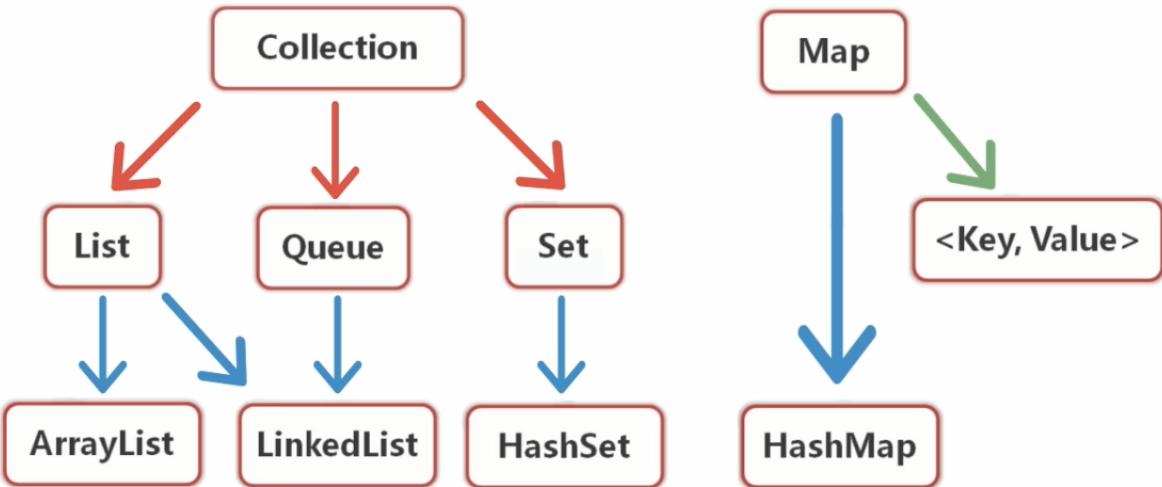
集合框架的体系结构
Collection 类的对象 Map 键值对(键是商品的编号,值是商品的信息)
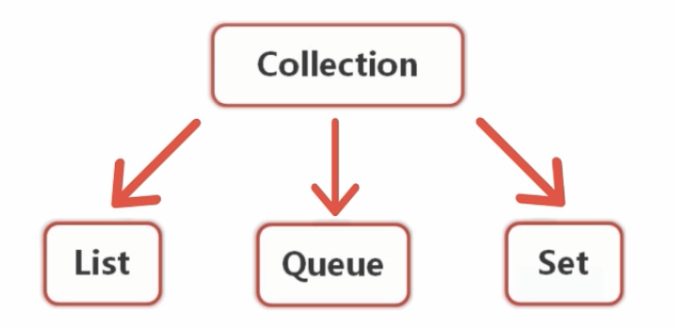
Collection下有三个子接口。List和Queue中存放的数据要求是有序的,并且允许重复的。Set中是无序的,并且不允许重复的。
每个接口下又有实现类: ArrayList 长度动态增长的数组。 LinkedList 同时实现List接口,表示链表的内容; HashSet
Map 的实现类是HashMap,里面存储以键值对表现的形式。
List(列表)概述
List是元素有序并且可以重复的集合,称为序列
List可以精确的控制每个元素的插入位置,或删除某个位置的元素
List的两个主要实现类是ArrayList和LinkedList
本课程主要介绍ArrayList类,因为这个类使用比较多。ArrayList和数组是比较相似的,只是它的长度是可以动态增长的,也是在内存上一片连续的存储空间进行存储的。LinkedList本身是一个链表,这两个中方法的作用是几乎相同的。
ArrayList底层是由数组实现的;动态增长,以满足应用程序的需求; 在列表尾部插入或删除数据非常有效(中间插入删除挪位过多);更适合查找和更新元素;ArrayList中的元素可以为null
java.util 包中的,是需要我们自己导入的。
add方法,向集合中添加元素。clear方法,清空集合中元素。contains方法 判断集合中是否包含给的对象。
isEmpty 集合是否为空, iterator 集合遍历时非常常用的方法。remove方法,移除集合中的某个元素。size()集合元素个数。
List 中 get方法,返回指定index的元素。 indexOf 返回某个对象在列表中的index; sort 对列表进行排序。
ArrayList 无参构造,容量为10, 有参 通过已存在的Collection 构造ArrayList。
案例: 在List中存储并操作字符串信息。
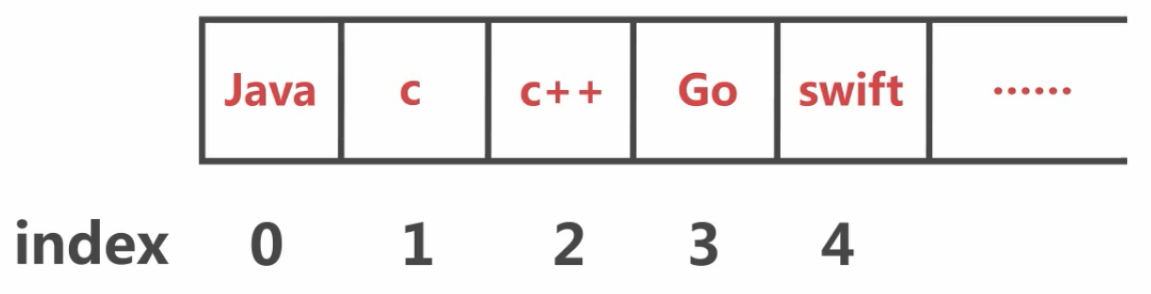
案例:用ArrayList存儲編程語言的名称,并輸出。
名称包括 Java C C++ Go和Swift
package cn.mtianyan.set;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class ListDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 用ArrayList存储编程语言的名称,并输出
List list=new ArrayList();
list.add("Java");
list.add("C");
list.add("C++");
list.add("Go");
list.add("swift"); // 输出列表中元素的个数
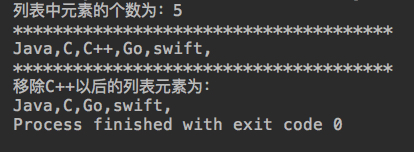
System.out.println("列表中元素的个数为:"+list.size());
// 遍历输出所有编程语言
System.out.println("**************************************"); for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.print(list.get(i)+",");
}
// 移除列表中的C++
System.out.println(); // list.remove(2);
list.remove("C++");
System.out.println("**************************************");
System.out.println("移除C++以后的列表元素为:"); for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.print(list.get(i)+",");
}
}
}
开辟内存空间,add()不断添加元素
运行结果:
remove有两种实现,可以移除指定下标,也可以移除某个对象(如"c++")。
公告需求管理
案例: 公告管理;首页等显示公告。
需求:公告的添加和显示;在指定位置处插入公告;删除公告;修改公告
公告类属性: 编号 id;标题 title;创建人 creator;创建时间 createTime
公告类方法: 构造方法,getId方法。获取和设置属性值的方法。
案例: 公告的添加和显示
package cn.mtianyan.set;import java.util.Date;public class Notice { private int id; // ID
private String title; // 标题
private String creator; // 创建人
private Date createTime; // 创建时间
public Notice(int id, String title, String creator, Date createTime) { super(); this.id = id; this.title = title; this.creator = creator; this.createTime = createTime;
} public int getId() { return id;
} public void setId(int id) { this.id = id;
} public String getTitle() { return title;
} public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title;
} public String getCreator() { return creator;
} public void setCreator(String creator) { this.creator = creator;
} public Date getCreateTime() { return createTime;
} public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) { this.createTime = createTime;
}
}后面会学习到一种叫Bean的定义方式。
package cn.mtianyan.set;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Date;public class NoticeTest { public static void prinf(ArrayList noticeList,int i){
System.out.printf("%-15s",(i + 1)+ ":" + ((Notice) (noticeList.get(i))).getTitle());
System.out.printf("%-6s","\t"+((Notice)(noticeList.get(i))).getCreator());
System.out.printf("%-20s","\t"+((Notice)noticeList.get(i)).getCreateTime());
System.out.println();
} public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建Notice类的对象,生成三条公告,new Date()当前时间
Notice notice1 = new Notice(1, "欢迎来到简书,天涯明月笙!", "管理员", new Date());
Notice notice2 = new Notice(2, "请同学们按时提交作业!", "老师", new Date());
Notice notice3 = new Notice(3, "请同学们按时完成试卷!", "老师", new Date()); // 添加公告
ArrayList noticeList = new ArrayList();
noticeList.add(notice1);
noticeList.add(notice2);
noticeList.add(notice3); // 显示公告
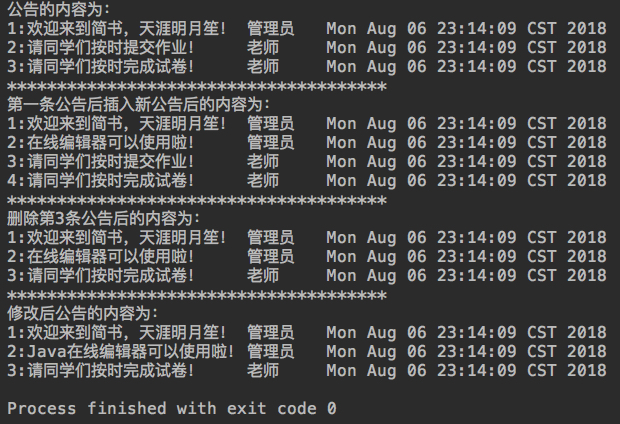
System.out.println("公告的内容为:"); for (int i = 0; i < noticeList.size(); i++) {
prinf(noticeList,i);
}
System.out.println("**************************************"); // 在第一条公告后面添加一条新公告
Notice notice4 = new Notice(4, "在线编辑器可以使用啦!", "管理员", new Date());
noticeList.add(1, notice4); // 显示公告
System.out.println("第一条公告后插入新公告后的内容为:"); for (int i = 0; i < noticeList.size(); i++) {
prinf(noticeList,i);
}
System.out.println("**************************************"); // 删除按时提交作业的公告
noticeList.remove(2); // 显示公告
System.out.println("删除第3条公告后的内容为:"); for (int i = 0; i < noticeList.size(); i++) {
prinf(noticeList,i);
}
// 将第二条公告改为:Java在线编辑器可以使用啦!
System.out.println("**************************************"); // 修改第二条公告中title的值
notice4.setTitle("Java在线编辑器可以使用啦!"); // noticeList.set(1, notice4);
System.out.println("修改后公告的内容为:"); for (int i = 0; i < noticeList.size(); i++) {
prinf(noticeList,i);
}
}
}
注意:在本例题中,使用setTitle就可以了,如果创建了一个新的对象用新的对象去替换notice4的时候需要调用ArrayList的set方法。
总计一下上面用到的方法: add(notice1);添加对象到队尾,add(1, notice4);添加到指定下标。noticeList.remove(2);移除指定下标。
noticeList.set(1, notice4); 修改某个下标的对象。
编程练习
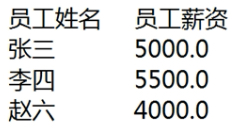
定义一个员工信息类Employee ,使用ArrayList对员工信息进行添加和显示。
效果图:
package cn.mtianyan.set;import java.util.ArrayList;public class EmployeeTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList employeeList = new ArrayList();
Employee employee1 = new Employee("张三",5000.0);
Employee employee2 = new Employee("李四",5500.0);
Employee employee3 = new Employee("赵六",4000.0);
employeeList.add(employee1);
employeeList.add(employee2);
employeeList.add(employee3);
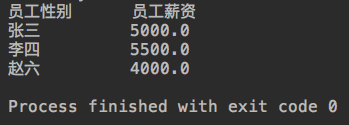
System.out.printf("%-10s","员工性别");
System.out.printf("%-5s","员工薪资");
System.out.println(); for (Object employee:employeeList) {
System.out.printf("%-11s",((Employee)employee).getName());
System.out.printf("%-5s",((Employee)employee).getSalary());
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Set概述
Set是元素无序并且不可以重复的集合,被称为集。实现类是HashSet
HashSet是Set的一个重要实现类,称为哈希集;HashSet中的元素无序并且不可以重复;HashSet中.只允许一个null元素;具有良好的存取和查找性能
HashSet的底层是HashMap,HashMap我们后面会讲到
Set的常用方法:
有equals方法和hashCode方法。
HashSet 有四个构造方法。加载因子。
案例:用HashSet存储多个表示颜色的英文单词,并输出。
单词包括: "blue","red","black","yellow"和"white"
package cn.mtianyan.set;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Set;public class WordDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 将英文单词添加到HashSet中
Set set = new HashSet(); // 向集合中添加元素
set.add("blue");
set.add("red");
set.add("black");
set.add("yellow");
set.add("white"); // 显示集合的内容
System.out.println("集合中的元素为:");
Iterator it = set.iterator(); // 遍历迭代器并输出元素
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println(); // 在集合中插入一个新的单词
// set.add("green");
set.add("white");
it = set.iterator(); // 遍历迭代器并输出元素
System.out.println("**************************");
System.out.println("插入重复元素后的输出结果为:"); while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
} // 插入失败,但是不会报错
}
}Iterator (迭代器): Iterator接口可以以统一的方式对各种集合元素进行遍历
hasNext()方法检测集合中是否还有下一个元素,遍历终止条件;next()方法返回集合中的下一个元素
Iterator it = set.iterator(); 将set中数据存放到迭代器中。
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}以hasNext为循环终止条件,next()取出值。
set.add("green");运行结果:
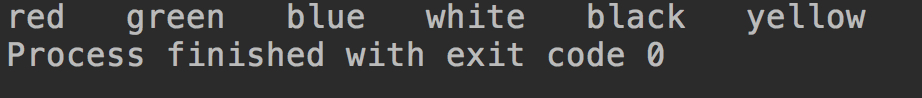
重复元素:插入失败,但是不会报错
宠物猫信息管理概述
演示如何在HashSet中添加自定义类的对象
需求:添加和显示宠物猫信息; 查找某只宠物猫的信息并输出;修改宠物猫的信息;删除宠物猫信息
属性: 名字name;年龄month;品种species
方法: 构造方法;获取和设置属性值的方法;其他方法
添加和显示信息
package cn.mtianyan.set;public class Cat { private String name; //名字
private int month; //年龄
private String species;//品种
//构造方法
public Cat(String name, int month, String species) { super(); this.name = name; this.month = month; this.species = species;
} //getter与setter方法
public String getName() { return name;
} public void setName(String name) { this.name = name;
} public int getMonth() { return month;
} public void setMonth(int month) { this.month = month;
} public String getSpecies() { return species;
} public void setSpecies(String species) { this.species = species;
}
}package cn.mtianyan.set;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Set;public class CatTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义宠物猫对象
Cat huahua = new Cat("花花", 12, "英国短毛猫");
Cat fanfan = new Cat("凡凡", 3, "中华田园猫"); // 将宠物猫对象放入HashSet中
Set<Cat> set = new HashSet<Cat>();
set.add(huahua);
set.add(fanfan); // 显示宠物猫信息
Iterator<Cat> it = set.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}运行结果:
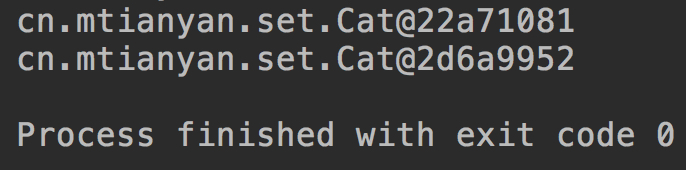
可以看到这是默认的toString方法的输出。 重写toString方法
@Override
public String toString() { return "[姓名:" + name + ", 年龄:" + month + ", 品种:" + species + "]";
}
添加重复数据
插入一个与花花一样属性的猫
// 再添加一个与花花属性一样的猫
Cat huahua01 = new Cat("花花", 12, "英国短毛猫");
set.add(huahua01);
System.out.println("**********************************");
System.out.println("添加重复数据后的宠物猫信息:");
it = set.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}运行结果:

使用了new关键字,有两个对象指向两块不同的内存。
疑问:之前相同的字符串不允许添加到集合呀?
// @Override// public int hashCode() {// final int prime = 31;// int result = 1;// result = prime * result + month;// result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());// result = prime * result + ((species == null) ? 0 : species.hashCode());// return result;// }
@Override
public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, month, species);
}对于普通的ArrayList要找100,得遍历到100才找得到

假如这100个数据中根本没有我们要找的数据,我们也得全部遍历一遍才可以。

通过HashCode规则对于数据进行分桶处理
我们可以使用n%3的余数这个规则来放入桶中

查找时,先判断数据在哪个桶里,如果一个都不满足,那么就提示找不到。遍历桶内元素。
这里确定是在哪一个桶里使用hashCode方法,在一个确定的桶里进行遍历时使用equals方法来比较正在遍历的元素和我们要找的元素。
hashCode就使用自动生成的。
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) { // 判断对象是否相等,相等则返回true,不用继续比较属性了
if(this==obj) return true; // 判断obj是否是Cat类的对象
if(obj.getClass()==Cat.class){
Cat cat=(Cat)obj; return cat.getName().equals(name)&&(cat.getMonth()==month)&&(cat.getSpecies().equals(species));
} return false;
}这里用到了一个反射,使用对象获取它所属的类,与Cat.class属性进行比较。

查找宠物猫信息
System.out.println("**********************************"); // 重新插入一个新宠物猫
Cat huahua02 = new Cat("花花二代", 2, "英国短毛猫");
set.add(huahua02);
System.out.println("添加花花二代后的宠物猫信息:");
it = set.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
第一种,使用对象名查找(传入一个对象)
System.out.println("**********************************"); // 在集合中查找花花的信息并输出
if (set.contains(huahua)) {
System.out.println("花花找到了!");
System.out.println(huahua);
} else {
System.out.println("花花没找到!");
}
第二种方法: 通过名字进行查找
// 在集合中使用名字查找花花的信息
System.out.println("**********************************");
System.out.println("通过名字查找花花信息"); boolean flag = false;
Cat c = null;
it = set.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) {
c = it.next(); if (c.getName().equals("花花")) {
flag = true;// 找到了
break;
}
} if (flag) {
System.out.println("花花找到了");
System.out.println(c);
} else {
System.out.println("花花没找到");
}编程练习
定义一个学生类,使用HashSet对学生类的对象进行管理:执行添加操作,然后解决重复数据的添加问题。
效果图:

任务
定义一个学生类Student:
属性为:学号stuld(int),姓名name (String),成绩score ( float )
方法为: 构造方法,getter和setter方法,toString方法
重写hashCode()和equals(方法,equals方法的判断依据是学号和姓名相等
定义三个Student类的对象,添加到HashSet中
显示HashSet中元素的内容
添加一个重复数据到Set中,观察输出结果
package cn.mtianyan.student;import java.util.Objects;public class Student { private int stuId; private String name; private float score; public Student(int stuId, String name, float score) { this.stuId = stuId; this.name = name; this.score = score;
} public int getStuId() { return stuId;
} public void setStuId(int stuId) { this.stuId = stuId;
} public String getName() { return name;
} public void setName(String name) { this.name = name;
} public float getScore() { return score;
} public void setScore(float score) { this.score = score;
} @Override
public String toString() { return "[" + "学号:" + stuId + ", 姓名: " + name + '\'' + ", 成绩: " + score + ']';
} @Override
public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; // 直接是一个对象,必然一样。
if (!(o instanceof Student)) return false; // 如果传入的不是学生类的对象,那么必然不是
Student student = (Student) o; // 将Object转换为Student
// 学号 & 姓名 是否相等
return getStuId() == student.getStuId() &&// Float.compare(student.getScore(), getScore()) == 0 &&
Objects.equals(getName(), student.getName());
} @Override
public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(getStuId(), getName());
}
}package cn.mtianyan.student;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;public class StudetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student(3,"William",65.0f);
Student student2 = new Student(1,"Tom",87.0f);
Student student3 = new Student(2,"Lucy",95.0f);
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(student1);
hashSet.add(student2);
hashSet.add(student3);
Iterator iterator = hashSet.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
Student student4 = new Student(2,"Lucy",16.0f);
hashSet.add(student4);
System.out.println("*****************");
Iterator iterator2 = hashSet.iterator(); while (iterator2.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator2.next());
}
}
作者:天涯明月笙
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/faaf4b23ebfc

 随时随地看视频
随时随地看视频



